Introduction
In the realm of options trading, understanding the concept of break-even is crucial to maximizing profits and minimizing losses. Break-even refers to the point at which the total cost of buying or selling an option contract is equal to the proceeds received upon its exercise or expiration. It is the price at which you would neither gain nor lose money on the trade, assuming no other factors, such as commissions or market fluctuations, come into play.
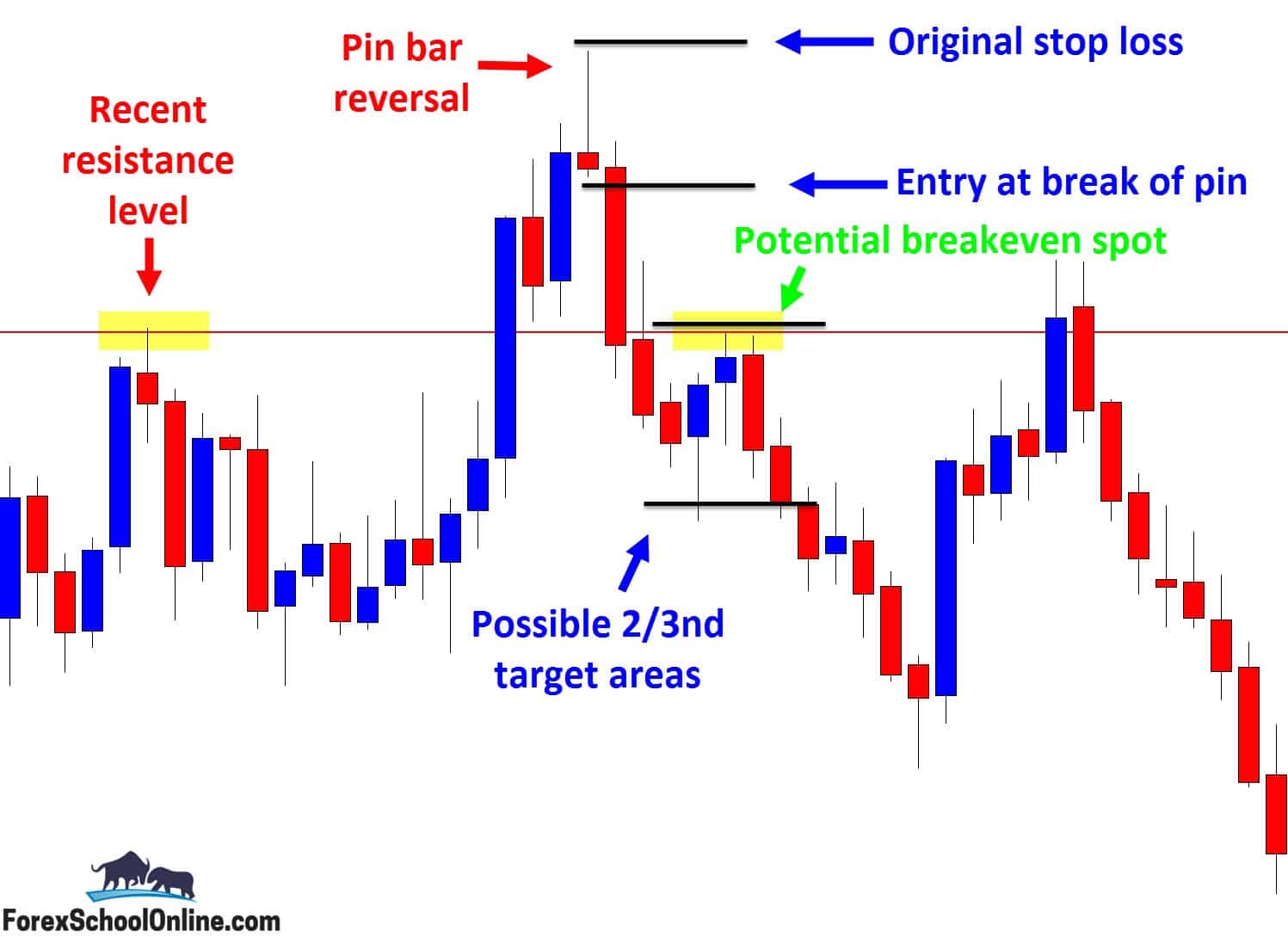
Image: www.forexschoolonline.com
This intricate trading strategy requires a deep understanding of options pricing models, technical analysis, and risk management. Whether you are a seasoned pro or a budding trader, navigating the intricacies of break-even options trading can unlock a path to substantial gains.
Fundamentals of Break Even Trading
An option contract grants the buyer the right, not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) a certain amount of an underlying asset (stock, ETF, or futures contract) at a predetermined price (strike price) by a certain date (expiration date). When you buy an option, you pay a premium to gain this right. When you sell (write) an option, you receive this premium, but you also undertake the obligation to buy or sell the underlying asset at the strike price if the option is exercised.
The break-even price is calculated differently for calls and puts. For a call option, it is determined as follows:
Break-even price = strike price + premium paid
For a put option, the calculation is slightly different:
Break-even price = strike price – premium received
Factors Affecting Break Even Prices
Several factors influence the break-even price of an options contract, including:
- Option premium: The premium is the price paid or received for buying or selling an option contract.
- Underlying asset price: Fluctuations in the price of the underlying asset can affect the break-even price of its options.
- Volatility: Volatility measures the expected price swings of the underlying asset. Higher volatility leads to higher option premiums and wider break-even ranges.
- Time to expiration: As the expiration date approaches, the time value of options contracts diminishes, leading to narrower break-even ranges.
How to Trade Break Even Options
There are several strategies traders can employ for break-even options trading:
-
Zero-cost collar: This strategy involves selling a call option above the current market price and buying a put option below the current market price, both with the same strike price and expiration date. The premiums received from selling the call option offset the premiums paid for buying the put option, resulting in a net zero cost for the collar.
-
Covered call: In this strategy, a trader owns the underlying asset and sells a call option against it. If the stock price rises above the strike price by expiration, the trader profits from the appreciation in the underlying asset, while the option is exercised, generating additional income.
-
Bull put spread: This strategy involves buying a call option at a lower strike price and simultaneously selling a call option at a higher strike price, both with the same expiration date. The net effect is the creation of a position that profits from a rise in the underlying asset’s price within a specific range.

Image: www.youtube.com
Break Even Options Trading
Conclusion
Break-even options trading can be a powerful tool in the hands of savvy traders. By understanding the concept of break-even prices and the factors that influence them, traders can develop effective strategies to reduce risk and potentially generate substantial profits. However, it is important to note that options trading involves significant risk and should only be undertaken after careful consideration and analysis.






