In the fast-paced world of finance, options trading has emerged as a powerful tool that allows investors to navigate market volatility and make informed decisions. Options provide a versatile way to gain exposure to underlying assets, hedge against risks, and amplify returns. To fully harness the potential of options trading, it’s crucial to grasp the fundamentals of call and put options.
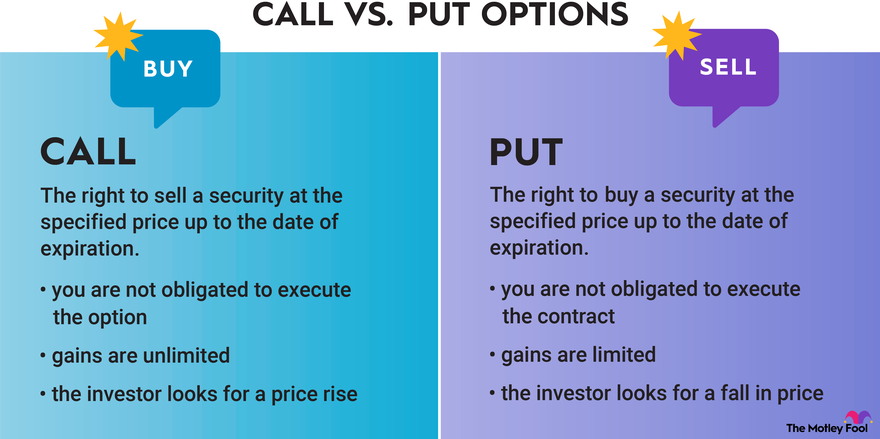
Image: www.fool.com
Defining Call Options
Call options are contracts that grant the buyer the right to purchase an underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) before a specified expiration date. By purchasing a call option, an investor expresses optimism about the potential price increase of the underlying asset. If the price does indeed rise, the call option becomes valuable, allowing the buyer to exercise their right to purchase the asset at a price lower than its current market value.
Unveiling Put Options
Put options, on the other hand, provide the buyer with the right to sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price before a specified expiration date. Put options are ideal for investors who anticipate a decline in the price of the underlying asset. By acquiring a put option, an investor gains the flexibility to sell the asset at a higher price than its current market value, thereby mitigating potential losses.
Types of Options Contracts
Options contracts can be classified based on two primary characteristics:
- Type of Option: Call options convey the right to purchase, while put options grant the right to sell.
- Expiration Date: Options contracts have a predetermined date when they expire. Expiring options lose their value if they are not exercised or sold before this date.
Real-World Applications
Options trading offers a myriad of applications in financial markets, including:
- Hedging Risks: Options can be employed to protect investment portfolios from adverse price fluctuations.
- Speculation: Options allow investors to speculate on the future direction of asset prices, potentially generating substantial profits.
- Income Generation: Selling options can generate income, especially when the underlying asset experiences low volatility.
- Leveraging Returns: Options can magnify returns on investment, although this comes with increased risk.
Expert Insights
“Options trading empowers investors to participate in market movements without the need for significant capital,” emphasizes renowned financial advisor, Allan Greenspan. “However, it’s essential to fully understand the risks and rewards before engaging in this sophisticated investment strategy.”
To enhance trading outcomes, industry expert Mary Buffett recommends “thorough research and careful strategizing. Options trading requires a disciplined approach and a deep understanding of market dynamics.”
Conclusion
Call and put options are indispensable tools in the financial toolkit, offering investors greater flexibility and potential returns. By understanding their core concepts and applications, traders can navigate market uncertainties, hedge against risks, and unlock the full potential of options trading. Remember, options trading carries inherent risks and should be approached with caution and a solid understanding of financial markets.

Image: www.youtube.com
What Is Call And Put Options In Trading






