The world of finance offers a plethora of investment opportunities, and among them, options trading stands out as an intriguing and potentially lucrative avenue. Yet, for newcomers to this arena, navigating its complexities can be a daunting task. To equip aspiring options traders with the knowledge they need, we present a comprehensive guide to essential terms, providing a solid foundation for successful trading endeavors.
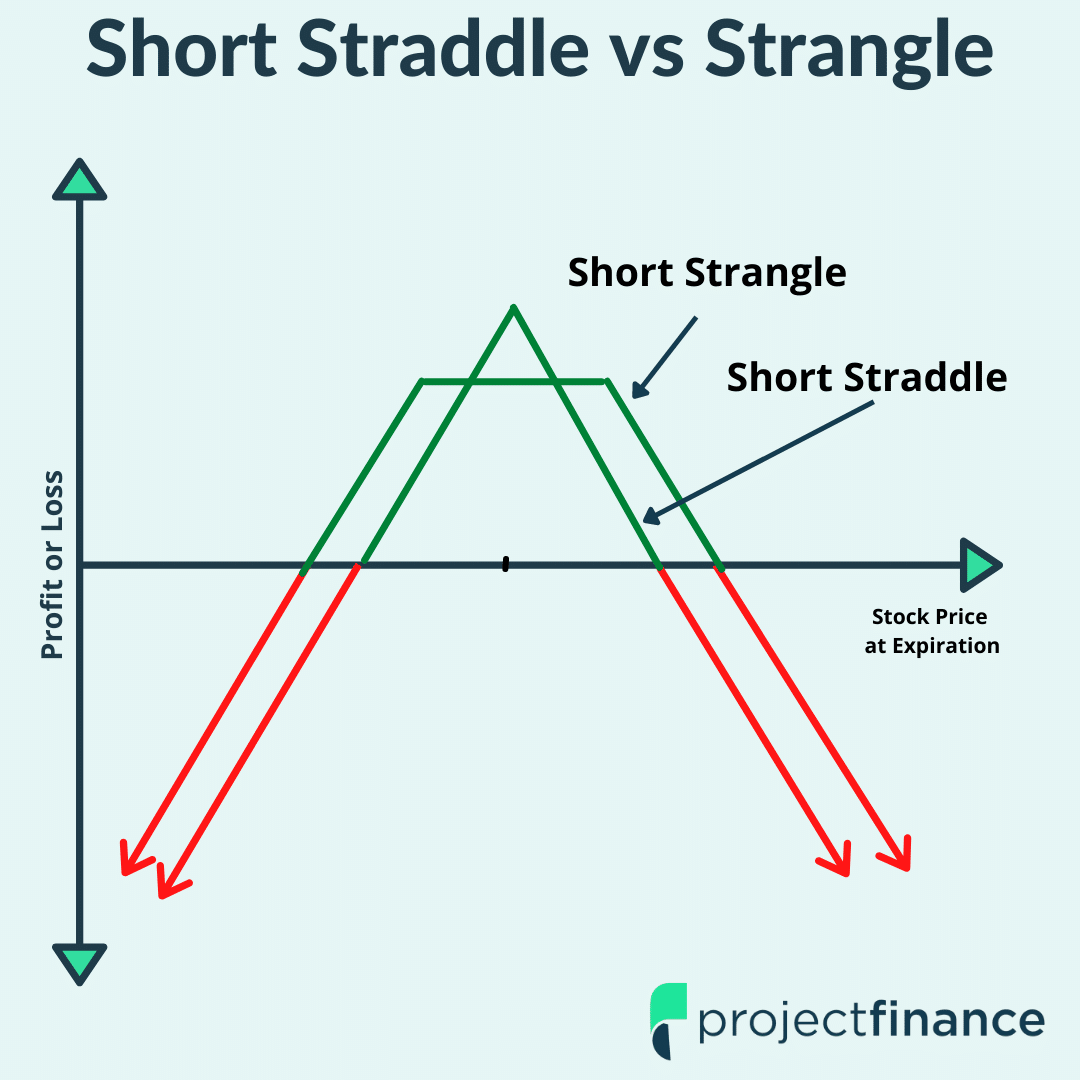
Image: www.projectfinance.com
Understanding the Mechanics of Options Trading
Options are financial contracts that grant the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) an underlying asset, such as a stock, at a specified price (strike price) on or before a certain date (expiration date). By purchasing an option, traders gain exposure to the underlying asset’s price fluctuations without committing to its ownership.
Key Options Trading Terms
Call Option: A call option grants the buyer the right to purchase the underlying asset at the strike price on or before the expiration date.
Put Option: A put option grants the buyer the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price on or before the expiration date.
Strike Price: The specified price at which the buyer has the right to buy or sell the underlying asset when exercising the option.
Expiration Date: The date on which the option contract expires, and the holder loses the right to exercise the option.
Option Premium: The amount paid by the buyer to the seller of the option in exchange for the option contract.
In the Money: An option is considered in the money when the strike price is below the current market price of the underlying asset for call options or above the current market price for put options.
Out of the Money: An option is considered out of the money when the strike price is above the current market price of the underlying asset for call options or below the current market price for put options.
At the Money: An option is considered at the money when the strike price is equal to the current market price of the underlying asset.
Delta: A Greek letter that measures the sensitivity of an option’s price to changes in the price of the underlying asset.
Theta: A Greek letter that measures the decay in an option’s value as the expiration date approaches.
Vega: A Greek letter that measures the sensitivity of an option’s value to changes in volatility.
Implied Volatility: The level of volatility expected in the future, as implied by option prices.
Leveraging Options Trading Terms for Successful Trading
Grasping these essential terms is crucial for understanding the intricacies of options trading. By comprehending the mechanics of options contracts and the different terms associated with them, traders can make informed decisions and navigate the market with confidence.

Image: www.compsuite.com
Actionable Tips for Aspiring Options Traders
- Seek guidance from experienced mentors and educational resources.
- Practice with paper trading or simulated accounts before engaging in real-money trading.
- Manage risk effectively by understanding the potential losses and implementing appropriate strategies.
- Monitor market trends and stay abreast of economic news that may impact option prices.
- Exercise caution and avoid making hasty decisions based on emotions or impulse.
Options Trading Terms Definitions
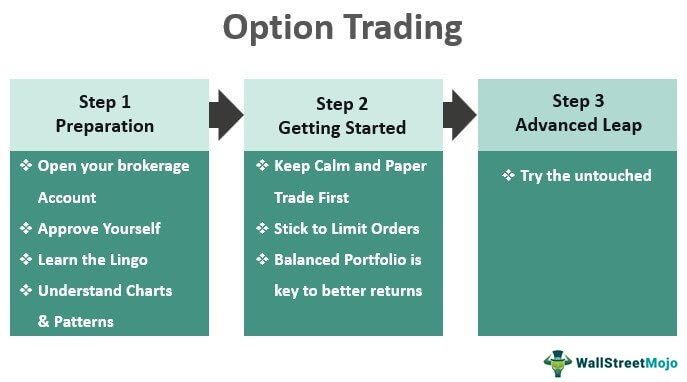
Image: voxt.ru
Conclusion
Options trading presents a vast and exciting opportunity for investors. By empowering yourself with a thorough understanding of essential terms, you can unlock the potential of options trading and make informed decisions that can lead to financial success. Remember to approach trading with a clear strategy, a disciplined mindset, and a keen eye on the market. As you delve deeper into the realm of options trading, you will continue to expand your knowledge and refine your skills, setting yourself on a path toward mastering this dynamic and potentially lucrative investment avenue.






