Understanding Limit Orders: The Basics
Options trading, a versatile financial strategy, enables investors to delve into complex markets with distinct levels of risk and potential rewards. Among the various order types in options trading, limit orders stand out as essential tools for executing trades at specific prices. This article delves into the intricacies of limit offset, an integral aspect of limit orders, empowering you to navigate the dynamic realm of options trading with greater precision.

Image: www.pinterest.com
Limit orders, in essence, allow traders to designate the highest price they are willing to pay for an option (in the case of buy orders) or the lowest price they are willing to accept (for sell orders). By setting these price limits, traders can exercise more control over the execution of their trades, ensuring that orders are filled only when the market conditions align with their stipulations.
Decoding Limit Offset: Precision in Execution
Limit offset, a crucial parameter in limit orders, quantifies the deviation from the current market price that a trader is willing to accept. It establishes a range around the designated limit price within which orders can be filled. This offset, when skillfully employed, can significantly enhance the effectiveness of limit orders in capturing favorable market conditions.
For instance, imagine a scenario where the underlying stock of an option contract you’re interested in is currently trading at $50. If you place a buy limit order with a limit price of $48 and a limit offset of $1, your order will be eligible for execution at any price between $48 and $49 (the limit price plus the offset). This flexibility ensures that you won’t miss out on potential trading opportunities due to minor market fluctuations around your desired price point.
Optimizing Limit Orders: Striking the Balance
While limit offset brings undeniable benefits to options trading, it’s imperative to approach its implementation with a balanced perspective. Setting excessively wide limit offsets may result in orders being filled at unfavorable prices, potentially undermining your trading strategy. Conversely, overly narrow offsets could limit the chances of order execution, especially in fast-moving markets.
Finding the optimal limit offset is akin to walking a tightrope, requiring careful consideration of various factors. Market volatility, liquidity, and order size all play significant roles in determining the ideal offset for your specific trading needs.
Limit Offset in Practice: Real-World Examples
To illustrate the practical application of limit offset, let’s consider two contrasting scenarios in the context of real-world options trading:
-
High-Volatility Market: In a highly volatile market characterized by rapid price fluctuations, a wider limit offset may be warranted. This expanded range increases the likelihood of order execution while mitigating the risk of missing out on potential trading opportunities.
-
Low-Volatility Market: In contrast, a more stable and less volatile market may call for a narrower limit offset. By setting a tighter range, traders can prioritize precision and aim for more favorable execution prices.
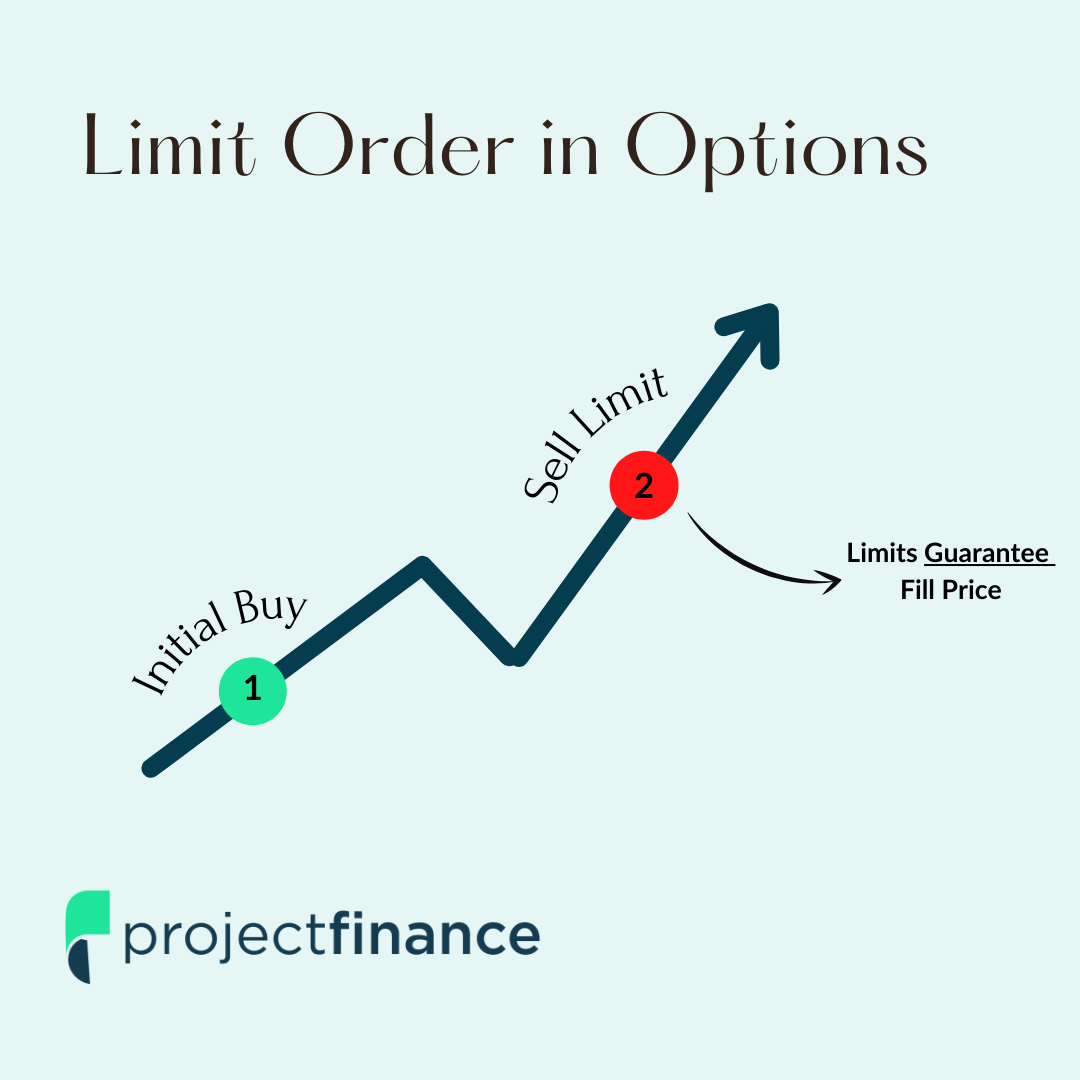
Image: www.projectfinance.com
What Does The Limit Offset Mean In Options Trading
Image: nolossforextradingstrategy.blogspot.com
Conclusion: Empowering Informed Decisions
Limit offset emerges as an indispensable tool in the arsenal of options traders, enabling them to execute trades with greater precision and finesse. By understanding the intricacies of limit offset, traders can harness its power to optimize their trading strategies, navigate market dynamics with agility, and enhance their overall trading performance.






