Navigating the Intricacies of Two Key Option Strategies
As an avid investor, I have often found myself grappling with the choice between trading and exercising options. Both strategies possess distinct advantages and implications, and understanding the nuances between them is critical for maximizing returns and mitigating risk.
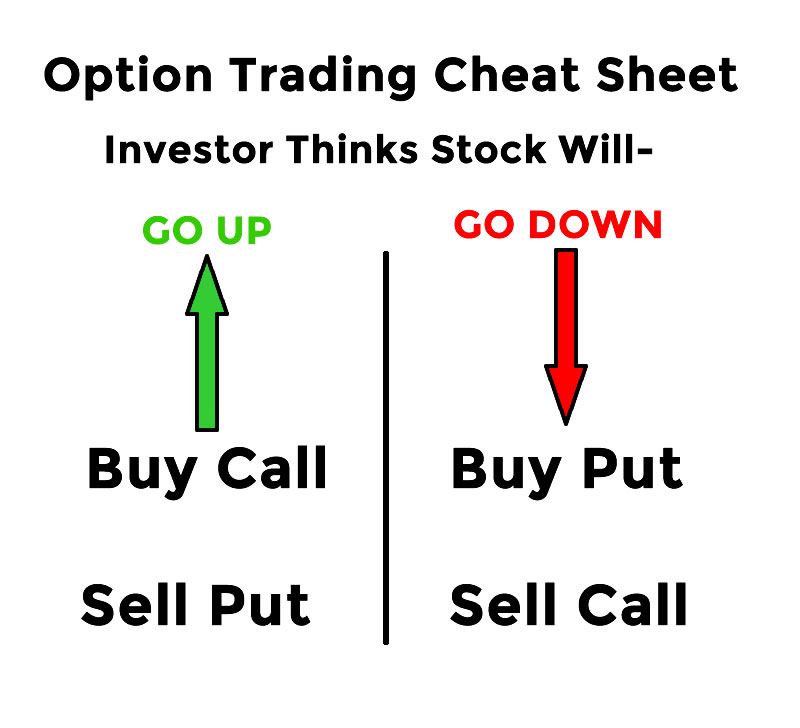
Image: alphabetastock.com
Trading vs. Exercising Options: A Conceptual Overview
An option contract grants the holder a specific right to either purchase (call option) or sell (put option) an underlying asset at a preset price (strike price) on or before a predetermined date (expiration date). Trading options entails buying and selling these contracts, benefiting from price fluctuations. Exercising options, on the other hand, involves utilizing the contractual right to buy or sell the underlying asset directly.
Choosing the Optimal Strategy: A Comparative Analysis
The decision between trading and exercising options hinges upon several key factors:
- Investment Horizon: Trading options offers greater flexibility for both short-term and long-term investment strategies, while exercising options typically aligns with long-term investments.
- Market Dynamics: In volatile markets, trading options can provide opportunities for quick profits, whereas exercising options is more suitable in stable or upward-trending markets.
- Risk Tolerance: Trading options carries inherent risks and substantial losses, making it appropriate for risk-tolerant investors. Exercising options entails limited risk, as the downside is capped at the premium paid for the contract.
- Financial Leverage: Trading options offers significant financial leverage, allowing investors to control a sizeable position with a relatively small investment. Exercising options does not provide leverage, so the investor must possess sufficient capital to cover the exercise price.
Tips and Expert Advice for Maximizing Option Trading Returns
- Thoroughly research the underlying asset: Understand its market dynamics, historical performance, and future prospects.
- Choose the right type of option: Call options are suitable for bullish expectations, while put options are appropriate for bearish forecasts.
- Set realistic trading goals: Determine specific profit targets and loss limits based on market conditions and risk tolerance.
- Manage risk effectively: Use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses and employ hedging strategies to reduce overall risk.
- Monitor market conditions closely: Stay informed about economic news, industry trends, and any factors that can impact option prices.

Image: www.esofund.com
Frequently Asked Questions on Trading and Exercising Options
Q: What is the difference between an option premium and an exercise price?
A: The option premium is the price paid for the right to exercise an option contract, while the exercise price is the preset price at which the underlying asset can be bought or sold upon exercising the option.
Q: Can I trade options without exercising them?
A: Yes, option trading involves buying and selling contracts without necessarily exercising the right to buy or sell the underlying asset.
Q: When is it advisable to exercise an option instead of selling it?
A: Exercising options is typically recommended when the underlying asset’s market price is significantly higher (for call options) or lower (for put options) than the exercise price.
Trading Vs Exercising Options

Image: bullishbears.com
Conclusion
Trading and exercising options are versatile strategies that cater to different investment goals and risk profiles. By understanding the key distinctions between these approaches and applying the tips provided, investors can navigate the complex world of options trading effectively.
Are you ready to delve deeper into the realm of trading and exercising options? Share your thoughts and questions in the comments section below!






