Have you ever wished you could buy a stock at a lower price than its current market value? Imagine being able to secure the right to purchase a stock at a predetermined price, even if the price rises significantly in the future. This is the power of call options, a fascinating and potentially lucrative tool in the world of options trading.

Image: www.youtube.com
Think of it like this: you’re at a farmer’s market, and you find an amazing deal on a bushel of apples. However, you’re not ready to buy them right now, but you don’t want to miss out on this incredible price. The farmer offers you a deal: you can pay a small fee, and you’ll have the option to buy the apples at that price anytime within the next few weeks. That’s essentially what a call option does for stocks.
Understanding Call Options: Your Key to Profiting from Rising Prices
In essence, a call option grants the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to purchase a specific underlying asset, like a stock, at a predetermined price (called the strike price) on or before a specific date (the expiration date). It’s like a ticket that gives you the power to buy the stock, but you don’t have to if you don’t want to.
The beauty of call options lies in their ability to generate potential profits when the price of the underlying asset rises. When you buy a call option, you are essentially betting that the price of the stock will go up. If the stock price surpasses the strike price, you can exercise your option, buy the stock at a lower price than the market, and then sell it at the current market price, pocketing the difference.
Breaking Down the Call Option: Key Components Explained
1. The Strike Price: Defining Your Purchase Price
The strike price is the price at which the option holder can buy the underlying asset, regardless of the market price. It acts as a guaranteed price for purchasing the asset. For example, if you buy a call option with a strike price of $50, you have the right to purchase the underlying stock at $50 per share, even if the stock is trading at $60 per share in the market.
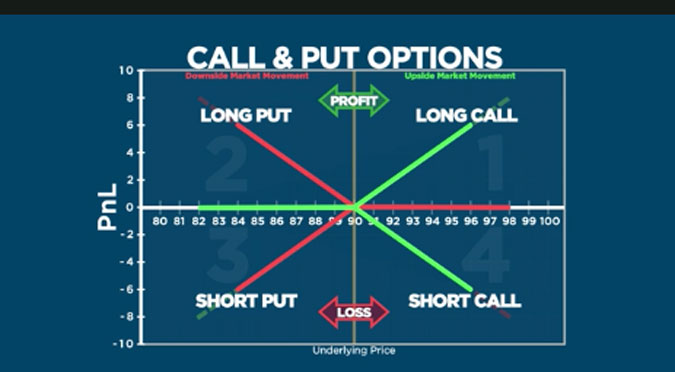
Image: hindi.adigitalblogger.com
2. The Expiration Date: Your Window of Opportunity
The expiration date is the final date on which the call option can be exercised. After this date, the option expires and becomes worthless. The expiration date can be anywhere from a few weeks to several months or even years in the future.
3. The Premium: Your Investment in the Option
The premium is the price you pay to purchase the call option. It represents the cost of securing the right to buy the underlying asset at the strike price. The premium is influenced by factors such as the time until expiration, the volatility of the underlying asset, and its current market price compared to the strike price.
Call Options: A Powerful Tool with Risks and Rewards
Call options offer a unique advantage: they allow investors to control a significant amount of assets with a relatively small investment. This leverage can lead to substantial profits if the stock price moves in the desired direction. However, the potential for high returns comes with a caveat: call options also come with the risk of losing your entire initial investment if the stock price doesn’t rise or doesn’t rise enough to cover the premium you paid.
Let’s say you invest $100 in a call option that gives you the right to buy a stock at $50 per share. If the stock price rises to $60 per share before the expiration date, you can exercise your option, buy the stock at $50, and sell it in the market at $60, making a profit of $10 per share. However, if the stock price drops below $50, your option will expire worthless, and you’ll lose your entire $100 investment.
Understanding Call Options: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
1. Call options are a way to bet on increasing stock prices:
If you believe in a company and think its stock price is likely to go up, call options can be a valuable tool. If your prediction is right and the stock price rises, your call option will increase in value, potentially generating significant returns.
2. Call options offer leverage:
Buying call options allows you to control a larger amount of stock with less upfront capital than simply buying shares directly. This leverage can magnify profits, but it can also magnify losses if the stock price moves against your prediction.
3. Call options have limited risk:
Unlike buying shares, where your potential losses are unlimited, with call options, your maximum loss is limited to the initial premium you paid. If the price of the underlying asset doesn’t rise, your call option will expire worthless, but you won’t lose more than what you paid for it.
4. Call options have a time-bound nature:
Remember, call options have an expiration date. If the stock price doesn’t reach your targeted price before the expiration date, your option will expire worthless, resulting in a total loss of your premium. That’s why it’s crucial to understand your investment horizon and choose an expiration date that aligns with your strategy.
5. Call options are a complex financial instrument:
While they can offer exciting opportunities, call options are relatively complex instruments. It’s essential to educate yourself thoroughly about the underlying stock, the option pricing models, and the risks involved before investing in call options.
Tips for Trading Call Options: Mastering the Art of Timing and Strategy
Trading call options effectively requires careful planning, a sound understanding of the market, and a strong risk management strategy. Here are some tips to help you navigate this exciting world and potentially maximize your returns:
1. Research the stock:
Before purchasing a call option, thoroughly research the underlying company’s fundamentals, its financial performance, and its industry outlook. This research process will help you make informed decisions about the potential for the stock price to rise.
2. Choose the right strike price and expiration date:
Select strike prices and expiration dates that align with your investment horizon and your price expectations. Think about how much the stock price needs to rise to be profitable. If you think it will take a significant price appreciation for your option to be profitable, consider a longer expiration date to give yourself more time.
3. Manage your risk:
Call options amplify risk, so it’s crucial to manage your risk prudently. Consider using stop-loss orders or other strategies to limit potential losses.
4. Know when to exit a trade:
Define your profit targets and exit points in advance. Don’t hold onto an underperforming option hoping for a turnaround, as this can lead to larger losses.
5. Stay informed about market conditions:
Stay informed about market news and trends, and be prepared to adjust your investment strategy accordingly. This could involve adjusting your strike price, expiration date, or even selling your position if the market changes direction unexpectedly.
Frequently Asked Questions: Demystifying Call Options
Q: Is a call option the same as buying a stock?
A: No, a call option is not the same as buying a stock. Buying a stock gives you ownership of that stock, while buying a call option gives you the right, but not the obligation, to buy the stock at a specific price before the expiration date.
Q: How much does it cost to buy a call option?
A: The cost of a call option is called the premium, and it is influenced by the price of the underlying stock, the strike price, the expiration date, and the volatility of the underlying stock.
Q: What happens if the stock price doesn’t move up?
A: If the stock price doesn’t rise above the strike price before the expiration date, your call option will expire worthless, and you’ll lose your entire initial investment (the premium). However, if the stock price falls below the strike price, you’ll also lose money, making call options more suitable for bullish market conditions.
Q: How can I learn more about options trading?
A: There are many resources available for learning about options trading, including online courses, books, and websites. It’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the basics of options trading before investing in them.
Q: What are some risks involved in trading call options?
A: As with any investment, there are risks involved in trading call options. These include the risk of losing your entire investment if the stock price doesn’t move in your favor, the time value decay of the option, and the volatility of the underlying asset. It’s crucial to understand these risks before investing and manage your risk appropriately.
What Is A Call In Options Trading
Conclusion: Embracing the Potential of Call Options
Call options can be a powerful tool for investors looking to profit from the potential upside of rising stock prices. They offer leverage and limited risk, but they also come with inherent risks. By carefully researching the underlying stock, understanding the option pricing models, and implementing a robust risk management strategy, investors can potentially capitalize on the opportunities presented by call options. Remember, education is key: the more you understand about the options trading market, the better equipped you’ll be to navigate this fascinating world.
Are you interested in learning more about call options or exploring further into options trading?






