Introduction
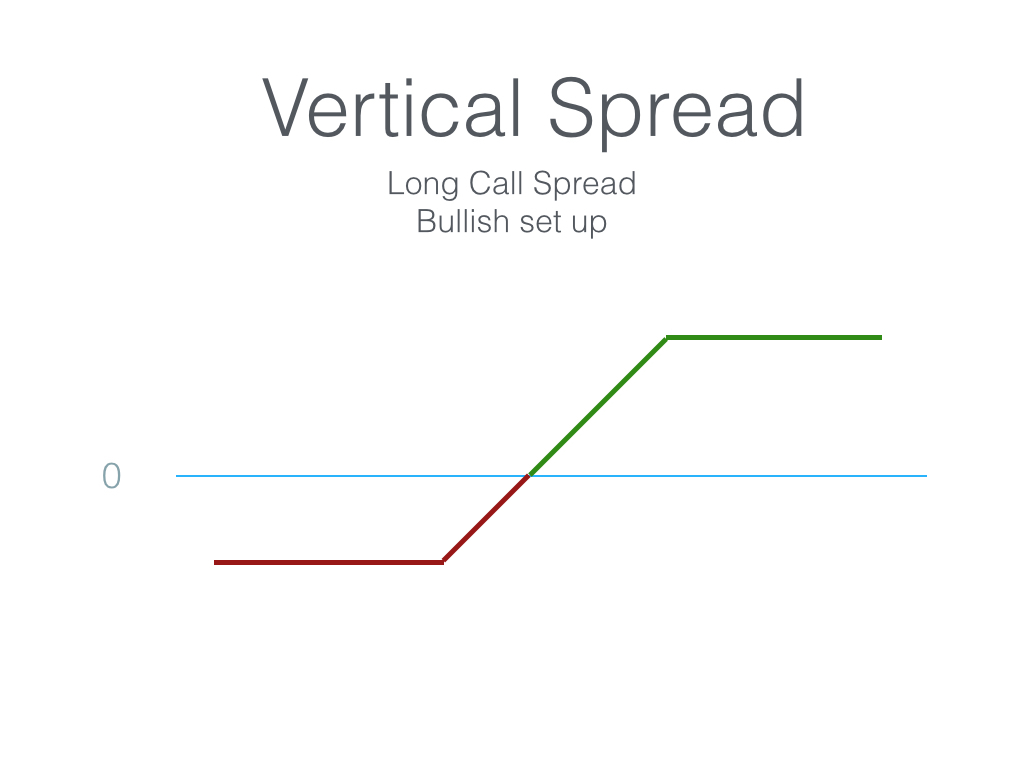
Image: www.randomwalktrading.com
In the realm of financial markets, options trading presents a sophisticated strategy that can enhance portfolio returns and mitigate risks. Among the myriad of options strategies, vertical options trading stands out as a flexible and versatile approach that offers both profit and hedging opportunities. This article delves into the intricacies of vertical options trading, explaining its mechanics, benefits, and potential pitfalls.
Understanding Vertical Options Trading
Vertical options trading involves simultaneously buying and selling options of the same underlying asset but with different strike prices and expiration dates. This creates a spread or combination that exploits the relationship between the underlying asset’s price and the options’ time value decay. Typically, a vertical spread consists of one option bought at a higher strike price (the long leg) and another option sold at a lower strike price (the short leg).
Types of Vertical Options Trading
There are two main types of vertical options spreads:
- Call spreads involve buying a call option and selling another call option with a higher strike price.
- Put spreads involve buying a put option and selling another put option with a lower strike price.
Bullish vs. Bearish Vertical Spreads
Based on the trader’s market预期 and the relationship between the strike prices of the options legs, vertical spreads can be either bullish or bearish:
- Bullish vertical spreads (call spreads in an upward market, put spreads in a downward market) profit if the underlying asset’s price rises (declines) beyond the breakeven point.
- Bearish vertical spreads (call spreads in a downward market, put spreads in an upward market) profit if the underlying asset’s price falls (rises) below (above) the breakeven point.
Benefits of Vertical Options Trading
- Limited risk: The maximum loss for a vertical spread is limited to the difference in premium prices between the bought and sold options.
- Defined profit potential: The profit potential is determined by the premium collected from the short leg and the difference in strike prices between the two options legs.
- Flexible strategy: Vertical spreads can be tailored to accommodate diverse market outlooks and risk tolerance levels.
Pitfalls of Vertical Options Trading
- Market volatility: Extreme price movements can cause rapid gains or losses in the spread.
- Margin requirements: Vertical spreads may require higher margin than single options due to the two legs.
- Time decay: The time value of the bought option (long leg) decays over time, reducing the spread’s value.
Conclusion
Vertical options trading offers a powerful tool for investors seeking to harness the potential of options markets. Its inherent flexibility and profit potential make it a compelling strategy for advanced traders. However, it is crucial to understand the risks associated with this form of options trading and to implement it within a well-defined trading plan. By leveraging the insights provided in this comprehensive guide, investors can navigate the intricacies of vertical options trading and enhance their portfolio performance.

Image: www.investingshortcuts.com
Vertical Options Trading

Image: www.youtube.com






