The stock market can be a daunting place, full of complex jargon and seemingly endless strategies. However, hidden within the labyrinth of financial instruments lies a powerful tool: call options. For the uninitiated, call options may seem like a mysterious concept, but they offer a unique and potentially lucrative way to play the market. Imagine this: you believe a certain stock is about to soar. With a call option, you can “bet” on that rise without owning the underlying stock, potentially reaping significant gains.
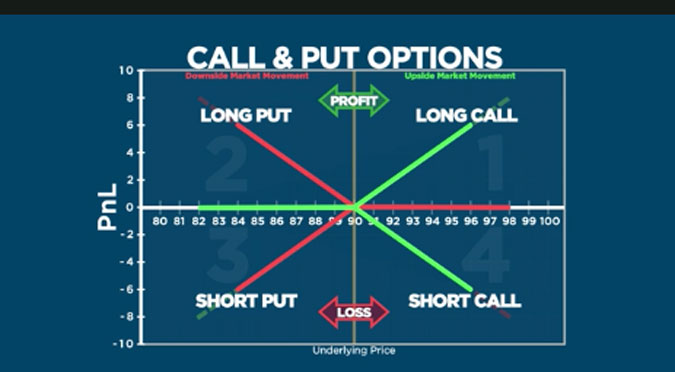
Image: hindi.adigitalblogger.com
My own foray into call options started with a simple investment philosophy: “What if I could gain exposure to a company’s growth without fully committing to purchasing shares?”. I researched call options and discovered a world of potential, where speculation met strategic investing. This journey into call options opened my eyes to a new way to approach the market, one filled with opportunities and nuanced strategies. This article aims to equip you with the knowledge and understanding to embark on your own call option adventure.
What are Call Options?
In essence, a call option gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to purchase a specific asset, like a stock, at a predetermined price (strike price) within a specified timeframe (expiration date). It’s like holding a ticket that lets you buy something at a set price, but you can choose to use it or not. The seller of the call option is obligated to sell the asset if the buyer exercises their right.
To illustrate, let’s imagine you buy a call option for 100 shares of Apple (AAPL) with a strike price of $150 and an expiration date of January 2024. If AAPL’s stock price rises above $150 before January, you can exercise your option, buying the 100 shares at $150 each, even though their market price is higher. The difference between the strike price and the current market price represents your profit. However, if the stock price doesn’t rise above $150 by the expiration date, your option expires worthless, and you only lose the premium you initially paid for it.
The Basics of Call Options: Understanding the Mechanics
The Premium: Your Initial Investment
When you buy a call option, you pay a premium to acquire the right to purchase the underlying asset. This premium is the price you pay for the potential to profit from price fluctuations. The premium reflects factors like the stock’s current price, the strike price, the time remaining until expiration, and the stock’s volatility.
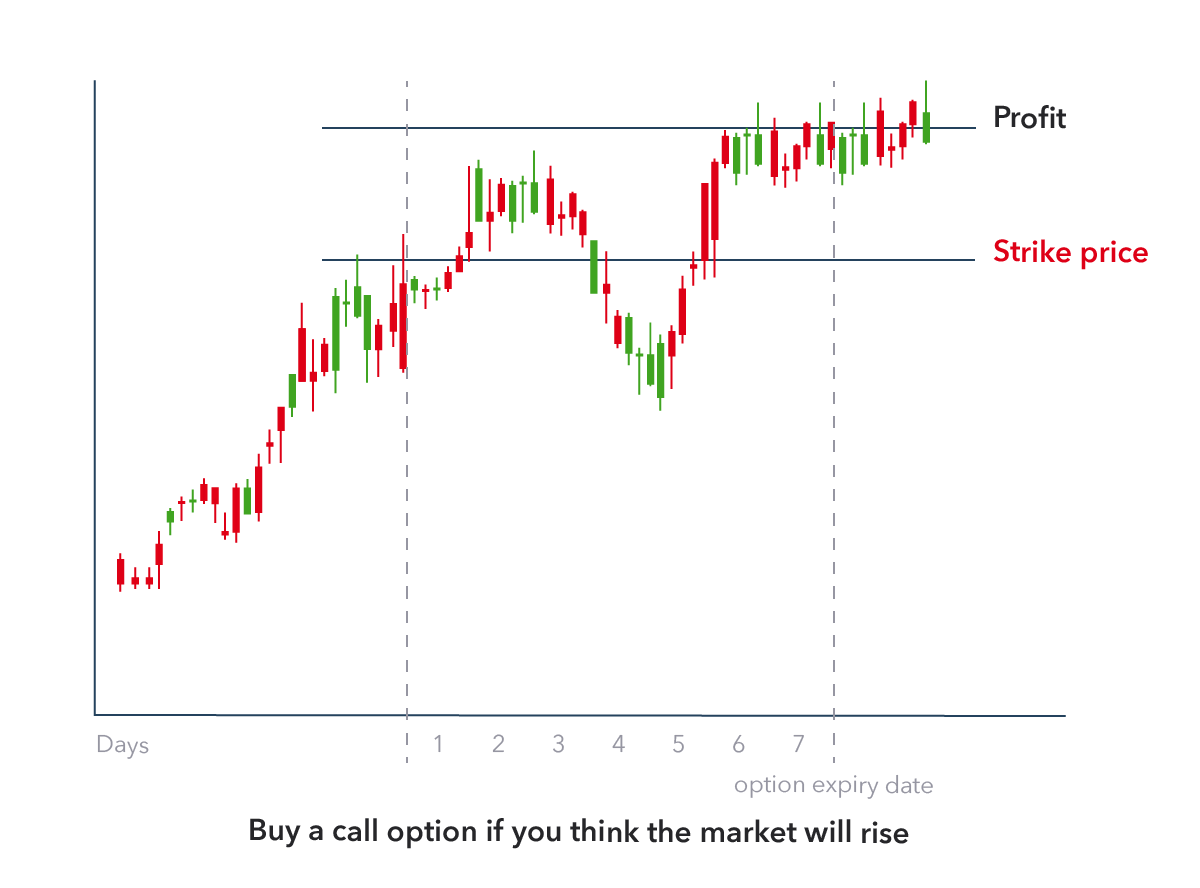
Image: varelgroup.com
Strike Price: Your Buying Price
The strike price is the set price at which you can buy the underlying asset if you choose to exercise your option. When you buy a call option, you’re essentially betting that the stock price will rise above the strike price before the expiration date. The further the stock price rises above the strike price, the greater your potential profit.
Expiration Date: Your Time Limit
Each call option has a specified expiration date. This is the deadline by which you must exercise your option if you want to purchase the underlying asset. If the expiration date passes, and you haven’t exercised your option, it expires worthless, and you lose the premium you paid.
Why Use Call Options?
Call options offer several potential advantages over directly buying shares:
- Leverage: Call options allow you to control a larger position in a stock using a smaller investment. You can potentially make large profits on smaller price movements.
- Limited risk: Your potential losses are limited to the premium you paid for the call option (excluding commissions). Unlike buying shares, you can’t lose more than the premium.
- Flexibility: Call options give you the flexibility to buy or not buy the underlying stock. You can choose to exercise your option if it’s profitable or let it expire if the stock doesn’t move in your favor.
- Market timing: Call options allow you to speculate on short-term market movements without holding the stock for an extended period.
Call Options in Action: Real-World Examples
Let’s look at a couple of real-world examples to illustrate how call options work in practice:
Scenario 1: A Bullish Bet on Tesla
You believe Tesla’s stock price is going to rise significantly in the next few months. You buy a call option for 100 shares of Tesla (TSLA) with a strike price of $1000 and an expiration date of six months from now. The premium for this call option is $50 per share.
If TSLA’s price rises to $1100 before the expiration date, you can exercise your option, buying 100 shares at $1000 each, even though the market price is $1100. You can then immediately sell the shares at the market price, making a profit of $100 per share ($1100 – $1000), minus the premium you paid ($50). Your total profit would be $5000 ($100 x 100 shares), minus the premium paid ($5000).
However, if TSLA’s price stays below $1000, you lose the entire premium (5000). You could potentially lose your entire investment in the premium if the price of the stock doesn’t rise above the strike price.
Scenario 2: A Short-Term Trade on Netflix
You believe Netflix (NFLX) will experience a jump in its stock price in the short term due to an upcoming movie release. You decide to buy a call option for 100 shares with a strike price of $350 and an expiration date of one month from now. The premium for this option is $20 per share.
If NFLX’s price rises to $370 before the expiration date, you exercise your option, buying 100 shares at $350 each. You immediately sell the shares at the market price of $370, making a profit of $20 per share ($370 – $350), minus the premium paid ($20). Your total profit would be $2000 ($20 x 100 shares), minus the premium paid ($2000).
However, if NFLX’s price stays below $370, you only lose the premium (2000). This strategy allows you to bet on a short-term price fluctuation without committing to holding the stock for longer.
Recent Trends in Call Options Trading
Recent trends in call options trading highlight growing interest in this tool as a potential avenue for profit.
- Increased Volatility: The heightened volatility in markets, driven by factors such as economic uncertainty, geopolitical events, and interest rate fluctuations, has seen investors turn to call options as a means to manage risk and maximize potential gains.
- Retail Investor Growth: The rise of online brokerages and increased accessibility to financial markets has empowered retail investors to participate actively in options trading. This has led to a surge in trading volume for call options, particularly among younger generations seeking to capitalize on growth opportunities.
- Technological Advancements: The advancement of trading platforms with user-friendly interfaces and access to real-time data and analytics has made options trading more accessible and intuitive for both experienced and novice investors.
Tips for Trading Call Options
While call options can provide significant potential gains, it’s essential to remember that they are a complex tool. Here are a few tips for navigating the world of call options:
- Understand the Risks: Call options involve risks that are different from buying shares outright. Be prepared to lose the entire premium you paid if the stock price doesn’t move in your favor.
- Conduct Thorough Research: Before investing in call options, conduct thorough research on the underlying stock. Analyze its financial performance, industry trends, and market sentiment to make informed decisions.
- Set Stop-Loss Orders: To limit potential losses, set stop-loss orders. This allows you to automatically sell the option if the price falls below a certain level.
- Consider Expiration Dates: Choose expiration dates wisely. Short-term options are more volatile and can offer greater returns, but they also carry higher risks. Longer-term options offer more time for the underlying stock to move in your favor, but they may also have lower potential returns.
- Start Small and Gradually Increase: If you’re new to options trading, start with small positions and gradually increase your investment as you gain experience and confidence.
Call options offer a powerful tool for investors seeking to take advantage of market opportunities. With careful research, risk management, and a well-defined strategy, they can potentially lead to significant returns. Remember, knowledge is power, and investing in yourself by learning about options trading can unlock a whole new world of financial possibilities.
FAQ
Q: Are call options suitable for all investors?
A: Call options are not suitable for all investors. They involve a higher level of risk than simply buying shares, and require a thorough understanding of options trading concepts. If you’re new to investing, consider starting with a simpler approach before venturing into options trading.
Q: How can I learn more about call options?
A: There are numerous resources available to learn more about call options. You can access online courses, webinars, books, and articles. Consult with a financial advisor if you have specific questions or would like personalized guidance.
Q: Where can I buy and sell call options?
A: Most online brokerages allow you to trade call options. Look for reputable brokerages that offer comprehensive options trading platforms and educational resources.
Call Options Trading
Conclusion
Call options can be a powerful tool for experienced investors seeking to maximize potential gains or hedge against downside risk. Remember, every investment comes with associated risks, and call options are no exception. Learning about this tool and understanding the risks involved is crucial to making informed investment decisions.
Are you interested in learning more about call options and how they can be used to enhance your investment strategy? Let me know in the comments below.






