The financial world is a vast and ever-evolving landscape, with a myriad of complex instruments that can confound even seasoned investors. Among these instruments, option trading stands out as a particularly intriguing and potentially lucrative form of derivative investing. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricate world of option trading, exploring its many facets, risks, rewards, and strategies.
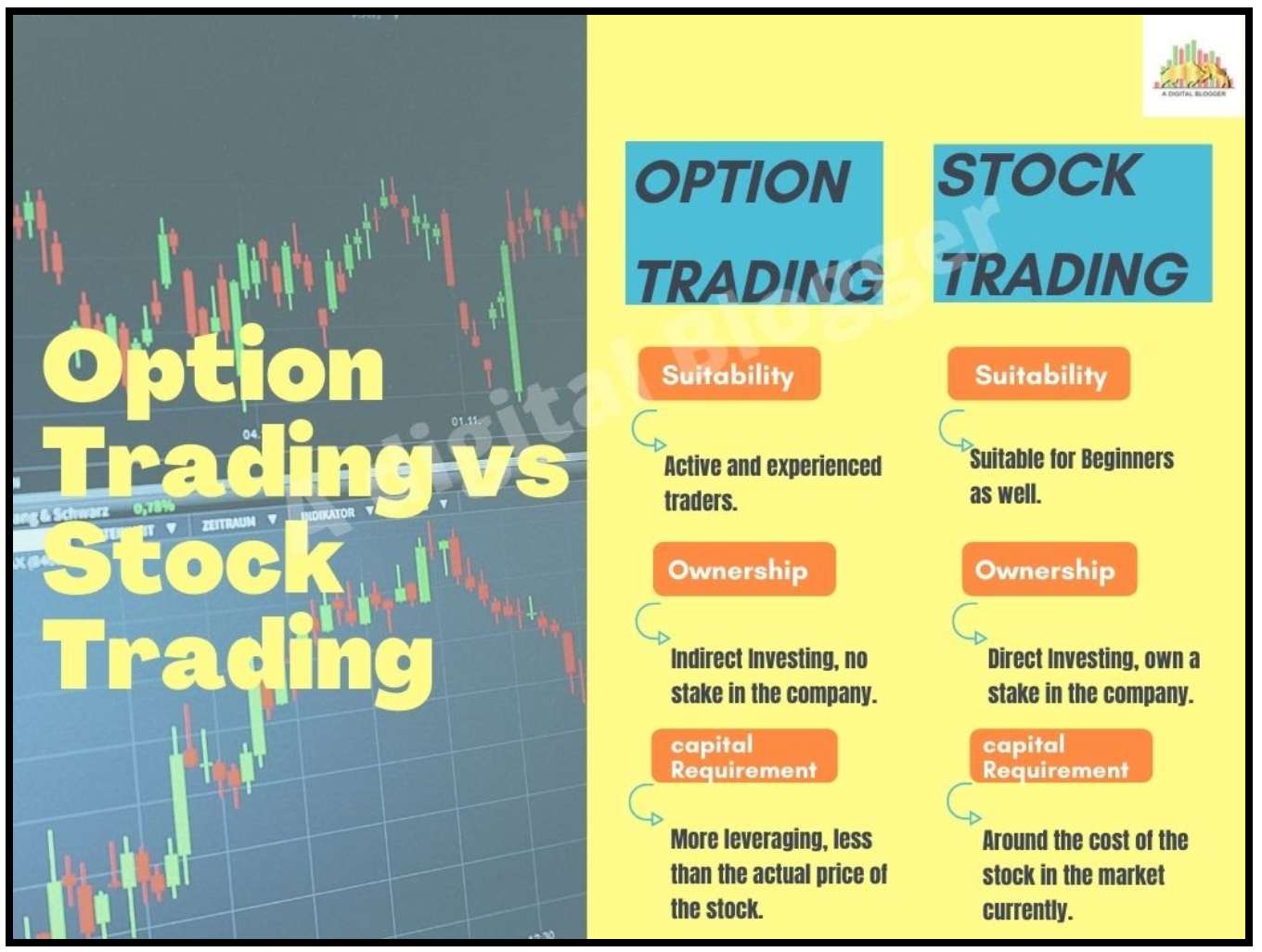
Image: www.adigitalblogger.com
Options, in the realm of finance, are contracts that grant the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy (in the case of a call option) or sell (in the case of a put option) a specified number of shares of an underlying asset at a predetermined price. They offer a versatile toolkit for investors to speculate on the price movements of assets, hedge against risk, and generate income. The ability to leverage option contracts can amplify both potential gains and losses, making it imperative for traders to understand the market thoroughly before venturing into this arena.
Types of Options
The option trading market offers two main types of options: call options and put options. Call options confer the right to buy the underlying asset at a future date, while put options provide the right to sell. Each type of option can be exercised by the buyer at any time up to the expiration date, or they can be sold back to the market for a profit or loss. Additionally, options are categorized into two distinct styles: American and European. American-style options can be exercised at any time up to expiration, while European-style options can only be exercised on the specified expiration date.
Option Pricing
The pricing of options is a complex art form that considers various factors, including the intrinsic value and the extrinsic value. Intrinsic value represents the potential profit that can be made by exercising the option immediately. It is calculated as the difference between the underlying asset’s price and the strike price (the predetermined price specified in the option contract). Extrinsic value, on the other hand, represents the time value and volatility premium embedded in the option. The time value gradually diminishes as the option approaches expiration, while the volatility premium can fluctuate based on market conditions.
Option Strategies
The option trading market offers a plethora of strategies that cater to different risk appetites and investment objectives. Some popular strategies include buying calls to speculate on an asset’s rise, selling puts to generate income and gain exposure to the underlying asset, and combining calls and puts to create spreads for various risk-reward profiles. By carefully selecting and implementing option strategies, traders can fine-tune their exposure to the market while potentially enhancing returns.
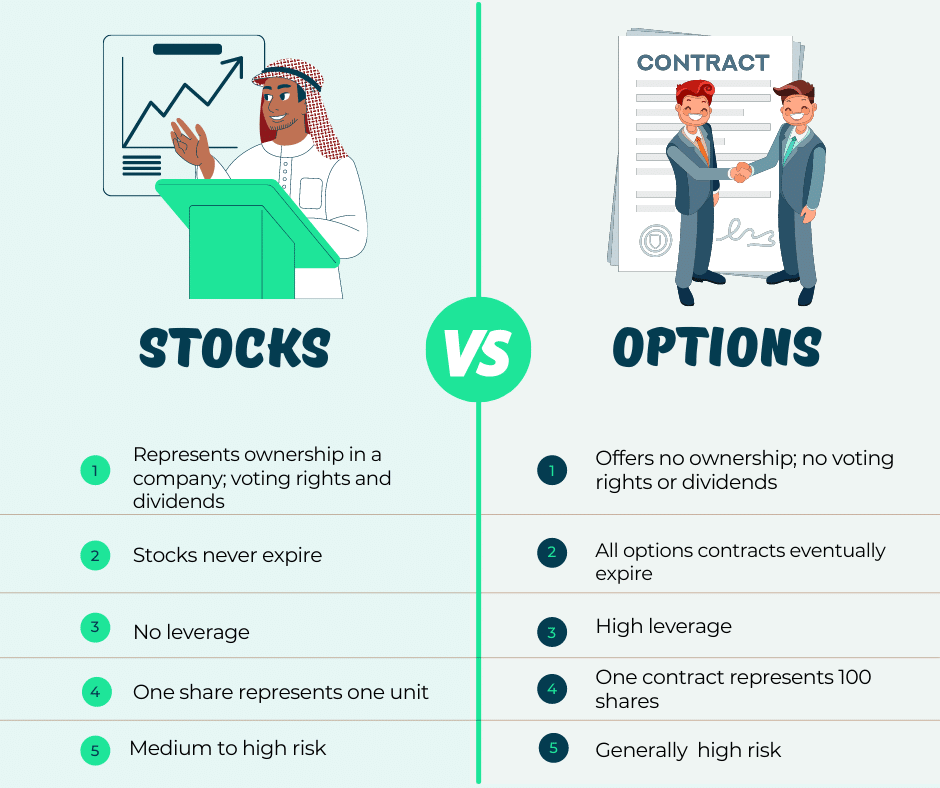
Image: www.projectfinance.com
Risks of Option Trading
It is imperative to acknowledge the inherent risks associated with option trading. While options can offer opportunities for substantial gains, they also carry the potential for significant losses. The leverage inherent in option contracts can magnify both profits and losses, amplifying both the upside and downside potential. Additionally, option values are highly sensitive to changes in the underlying asset’s price, making them unsuitable for risk-averse investors.
Option Trading Market

Image: www.fidelity.com
Conclusion
The option trading market presents a fascinating opportunity for investors to capitalize on market fluctuations, hedge risks, and potentially generate income. However, it is crucial to approach option trading with a clear understanding of its nuances and risks. Thorough research, a comprehensive grasp of option pricing, and meticulous strategy selection are essential for navigating this intricate market effectively. By embracing these principles, investors can harness the power of options to enhance their investment portfolios and achieve their financial objectives.






