Introduction

Image: www.binaryoptions.co.uk
In the enigmatic realm of financial markets, options trading presents a labyrinth of intricacies that can perplex even seasoned investors. Among these complexities, the ethereal and often enigmatic concept of Greeks holds sway, influencing the behavior of options and endowing traders with a profound impact on risk management and profit optimization. This comprehensive guide unveils the secrets of Greek options trading, unraveling their intricate workings and illuminating their practical applications.
From the humble beginnings of ancient Greece, the concept of options has evolved significantly, shaping the modern financial landscape. Today, options empower traders with the ability to hedge existing positions, offset market volatility, and amplify potential gains—a veritable Pandora’s Box of opportunities. However, understanding the nuances of Greeks is paramount to navigating these uncharted waters successfully.
What are Greeks?
Greeks, named after the Greek alphabet, embody a series of indispensable metrics that quantify the sensitivity of an option’s price to underlying factors such as time, volatility, and price. These metrics, expressed in Greek letters, provide traders with invaluable insights into the dynamic interplay between options and the underlying asset, empowering them to make informed trading decisions.
Delta: A Measure of Price Sensitivity
Delta, denoted by the Greek letter Δ, quantifies the rate of change in an option’s price relative to the underlying asset’s price. A positive Delta signifies that the option’s price moves in the same direction as the underlying asset, whereas a negative Delta indicates an inverse correlation. Understanding Delta is crucial for gauging the potential impact of price fluctuations on the option’s value.
Gamma: Capturing Volatility’s Effect
Gamma, designated by Γ, measures the sensitivity of Delta to changes in the underlying asset’s volatility. A positive Gamma implies that Delta will increase as volatility rises, while a negative Gamma indicates that Delta will decrease with increasing volatility. Gamma analysis enables traders to assess an option’s sensitivity to fluctuations in market uncertainty.
Theta: The Time Value Factor
Theta, represented by θ, quantifies the rate of decay in an option’s price as time elapses. Since options have a limited lifespan, Theta measures the value lost as time ticks away. This metric helps traders understand how the passage of time erodes an option’s premium.
Vega: Volatility’s Impact on Value
Vega, denoted by ν, gauges the sensitivity of an option’s price to changes in implied volatility. A positive Vega implies that the option’s price will increase with increasing implied volatility, while a negative Vega signifies an inverse relationship. Vega analysis helps traders determine the impact of volatility shifts on option value.
Rho: The Interest Rate Influence
Rho, symbolized by ρ, quantifies the sensitivity of an option’s price to changes in the risk-free interest rate. A positive Rho means that the option’s price rises as interest rates increase, while a negative Rho indicates that the price will decrease with increasing interest rates. Rho analysis is critical for understanding the impact of interest rate changes on option value.
Practical Applications of Greek Options Trading
The mastery of Greek options trading techniques empowers traders with a formidable toolkit to navigate the treacherous waters of financial markets. These techniques find practical applications in various trading strategies, including:
- Delta Hedging: Neutralizing price risk by adjusting the position in the underlying asset to match the Delta of the option.
- Gamma Scalping: Exploiting changes in Gamma to profit from rapid price movements in the underlying asset.
- Theta Harvesting: Selling options with a short time to expiration to capture the premium erosion (time decay).
- Vega Trading: Trading options based on their sensitivity to implied volatility to profit from volatility spikes or declines.
- Rho Hedging: Managing interest rate risk by offsetting the Rho exposure of an option position with an appropriate hedging strategy.
Conclusion
Greek options trading, although intricate and challenging, offers traders a wealth of opportunities to enhance risk management, optimize profits, and deepen their understanding of the financial markets. By grasping the complexities of these elusive metrics, traders can unlock the full potential of options trading and navigate the market’s ever-changing tides with greater confidence and success. As with all financial endeavors, thorough research, continuous learning, and prudent risk management are essential for successful Greek options trading.
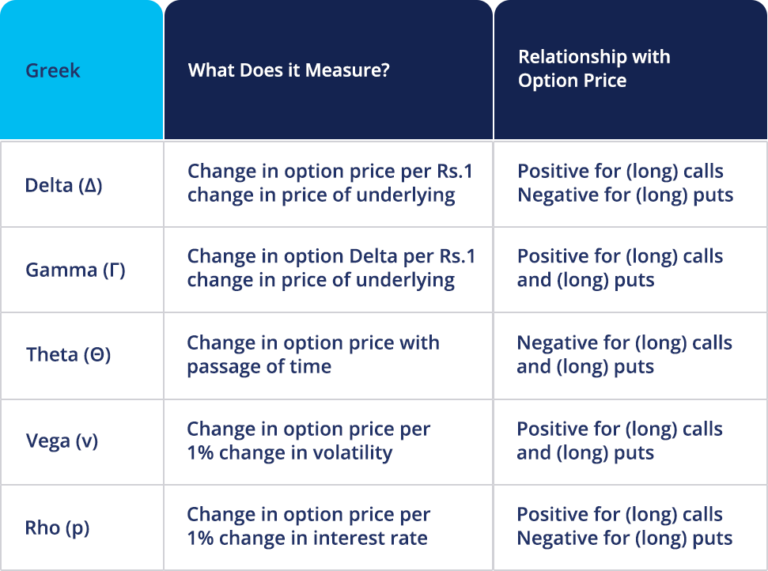
Image: www.paytmmoney.com
Complicated Greeks Options Trading
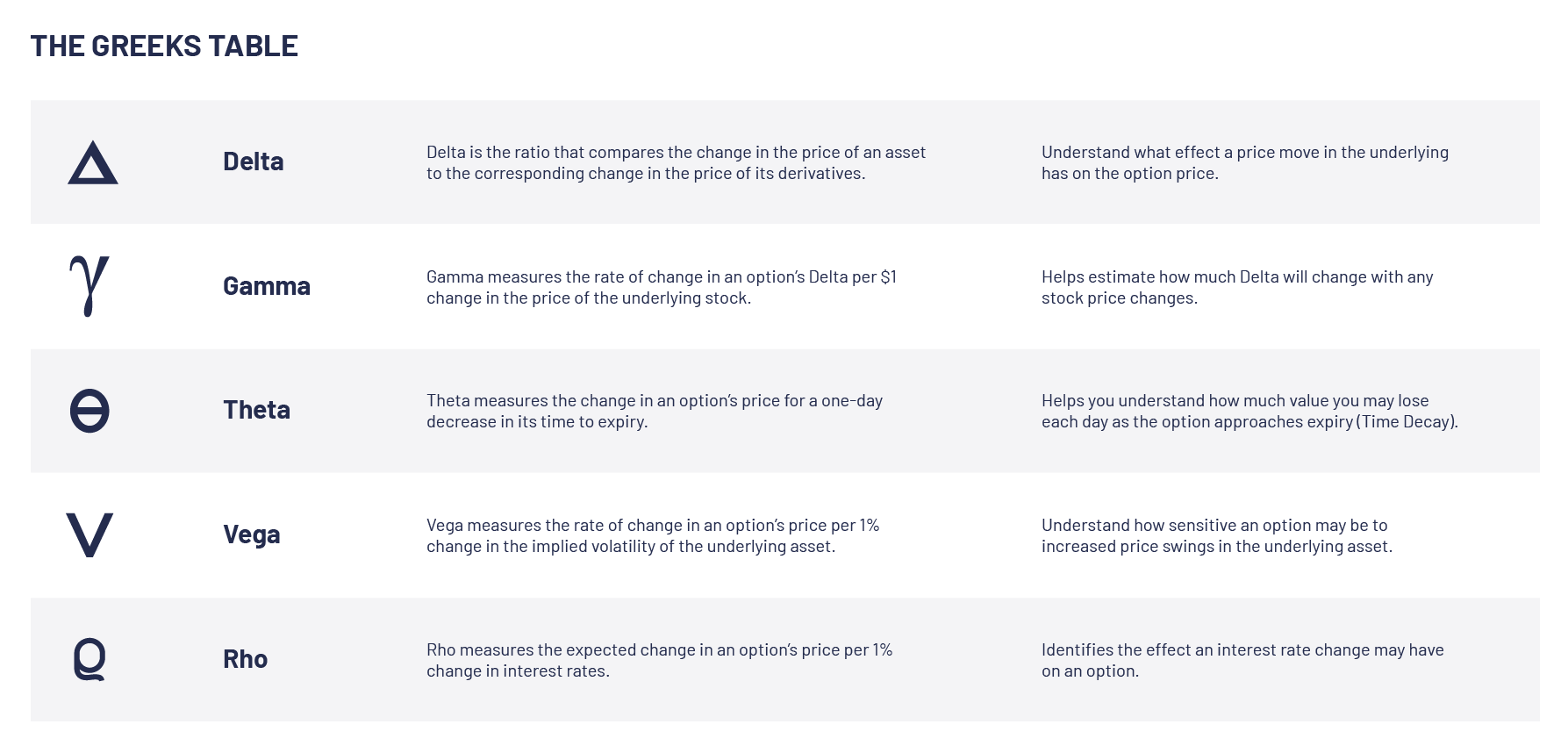
Image: optionsdesk.com






