In the realm of financial markets, option trading offers a powerful tool for investors to navigate market volatility and potentially enhance their returns. Options are contracts that grant the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) an underlying asset at a predetermined price on or before a specific date.
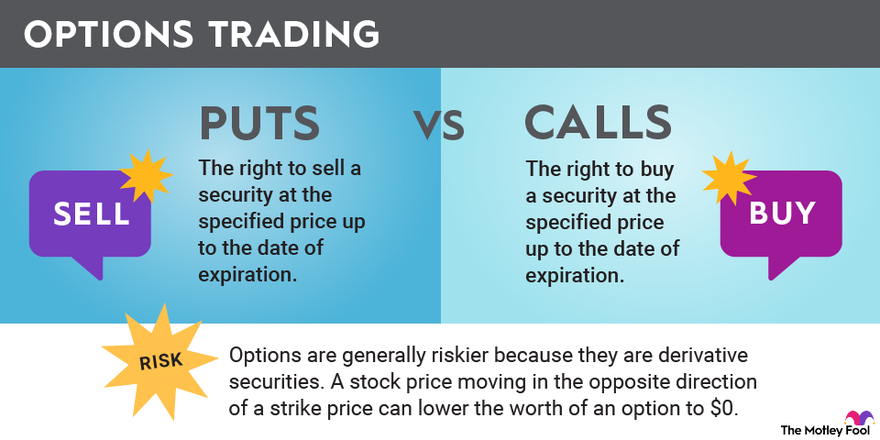
Image: www.fool.com
Understanding the fundamentals of call and put options is essential for investors looking to venture into this aspect of trading. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of these options, their significance, and how they can impact your investment strategies.
Calls: The Right to Buy
A call option provides the holder with the right to buy an underlying asset at a predetermined price, known as the strike price, on or before a specific expiration date. By purchasing a call option, the holder gains the potential to profit from an increase in the underlying asset’s value above the strike price.
Call options are commonly employed when an investor anticipates an upward movement in the underlying asset’s price. If the asset price rises above the strike price, the holder can exercise their right to buy the asset at the advantageous strike price, potentially generating a profit from the difference between the market price and the strike price. However, if the asset price falls below the strike price, the call option expires worthless, resulting in a loss of the premium paid to acquire the option.
Puts: The Right to Sell
A put option, on the other hand, grants the holder the right to sell an underlying asset at a predetermined strike price on or before the expiration date. By owning a put option, investors gain the potential to benefit from a decline in the underlying asset’s value below the strike price.
Put options are typically used when an investor anticipates a downward movement in the underlying asset’s price. If the asset price falls below the strike price, the holder can exercise their right to sell the asset at the profitable strike price, generating a potential gain from the difference between the market price and the strike price. However, as with call options, if the asset price rises above the strike price, the put option expires worthless, resulting in a loss of the premium paid to acquire the option.
Tips and Expert Advice
- Thoroughly Research: Before venturing into option trading, it’s vital to conduct thorough research and understand the risks and potential rewards involved. Develop a clear trading plan outlining your goals, risk tolerance, and exit strategies.
- Learn Option Greeks: Option Greeks are metrics that measure an option’s sensitivity to changes in underlying factors, such as price, volatility, time, and interest rates. Understanding option Greeks can provide insights into the potential risks and potential rewards associated with a specific option.
- Monitor Market Conditions: Stay abreast of market news, economic indicators, and company-specific developments that may impact the underlying asset’s value. Volatility and liquidity can significantly affect option prices.
- Manage Risk: Option trading involves substantial risk. Implement sound risk management strategies, such as setting stop-loss orders, limiting position size, and diversifying your portfolio.
- Choose the Right Options: Carefully evaluate the underlying asset, strike price, expiration date, and current market conditions to select the most suitable options for your investment goals.

Image: www.financialexpress.com
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Q: What are the key differences between call and put options?
A: Call options grant the holder the right to buy, while put options provide the right to sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price.
- Q: When is it appropriate to buy a call option?
A: Call options are appropriate when an investor anticipates an upward movement in the underlying asset’s price.
- Q: What are the risks associated with option trading?
A: Option trading involves the potential for substantial losses. Volatility, poor market conditions, and incorrect timing can lead to significant financial losses.
- Q: How can I protect myself from excessive losses?
A: Effective risk management strategies, such as setting stop-loss orders, limiting position size, and diversifying your portfolio, can mitigate potential losses.
What Is Call And Put In Option Trading
Conclusion
Understanding call and put options is fundamental to successful option trading. By grasping the concepts outlined in this guide, investors can navigate the complexities of options and harness their potential benefits. However, it’s crucial to remember that option trading involves substantial risk and should only be undertaken by knowledgeable and experienced investors.
Are you intrigued by the world of option trading and keen on exploring it further? If so, we encourage you to delve deeper into this fascinating topic and consider the powerful opportunities and potential pitfalls that come with it.






