Navigating the world of options trading requires a solid understanding of its specialized language. This detailed dictionary defines key terms, explains intricate concepts, and empowers investors with the knowledge to decipher the complexities of this dynamic market.
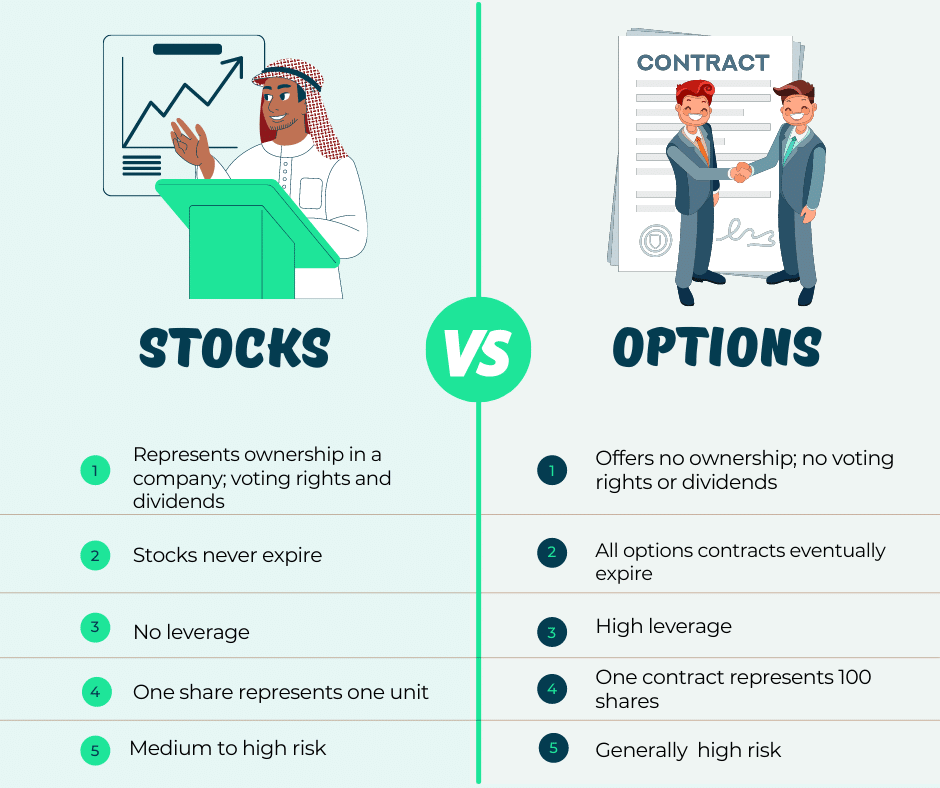
Image: www.projectfinance.com
Defining Options: A Contractual Right with Controlled Risk
An option is a financial contract that grants an investor the right, but not the obligation, to buy (a call option) or sell (a put option) an underlying asset at a predetermined price (the strike price) within a specified time frame (the expiration date). This contractual agreement conveys flexibility and controlled risk to investors, allowing them to participate in potential market gains while limiting their potential losses.
Call Option: The Right to Buy at a Future Price
A call option grants the holder the right to purchase the underlying asset. If the market price exceeds the strike price before expiration, the owner can exercise the option and buy the asset at a favorable price. This strategy is often employed by investors who anticipate a rise in the asset’s value.
Put Option: The Right to Sell at a Future Price
A put option provides the holder with the right to sell the underlying asset. If the market price falls below the strike price before expiration, the owner can exercise the option and sell the asset at a price above the current market value. This strategy is suitable for investors who expect the asset’s worth to decline.

Image: traders-paradise.com
Premium: The Cost of Acquiring an Option Contract
An option’s premium represents the price an investor pays to acquire the contract. It reflects the market’s assessment of the option’s potential value, which is influenced by factors such as the asset’s price, time to expiration, volatility, and strike price. The premium can fluctuate significantly, especially during periods of high market volatility.
Expiration Date: The Option’s Limited Lifespan
Each options contract has a predetermined expiration date, signifying the end of its validity. The option can only be exercised on or before this date; after expiration, it becomes worthless. Understanding the time remaining before expiration is crucial for options traders, as it impacts the option’s value and dictates trading strategies.
Underlying Asset: The Target of Option Contracts
The underlying asset is the security or commodity that an options contract represents. It can be a stock, bond, currency pair, or any other tradable asset. The value of the option contract is directly tied to the performance of the underlying asset.
Strike Price: The Predetermined Purchase or Sale Price
The strike price is the predetermined price at which the holder of an option can exercise their right to buy (call option) or sell (put option) the underlying asset. This price remains constant throughout the life of the option and plays a pivotal role in determining the option’s value.
In the Money (ITM): Options with Immediate Intrinsic Value
An option is considered in the money (ITM) when its strike price is more favorable than the current market value of the underlying asset. For example, a call option is ITM if its strike price is below the prevailing market price. This intrinsic value allows investors to profit from the option’s exercise immediately.
Option Trading Dictionary

Image: www.kobo.com
Out of the Money (OTM): Options with No Intrinsic Value
An option is out of the money (OTM) when its strike price is less (for call options) or more (for put options) favorable than the current market price of the underlying asset. In this scenario, the option has no immediate intrinsic value, but it may gain value if the market price moves in a favorable direction before expiration.






