In the realm of financial markets, option trading offers investors a potent tool for speculating on the future price of an asset. Among the various nuances associated with options, understanding the concepts of ‘in the money’ and ‘out of the money’ is pivotal for informed decision-making.

Image: steadyoptions.com
What are Options?
An option is a derivative security that conveys the right, not an obligation, to buy (with call options) or sell (with put options) an underlying asset at a pre-determined price, known as the strike price, on or before a specified date, referred to as the expiration date.
In the Money vs. Out of the Money Options
When evaluating options, it’s crucial to understand their relationship to the current market price of the underlying asset. Options are classified as:
- In the Money (ITM): When the current market price is higher than the strike price for call options or lower than the strike price for put options.
- Out of the Money (OTM): When the current market price is lower than the strike price for call options or higher than the strike price for put options.
Key Differences Between ITM and OTM Options
Their in-the-money or out-of-the-money status has significant implications:
- Intrinsic Value: ITM options have inherent value, while OTM options have zero intrinsic value.
- Probability of Exercise: ITM options are more likely to be exercised, conferring the right to either buy or sell the underlying asset at a profitable price.
- Premiums: ITM options typically command higher premiums than OTM options due to their greater potential for profitability.
- Risk and Reward: ITM options carry lower risk but also offer more limited profit potential compared to OTM options with higher risk and higher reward.
Trading Strategies Involving ITM and OTM Options
Savvy traders employ various strategies utilizing ITM and OTM options to capitalize on market movements:
- Selling Covered Calls (ITM): Selling call options against underlying assets is a conservative strategy that generates premium income while limiting potential losses.
- Buying Protective Puts (ITM): Purchasing put options acts as insurance against price declines in the underlying asset.
- Bull Put Spread (OTM): Combining a long call option and a short call option with a higher strike price creates a bullish strategy that benefits from small to moderate gains in the underlying asset’s price.
- Bear Put Spread (OTM): Combining a long put option and a short put option with a higher strike price allows traders to profit from small to moderate declines in the underlying asset’s price.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinction between in-the-money and out-of-the-money options is paramount for successful option trading. By considering the current market price relative to the strike price, investors can evaluate which options align with their risk tolerance, trading objectives, and market expectations. Whether seeking income generation, protection against loss, or speculative plays, utilizing ITM and OTM options strategies empowers traders with a broad spectrum of opportunities to navigate the dynamic financial markets.

Image: www.youtube.com
Option Trading In The Money Out The Money
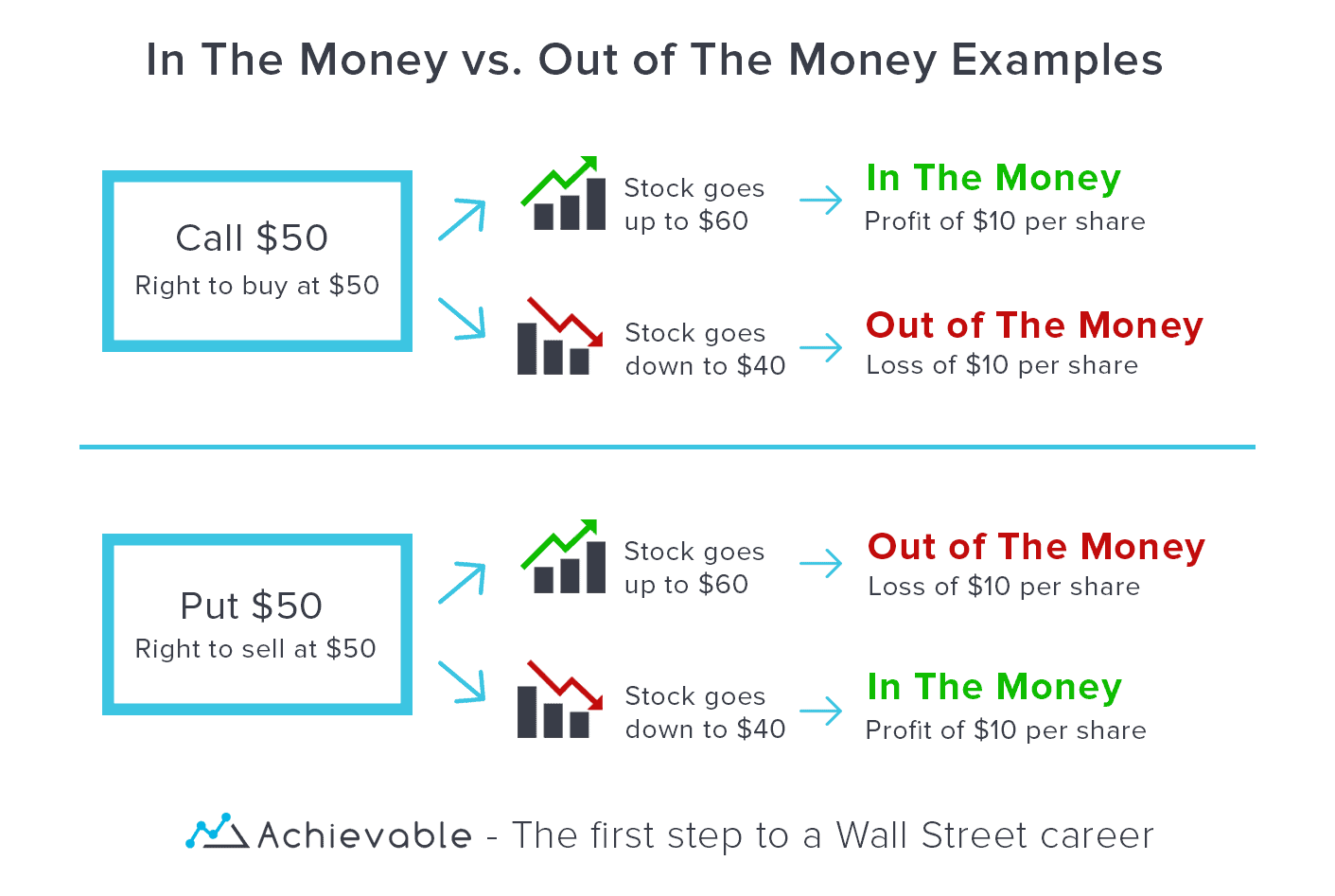
Image: blog.achievable.me






