In the ever-evolving landscape of financial markets, options trading has emerged as a powerful tool for investors seeking to mitigate risk and maximize returns. Among the various options strategies, Average True Range (ATR) options trading stands out as a particularly effective approach. This article delves into the intricacies of ATR options trading, empowering you with a comprehensive understanding of its definition, principles, and strategies.
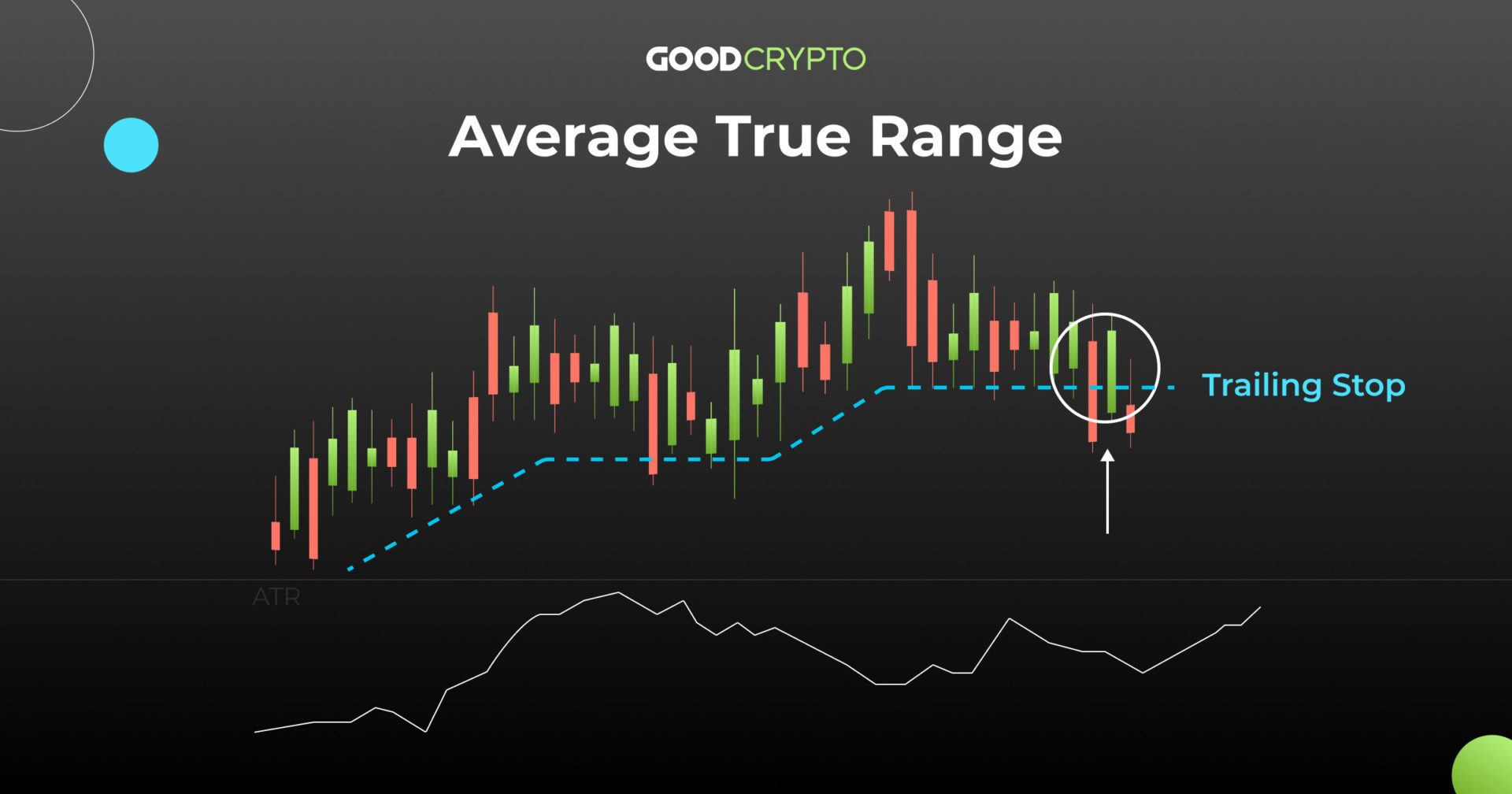
Image: goodcrypto.app
Understanding Average True Range
Introducing ATR
Average True Range (ATR) is a technical indicator that measures the volatility of a financial instrument, such as a stock, index, or currency pair, over a specified period. It provides an objective assessment of the asset’s price fluctuations, helping traders gauge the potential risk and reward associated with a trade.
ATR was developed by J. Welles Wilder and introduced in his book “New Concepts in Technical Trading Systems.” It calculates the true range of an asset over a set number of periods (usually 14) and then averages those true ranges to produce the ATR value.
Components of ATR Calculation
The true range of an asset is defined as the greatest of the following three values:
- Current High minus Current Low
- Absolute value of Current High minus Previous Close
- Absolute value of Current Low minus Previous Close
By incorporating these three components, ATR effectively captures price movements that may not be reflected in traditional range calculations, such as gaps and wick shadows.
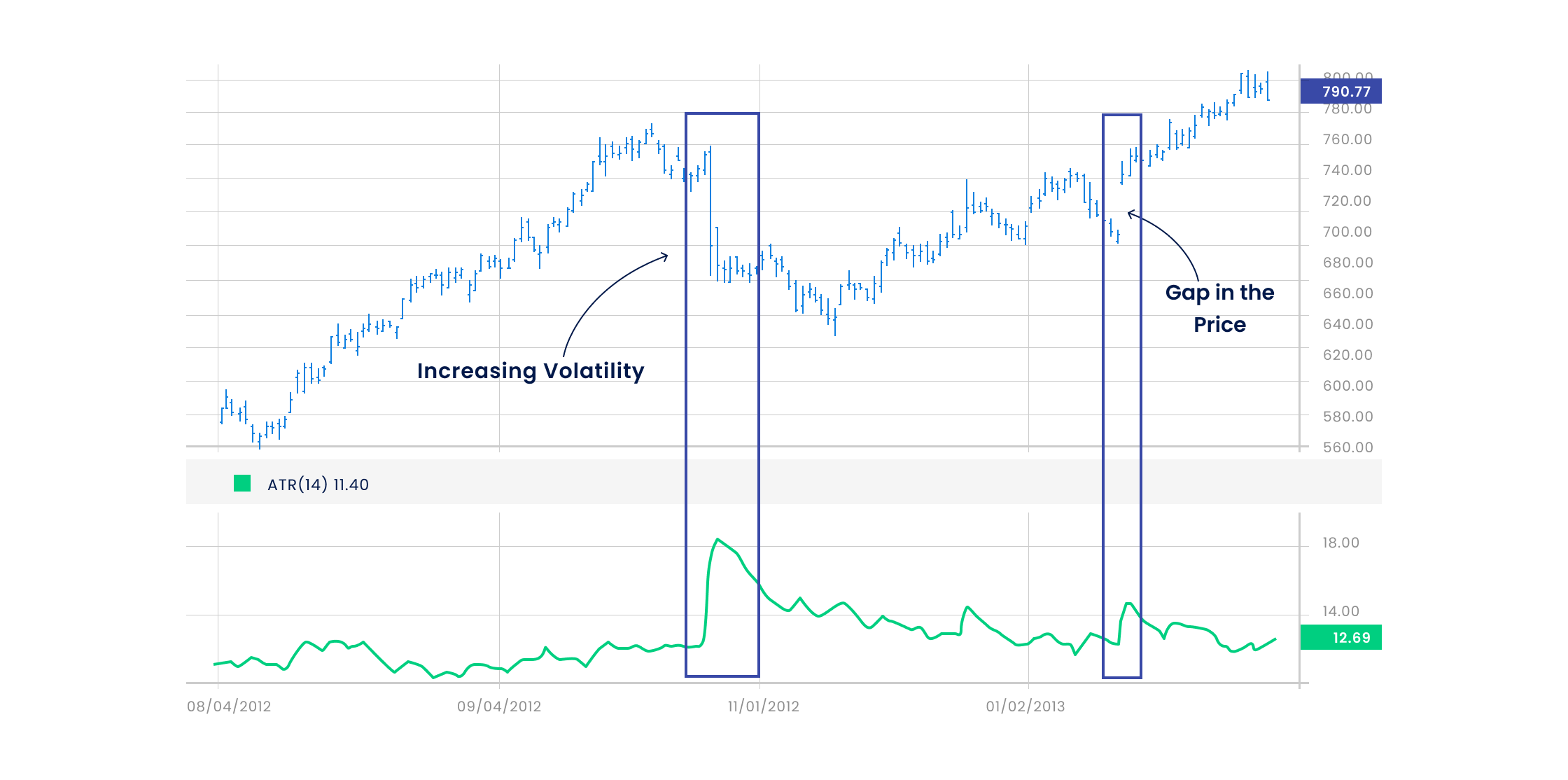
Image: blueberrymarkets.com
ATR Options Trading Strategies
Options trading involves the use of contracts that give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specified price on or before a certain date. By utilizing ATR, traders can enhance their options trading strategies by:
1. Volatility Assessment
ATR provides a quantifiable measure of volatility, enabling traders to make informed decisions about option strike prices and expiration dates. High ATR values indicate increased volatility, warranting wider strikes and longer expiration periods to accommodate larger price movements.
2. Risk Management
By estimating the potential range of an asset’s price fluctuations using ATR, traders can adjust their positions accordingly to manage risk. Higher ATR values signal potentially greater price swings, prompting traders to adopt more conservative strategies, such as using wider stop-losses or limiting trade size.
3. Trade Timing
ATR helps traders identify periods of low and high volatility. During periods of low ATR, option premiums tend to be lower, offering opportunities for traders to enter positions at more favorable prices. Conversely, during periods of high ATR, premiums are typically higher, requiring traders to carefully consider the risk-reward balance.
Tips and Expert Advice for ATR Options Trading
To maximize the effectiveness of ATR options trading, consider the following expert advice:
1. Determine Optimal ATR Parameters
The ideal ATR period depends on the specific asset and trading timeframe you are using. Experiment with different periods (e.g., 14, 21, 50) to find the one that best suits your trading style and risk tolerance.
2. Combine ATR with Other Indicators
Do not rely solely on ATR. Use it in conjunction with other technical indicators, such as moving averages, support and resistance levels, and volume patterns, to enhance your market analysis and decision-making.
3. Manage Risk Prudently
Always remember that trading involves risk. Use stop-loss orders to protect your capital in case of adverse price movements. Limit your trade exposure to a level that aligns with your risk tolerance and financial situation.
Frequently Asked Questions about ATR Options Trading
Q: What is the difference between ATR and volatility?
ATR is a specific indicator that measures volatility, but it is not the only one. Other volatility indicators include Bollinger Bands, the Keltner Channel, and the Volatility Index (VIX).
Q: How can I use ATR to identify trading opportunities?
Look for periods of high and low ATR to assess market volatility. During periods of low ATR, option premiums may be lower, providing potential buying opportunities. Conversely, during periods of high ATR, premiums may be higher, indicating a potentially riskier environment for entering positions.
Q: Is ATR suitable for all types of options trading strategies?
ATR can be incorporated into various options trading strategies, including calendar spreads, butterfly spreads, and iron condors. However, it is essential to tailor your strategy to your specific risk tolerance, investment goals, and market conditions.
Atr Options Trading
Conclusion
ATR options trading offers a powerful tool for traders to navigate the volatile world of financial markets. By understanding the principles of ATR and incorporating it into your trading strategies, you can improve your risk management, identify trading opportunities, and maximize your returns.
So, are you ready to embark on the journey of ATR options trading? Embrace the knowledge and insights presented here and start exploring the potential of this remarkable technique. May the markets favor your endeavors!






