In the realm of finance, options trading presents a unique opportunity to generate substantial profits. However, understanding how to accurately calculate these profits is crucial for effective decision-making and long-term success. This comprehensive guide will demystify the intricacies of options profit calculation, empowering you with the knowledge to navigate this dynamic市場with confidence.
Image: yzypohu.web.fc2.com
Understanding Options Contracts
An options contract grants the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specified period. The two main types of options contracts are calls (the right to buy) and puts (the right to sell). Each contract has specific terms that define its underlying asset, strike price, expiration date, and premium.
Calculating Profit in Options Trading
The profit potential in options trading is determined by the price movement of the underlying asset in relation to the strike price. Here are the steps involved in calculating profit:
-
Determine the Net Proceeds: Subtract the premium paid from the sale price for call options or add the premium received to the sale price for put options.
-
Profit Calculation:** For call options, subtract the strike price from the current asset price and multiply the difference by the number of contracts held. For put options, subtract the current asset price from the strike price and multiply the difference by the number of contracts held.
Call Option:
Net Proceeds – (Strike Price x Number of Contracts)
Put Option:
Net Proceeds + (Current Asset Price – Strike Price) x Number of Contracts
- Adjust for Option Fees:** Include any additional fees incurred, such as brokerage commissions or regulatory charges, to determine the net profit.
Options Pricing Factors
The final profit in options trading is influenced by various factors that affect option prices. These include:
-
Underlying Asset Price: The price of the underlying asset directly impacts the value of the option contract.
-
Volatility: Options with higher volatility are typically more expensive due to increased uncertainty in the asset’s price fluctuations.
-
Time to Expiration:** Options that expire sooner have lower time value and are cheaper compared to options with longer expiration periods.
-
Interest Rates:** Options can be valued based on the prevailing interest rates, which can impact the option’s time value.
-
Dividends:** Dividend payments on the underlying asset can affect options pricing, especially for call options.
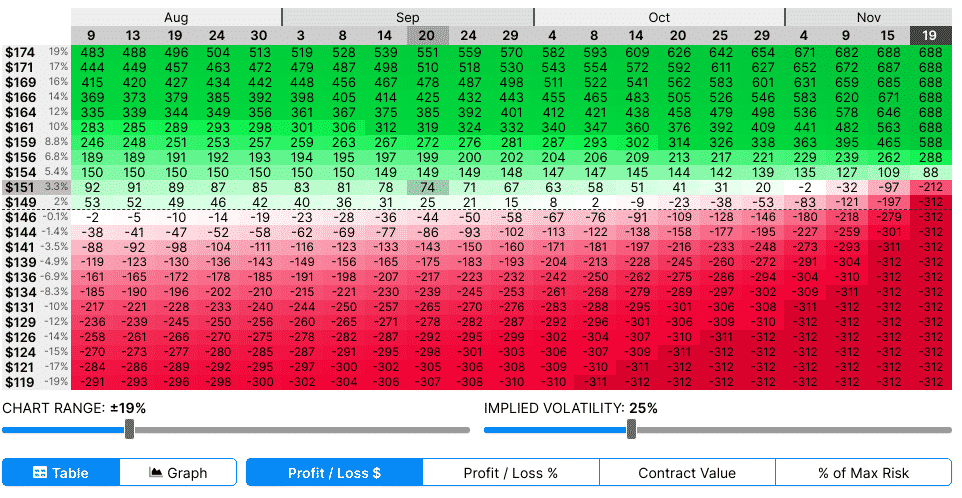
Image: optionstradingiq.com
How To Calculate Profit In Options Trading
https://youtube.com/watch?v=qbGZ4D5QTiI
Maximizing Profit in Options Trading
To enhance your profit potential in options trading, consider these strategies:
-
Choose the Right Options:** Select options with the appropriate strike prices and expiration dates to align with your risk tolerance and trading objectives.
-
Manage Risk:** Employ risk management techniques such as stop-loss orders to protect against potential losses.
-
Monitor the Market:** Stay informed about market conditions, news, and economic indicators that can impact options prices.
-
Have a Clear Trading Plan:** Develop a comprehensive trading plan that outlines your entry and exit strategies, as well as risk management measures.
-
Seek Professional Advice:**Consult with a financial advisor or broker for guidance and support if needed.






