Introduction
In the realm of options trading, deciphering acronyms and evaluating complex metrics is imperative for astute decision-making. Among these, the Average True Range (ATR) stands out as a valuable tool for assessing market volatility and managing risk. This article delves into the significance of ATR, elucidating its calculation, interpretation, and practical applications in options trading.

Image: capital.com
Unraveling What ATR Signifies
The Average True Range, commonly referred to as ATR, is a technical analysis indicator that quantifies the level of volatility in a given financial instrument. It measures the size of price movements over time, reflecting the extent of fluctuations in the underlying asset’s value.
The Mathematical Formula Behind ATR
The calculation of ATR involves a specific formula that considers the true range of prices over a designated period. The true range is determined as the maximum of the following three values:
- Current high minus current low
- Absolute value of current high minus previous close
- Absolute value of current low minus previous close
By averaging these true range values over a predefined period (typically 14 days), the ATR is derived.
Interpreting ATR Values
The ATR provides insights into market volatility by assigning numerical values:
- High ATR: Indicates significant price fluctuations, suggesting greater volatility and risk.
- Low ATR: Denotes relatively stable prices, implying reduced volatility and lower risk.
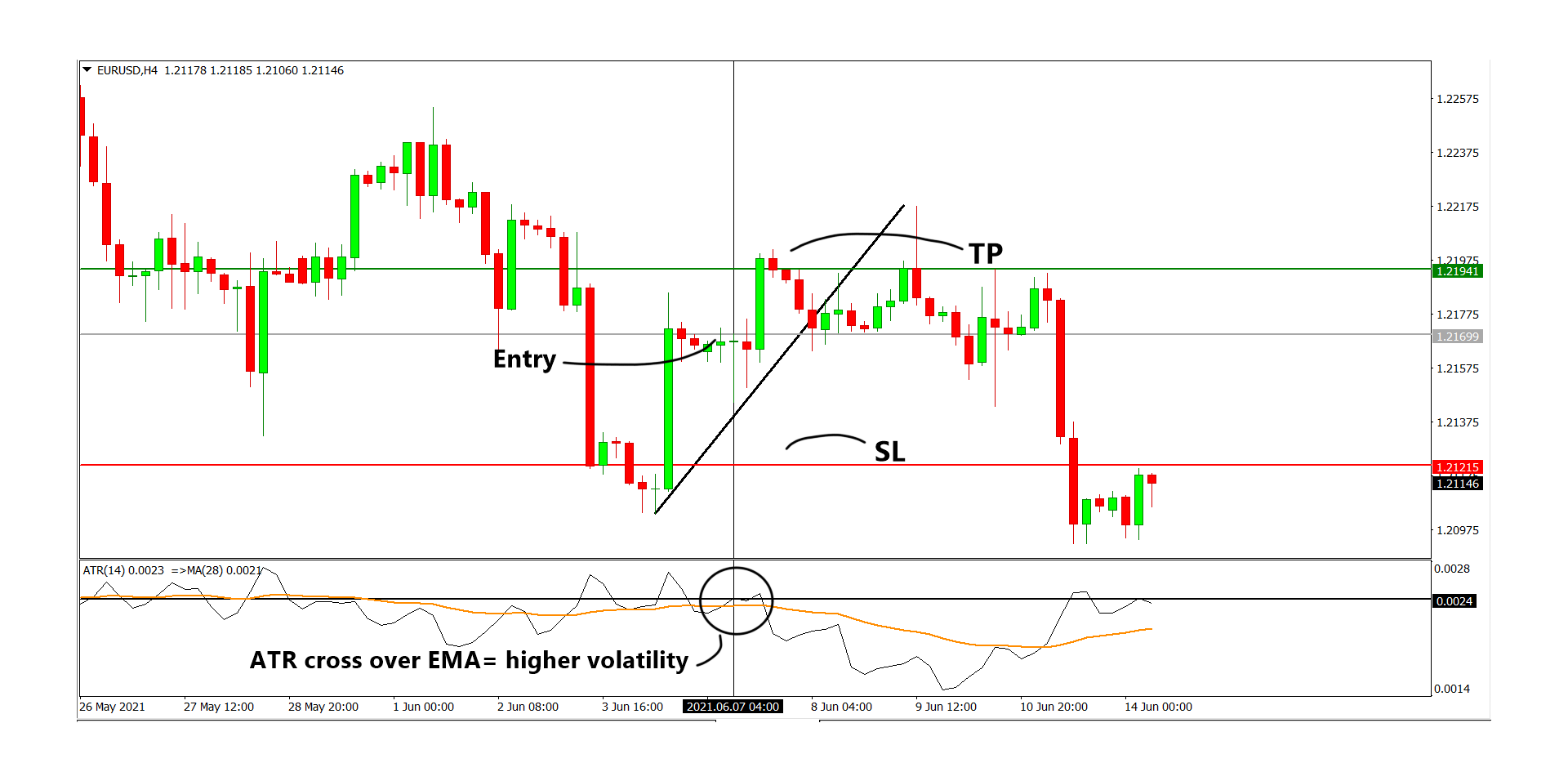
Image: www.asiaforexmentor.com
The Significance of ATR in Options Trading
ATR plays a crucial role in options trading, enabling traders to:
- Assess Market Volatility: ATR gauging market volatility helps determine the appropriate option strategies based on the expected level of price fluctuations.
- Manage Risk: By incorporating ATR in risk management strategies, traders can set appropriate stop-loss levels and calculate potential losses based on the expected range of price movements.
- Identify Trading Opportunities: High ATR values may indicate potential trading opportunities by suggesting the likelihood of significant price swings or breakouts.
Real-World Applications of ATR
In practical applications, ATR finds its use in various options trading scenarios:
- Day Trading: Scalpers and day traders utilize ATR to determine entry and exit points, leveraging its volatility insights for short-term profit-taking.
- Trend-Following: Traders following momentum or trend-following strategies employ ATR to assess the strength of a trend and calibrate their trading approach.
- Hedging Strategies: Incorporating ATR in hedging strategies enables traders to optimize their risk exposure by counterbalancing potential price swings.
Refining Your Options Trading with ATR
To effectively leverage ATR in options trading:
- Set Realistic Parameters: Determine appropriate ATR calculation periods based on the time frame of your trading strategy.
- Combine with Other Indicators: Use ATR in conjunction with other technical indicators for more comprehensive market assessments.
- Consider Market Context: Interpret ATR values relative to market conditions and overall industry dynamics.
What Does Atr Stand For In Options Trading

Image: www.youtube.com
Conclusion
The Average True Range (ATR) stands as a fundamental tool for evaluating market volatility and managing risk in options trading. Understanding its calculation, interpretation, and practical applications empowers traders to make informed decisions, navigate market fluctuations, and enhance their overall trading performance. By integrating ATR into your trading arsenal, you can elevate your strategies and achieve greater financial success.






