Exploring the Basics of Options Trading for Informed Decisions
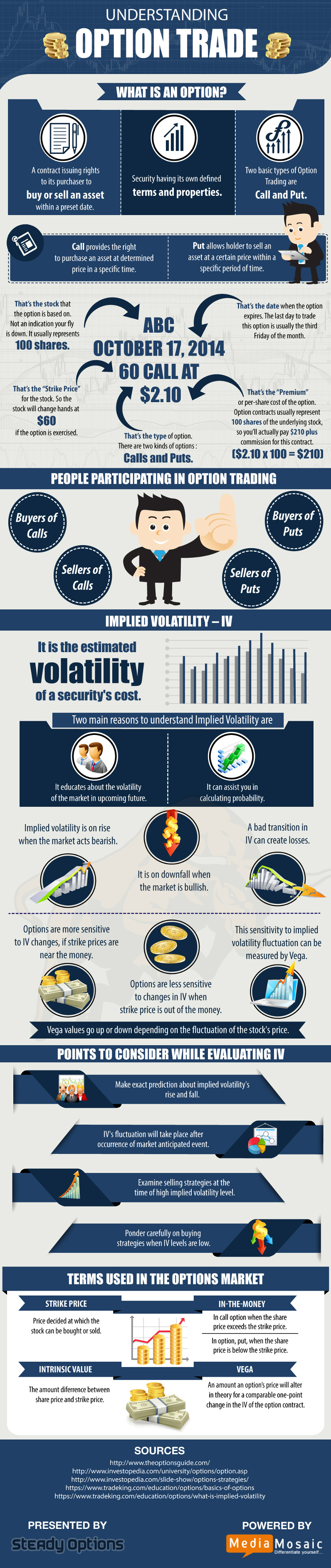
Image: www.visualcapitalist.com
In the realm of financial markets, options stand as versatile instruments that empower traders with unique strategies and unparalleled flexibility. Understanding the basics of options trading is paramount to navigating this dynamic landscape. In this article, we will delve into the fundamentals, unlocking the true potential of options for informed trading.
Defining Options: The Basics
Options, in essence, convey the right (but not the obligation) to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price and within a specific time frame. They come in two primary flavors: calls and puts. Calls grant the holder the right to purchase an underlying asset at the strike price by its expiration date, while puts offer the right to sell.
Understanding the Crux of Options Contracts
Options contracts are multifaceted instruments, each carrying a unique set of characteristics. These attributes include:
- Underlying Asset: The security, such as a stock, bond, or commodity, to which the option applies.
- Strike Price: The predetermined price at which the holder may exercise their option right.
- Expiration Date: The specified date on which the option contract expires, rendering it void.
- Premium: The price paid to acquire the option contract, representing its intrinsic and time value.

Image: www.pinterest.com
Basic Of Options Trading
https://youtube.com/watch?v=7_A6X82B56I
Types of Options: Customizing Your Strategy
The options market offers a wide spectrum of types, catering to diverse trading strategies:
- Calls: Bestowing upon the holder the right to purchase the underlying asset.
- Puts: Granting the right to sell the underlying asset.
- Covered Call: A call option secured by ownership of the underlying asset.
- Protective Put: A put option acquired to hedge against potential losses in the underlying asset.
- Naked Call / Naked Put: Options strategies without ownership (naked call) or sale commitment (naked put) of the underlying asset, introducing higher risk.






