Understanding Historical Volatility for Option Traders

Image: www.youtube.com
When venturing into the realm of options trading, historical volatility (HV) plays a pivotal role in determining the potential risks and rewards involved. HV measures the statistical dispersion of past price movements within a given timeframe, providing insights into the expected magnitude of future price fluctuations. This article explores the multifaceted concept of historical volatility and its implications for option traders.
Historical Volatility: A Measure of Past Volatility
Historical volatility is calculated by analyzing past price data over a predefined period, typically one year or more. It quantifies the standard deviation of daily price changes, represented as an annualized percentage. A high HV indicates that the asset’s price has exhibited substantial fluctuations in the past, while a low HV suggests relatively stable price movements.
Importance of Historical Volatility for Option Pricing
Option premiums are directly influenced by historical volatility. Options with higher HVs tend to command higher premiums, as they entail a greater potential for significant price movements. Conversely, options with lower HVs are generally priced lower due to the reduced likelihood of substantial price swings.
Using Historical Volatility in Option Strategies
Understanding historical volatility allows option traders to craft informed strategies.
-
Bullish Strategies: Traders anticipating upward price movements may purchase call options with higher HVs. The potential for large price gains amplifies as HV increases.
-
Bearish Strategies: Conversely, those anticipating downward price movements might consider selling put options with higher HVs. High HV indicates a greater chance of significant price declines, potentially leading to substantial profits.
-
Neutral Strategies: Traders seeking to capitalize on market volatility can employ strategies such as straddles or strangles, which simultaneously buy and sell options with different strike prices and HVs.
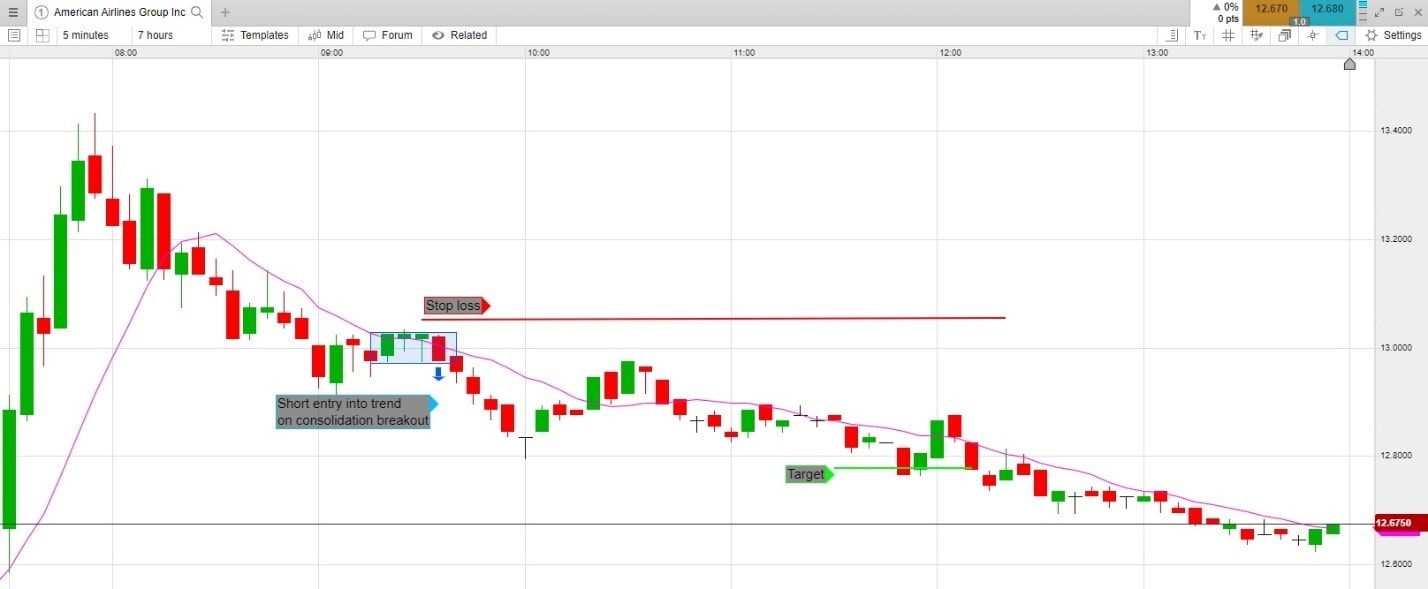
Image: stardolllcoll-jasmin.blogspot.com
Contextualizing Historical Volatility
Historical volatility is a nuanced concept, and its significance varies across asset classes and market conditions.
-
Equity Options: HV is highly influential for equity options, as it reflects the potential for substantial price movements due to earnings reports, industry trends, and economic events.
-
Currency Options: Currency options exhibit lower HVs compared to equity options, as currency fluctuations tend to be less volatile over extended periods.
-
Commodity Options: High HVs are common in commodity options, particularly agricultural or energy commodities, which are subject to volatile price swings influenced by weather conditions, supply-demand dynamics, and geopolitical factors.
Limitations of Historical Volatility
While historical volatility is a valuable indicator, it has certain limitations:
-
Past Performance Not Future Performance: HV measures past volatility, but it does not guarantee future volatility. Market conditions can change rapidly, rendering past data less predictive.
-
Extreme Events: HV may underestimate the potential for extreme events, such as flash crashes or sudden market reversals, which can significantly impact option prices.
Historiucal Volatility In Option Trading
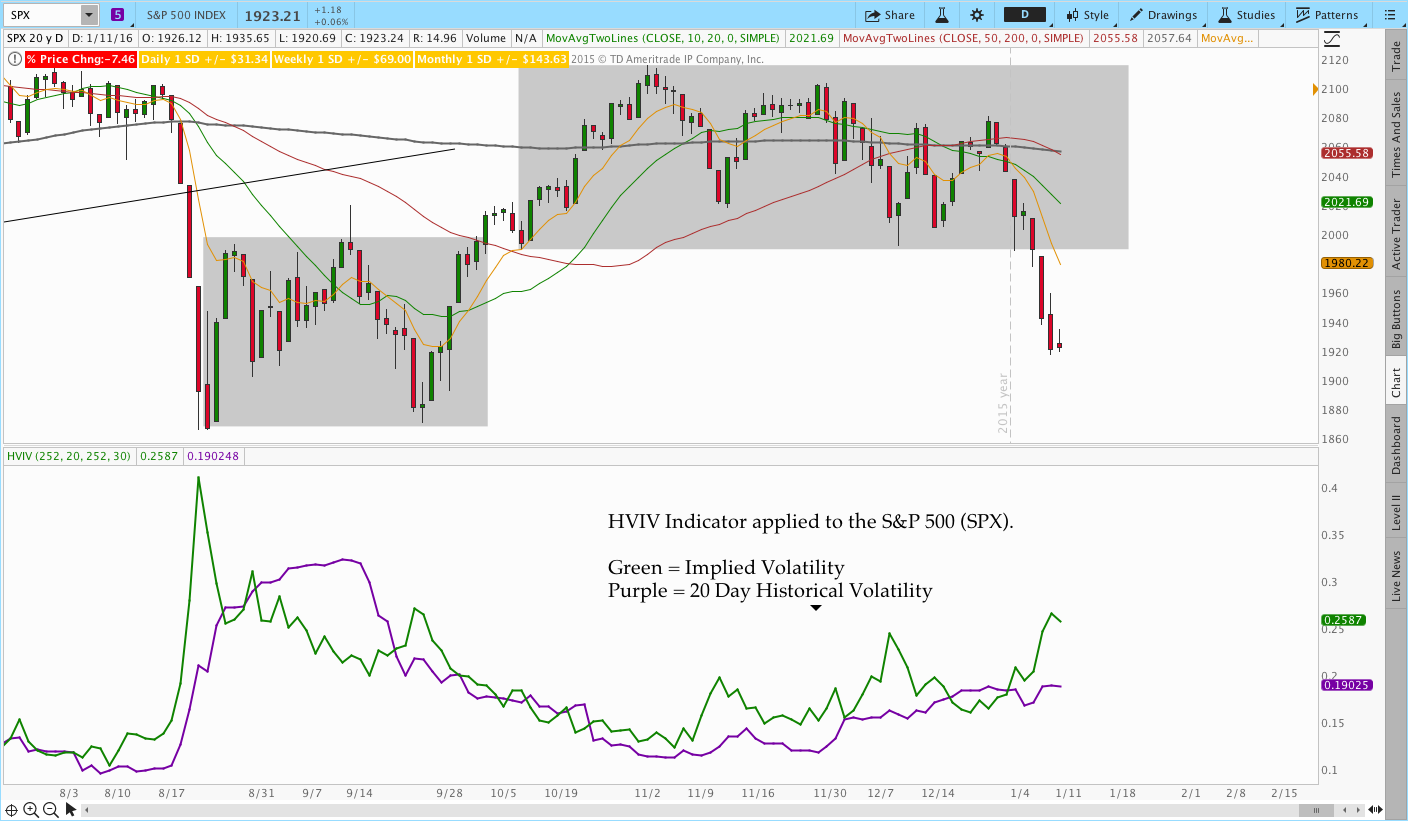
Image: littderole.weebly.com
Conclusion
Historical volatility is an essential consideration for option traders, impacting option pricing and guiding strategy development. By understanding historical volatility and its implications, traders can make informed decisions and manage risk effectively. However, it’s crucial to remember the limitations of HV and approach option trading with caution, thorough research, and appropriate risk management practices.






