Introduction
The world of options trading offers investors two primary choices: trading options or exercising them. Each approach has its unique advantages and disadvantages, and the decision of which to pursue depends on the investor’s objectives, risk tolerance, and investment timeline. This article delves into the intricate details of trading options versus exercising options, providing a thorough understanding to help investors make informed decisions.

Image: starecat.com
Trading Options
Options trading involves buying or selling contracts that represent the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specified price on or before a certain date. Traders can engage in various strategies, including buying calls (the right to buy) or puts (the right to sell), selling calls (the obligation to sell) or puts (the obligation to buy), or using more complex strategies such as spreads or iron condors.
The primary advantage of trading options lies in their flexibility. Traders can speculate on price movements without committing to an actual purchase or sale. This allows for limited risk exposure and the potential for substantial profits with relatively small investments. Additionally, options provide traders with the opportunity to hedge their positions, reducing potential losses from adverse price fluctuations.
Exercising Options
Exercising an option refers to the act of buying or selling the underlying asset at the agreed-upon price. This is typically done when the trader believes that the underlying asset has reached a favorable price for their strategy. For example, an investor holding a call option may exercise it to purchase the stock at a lower price than the prevailing market rate. Conversely, an investor holding a put option may exercise it to sell the stock at a price higher than the market rate.
Exercising options carries the obligation to complete the transaction. This means that the investor assumes full ownership of the underlying asset for a call option (long position) or theobligation to deliver the underlying asset for a put option (short position). While exercising options provides the potential for substantial profits, it also comes with unlimited risk as the trader remains exposed to any price fluctuations after the exercise date.
Comparison: Trading vs. Exercising
The choice between trading and exercising options hinges on several factors:
Investment Objectives: Traders focused on short-term speculation or hedging may prefer trading options due to their flexibility and limited risk exposure. Investors seeking long-term capital gain or specific ownership of an asset may prefer exercising options.
Risk Tolerance: Trading options allows investors to cap their potential losses to the premium paid for the contract. Exercising options, on the other hand, exposes investors to unlimited potential losses, making this approach more suitable for those with a high risk tolerance.
Investment Timeline: Trading options typically involves shorter-term strategies, with contracts expiring within a few weeks or months. Exercising options requires a longer-term investment horizon, as the investor takes full ownership of the underlying asset.

Image: www.excalibur.com.hk
Practical Examples
Trading Options for Profit:
- Trader A buys a call option on XYZ stock for $5 per share, expiring in two months. If the stock price rises to $100 per share, the trader has the right to buy the stock at $105 per share (the strike price plus the premium). The trader can then sell the stock in the market for a profit of $45 per share.
Exercising Options for Investment:
- Trader B holds a long-term investment strategy in XYZ stock. They purchase a call option on XYZ stock with a strike price of $100 per share, also expiring in two months. As the stock price increases to $110 per share, Trader B exercises the call option and purchases the stock at $105 per share. They now own the stock for $10 per share below the market price.
Trading Options Vs Exercising Options
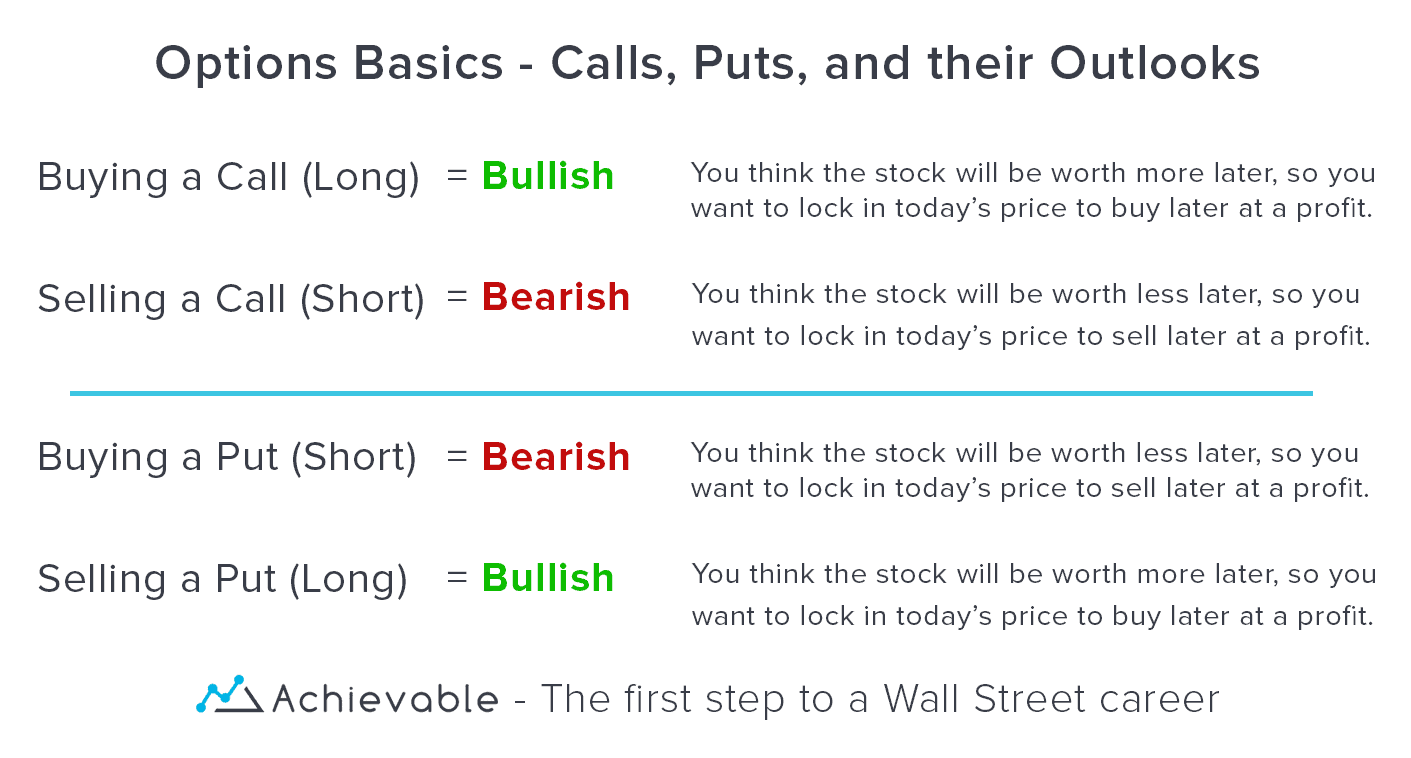
Image: blog.achievable.me
Conclusion
Understanding the nuances of trading options versus exercising options is crucial for investors navigating the complex world of options trading. By carefully considering their investment objectives, risk tolerance, and investment timeline, investors can make informed decisions that align with their financial goals. Whether seeking short-term speculation or long-term capital appreciation, both approaches offer unique opportunities for financial success in the options market.






