Introduction
In the realm of options trading, understanding the complexities of option pricing is imperative. Vega is a crucial Greek letter that quantifies the sensitivity of an option’s price to changes in implied volatility. Volatility, often characterized as the market’s perception of price uncertainty, plays a pivotal role in determining the value of options contracts. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of Vega, equipping traders with a profound understanding of its mechanics, applications, and strategic implications.
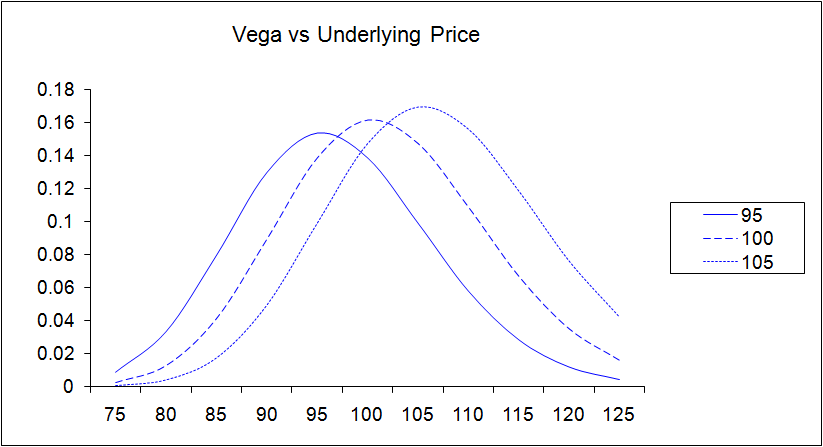
Image: www.bigtrends.com
Delving into the Dynamics of Vega
Vega represents the sensitivity of an option’s premium to implied volatility changes, quantified as the dollar change in the option’s price for each 1% increase in implied volatility. To illustrate, if an option has a Vega of 0.15 and implied volatility rises by 1%, the option’s premium would increase by $0.15 per contract. Intuitively, higher implied volatility enhances the potential for significant price movements, leading to increased option premiums. Conversely, lower implied volatility implies a lesser likelihood of extreme price fluctuations, which corresponds to diminished option premiums.
Vega’s Peculiar Traits
Vega exhibits distinctive attributes that set it apart from other Greek letters. Its value is typically positive for both call and put options, implying that an increase in implied volatility generally results in higher option prices. Notably, the magnitude of Vega is influenced by factors such as option type, strike price, time to expiration, and the underlying asset’s characteristics. For instance, at-the-money options tend to have higher Vega compared to deep out-of-the-money or deep in-the-money options.
Exploiting Vega in Trading Strategies
Traders can capitalize on Vega’s unique characteristics by incorporating it into their trading strategies. One such strategy involves selling options when implied volatility is elevated and buying them back when volatility subsides. This approach aims to profit from the decline in option premiums as volatility normalizes. Conversely, buying options when implied volatility is low and selling them as volatility rises can be a lucrative strategy if volatility increases more than anticipated.
Image: www.bigtrends.com
Harnessing Vega for Risk Management
Vega also serves as a crucial tool for risk management in options trading. Understanding the Vega profile of an options portfolio provides valuable insights into its sensitivity to volatility fluctuations. This knowledge enables traders to make informed adjustments to their positions, such as reducing exposure to Vega risk or implementing hedging strategies to mitigate potential losses.
Vega Option Trading

Image: haikhuu.com
Conclusion
Vega holds a prominent position among the Greek letters in the options trading lexicon. Its role in quantifying the impact of implied volatility changes on option prices is fundamental to understanding option pricing dynamics and risk management. By harnessing the knowledge gained from this comprehensive guide, traders can skillfully incorporate Vega into their strategies, empowering them to make informed decisions and optimize their trading outcomes.






