In the realm of financial markets, options trading offers lucrative opportunities to harness market movements and amplify returns. Among the various order types available to traders, limit orders stand out as an essential tool for managing risk and maximizing profits. This detailed guide will delve into the intricacies of options trading limit orders, providing investors with a comprehensive understanding and empowering them to navigate this dynamic trading landscape.

Image: www.youtube.com
Understanding Limit Orders:
Options limit orders are specific instructions placed with a broker to buy or sell an option at a predetermined price or better. When placing a buy limit order, a trader sets the highest price they’re willing to pay, while in a sell limit order, they specify the lowest price they’re willing to accept. Limit orders differ from market orders, which are executed immediately at the current market price, providing greater control and flexibility over the execution of the trade.
Benefits of Limit Orders:
Precision and Control: Limit orders allow traders to define their trading terms, ensuring trades are executed at the desired price. This eliminates the uncertainty associated with market orders, where the execution price is unknown until the trade is filled.
Cost Efficiency: In volatile markets, market orders can result in unfavorable prices that deviate significantly from the intended trading price. Limit orders safeguard against such scenarios, preventing unexpected trading costs.
Risk Management: Limit orders empower traders to set stop-loss and take-profit levels, providing a structured approach to managing risk and preserving capital. Automating these risk parameters allows traders to stay disciplined and avoid emotional decision-making.
Types of Limit Orders:
Day Order: A limit order that remains active for the day and automatically expires at market close.
Good Till Canceled (GTC): A limit order that remains active until manually canceled or executed, regardless of market hours or trading days.
Immediate or Cancel (IOC): A limit order that attempts to execute immediately but is canceled if the full order cannot be filled at the limit price.
Fill or Kill (FOK): A limit order that demands execution of the entire order quantity at the limit price or is immediately canceled.
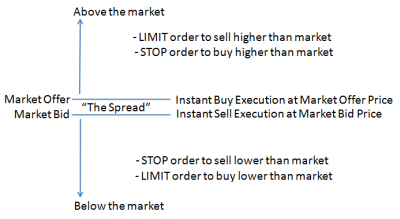
Image: www.whatbizopp.com
Executing Limit Orders:
Matching Buyers and Sellers: When a trader places a limit order to buy an option, it’s matched with a compatible sell limit order placed at or above the specified limit price. Similarly, sell limit orders are executed when matched with buy limit orders at or below the limit price.
Order Display: Limit orders are typically displayed on electronic trading platforms, visible to other market participants. This transparency provides insights into market sentiment and can influence the decision-making process.
Order Placement: Traders can place limit orders through their brokerage’s trading platform or through electronic trading systems, either manually or using automated trading software.
Strategies for Effective Limit Orders:
Dynamic Order Placement: Adapting limit order prices based on changing market conditions allows traders to capitalize on market movements and improve trading outcomes.
Scenario Analysis: Traders should carefully consider various market scenarios before placing limit orders, using tools like probability calculators and implied volatility charts.
Technical Analysis: Incorporating technical indicators and patterns into limit order trading strategies helps traders identify potential trading opportunities and optimize entry and exit points.
Risk Assessment and Position Sizing: Determining appropriate position sizes and defining clear risk parameters are crucial for successful limit order trading. Traders must balance potential rewards with the risks involved.
Example of Limit Order Trading:
Consider a trader who wants to buy a Call option on Apple stock (AAPL). They anticipate a rise in AAPL’s price but wish to purchase it at a favorable price. The current market price is $165 per share, and the trader places a buy limit order for an AAPL Call option with a strike price of $167 at a limit price of $5.
If AAPL’s price rises above $167, the trader’s limit order will be executed, and they will acquire the option at a price of $5 or less. However, if AAPL’s price remains below $167, the limit order will not be filled, and no trade will occur.
Options Trading Limit Order

Image: ladebisafic.web.fc2.com
Conclusion:
Limit orders are a cornerstone of options trading. They offer traders precise control over trade executions, enable efficient cost management, and facilitate risk mitigation. By comprehending the different types of limit orders, their strategic implementation, and the associated strategies, traders can enhance their trading outcomes and capitalize on the opportunities presented by options markets. It’s important to remember that trading involves inherent risks, and traders should always exercise due diligence and consult with financial professionals before making any investment decisions.






