Introduction
Navigating the financial world can be daunting, but understanding the basics of trading options can provide a valuable tool to enhance your investment strategy. Options, financial instruments that grant the right but not the obligation to buy or sell an underlying asset, offer a unique opportunity to potentially profit from market fluctuations. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the realm of options trading, breaking down key concepts and strategies to help you master this essential aspect of modern finance.

Image: financefordummies.net
Understanding Options Contracts
At its core, an option contract represents an agreement between two parties, the buyer and seller. The buyer of an option acquires the right to exercise that option at a predetermined time, known as the expiration date. The seller, on the other hand, has an obligation to fulfill the terms of the contract if the buyer chooses to exercise it. Options grant the buyer a choice between两种类型: calls and puts. Call options provide the buyer with the right to purchase an underlying asset, while put options offer the right to sell it.
Key Terminology in Options Trading
To fully grasp the world of options trading, understanding the associated terms is crucial:
- Underlying Asset: The asset that the option represents, such as stocks, bonds, commodities, or currencies.
- Strike Price: The price at which the option can be exercised.
- Premium: The price paid to the seller to purchase the option.
- Expiration Date: The date on which the option contract expires and becomes void.
- In the Money: An option is “in the money” when it has a positive intrinsic value.
- Out of the Money: An option is “out of the money” when it has a negative or zero intrinsic value.
- Intrinsic Value: The difference between the strike price and the current market price of the underlying asset.
- Time Value: The portion of the option premium that represents the remaining time until expiration.
Types of Options Strategies
Options trading offers a wide range of strategies to suit varying investment goals and risk tolerance levels:
- Covered Call: Selling a call option while owning the underlying asset.
- Protective Put: Buying a put option to protect against potential losses in an existing asset position.
- Bull Call Spread: Buying a lower-strike-price call option and selling a higher-strike-price call option to profit from a bullish market.
- Bear Put Spread: Buying a higher-strike-price put option and selling a lower-strike-price put option to benefit from a bearish market trend.

Image: qustcenters.weebly.com
Factors Influencing Option Prices
The value of an option is influenced by several crucial factors:
- Volatility: The expected degree of price fluctuations in the underlying asset.
- Time to Expiration: The duration remaining until the option contract expires.
- Interest Rates: The prevailing interest rate environment affects the cost of financing transactions and influences the pricing of options.
- Dividend Yield: Dividends paid by the underlying asset can impact option values, especially for longer-term options.
- Supply and Demand: Trading activity and market sentiment can influence the supply and demand for specific options contracts.
Risk Management in Options Trading
Options trading, while potentially lucrative, also carries inherent risks that require careful management:
- Limited Profit Potential: Unlike stocks, options have limited profit potential as it is capped at the premium paid.
- Unlimited Loss Potential: As a seller of an option, your losses can potentially be unlimited, potentially exceeding the premium received.
- Expiration Risk: Time decay can significantly impact options value, reducing their worth as they approach expiration.
- Volatility Risk: Options are highly sensitive to price fluctuations in the underlying asset, and large price swings can result in substantial gains or losses.
Trading Options The Basics
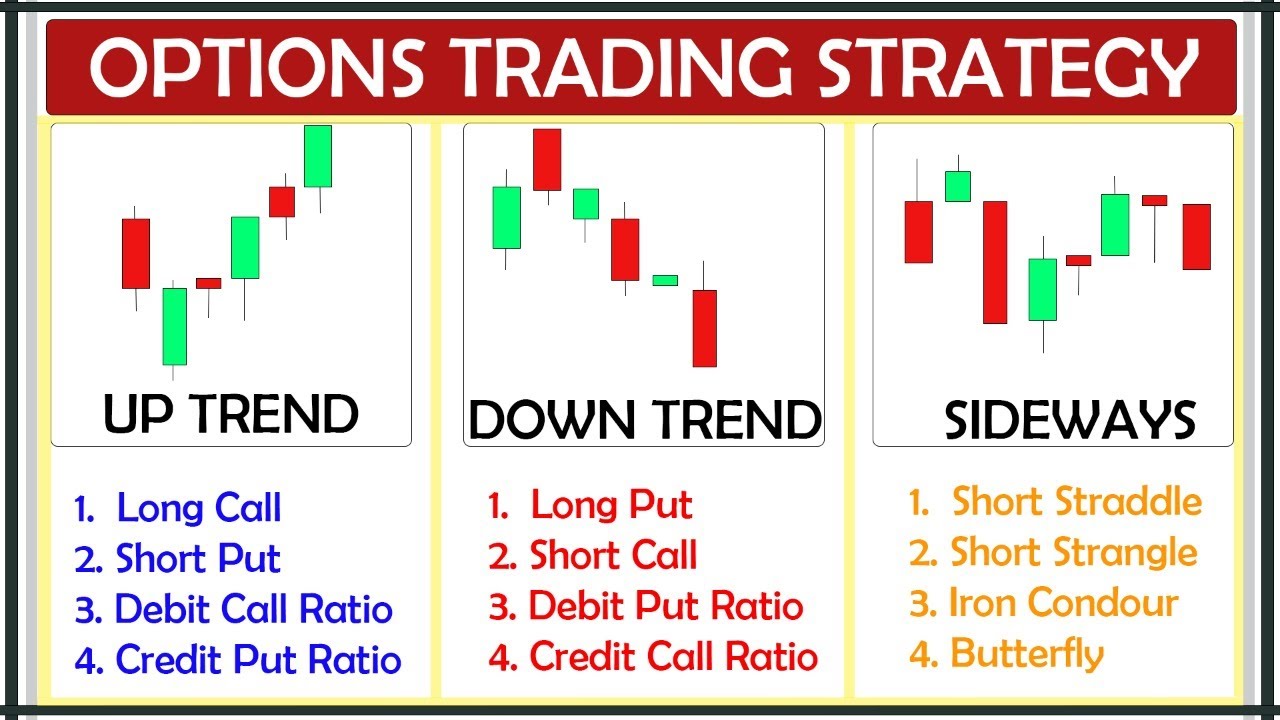
Image: www.youtube.com
Conclusion
Trading options is a multifaceted field that offers a range of opportunities and risks. By understanding the basics of options contracts, key terminology, and trading strategies, you can potentially expand your investment horizons and enhance your financial returns. Remember to manage risk wisely and seek professional guidance when needed. Whether you are an experienced investor or just starting to explore the world of options trading, embracing the principles outlined in this guide will equip you with a solid foundation for success.






