Introduction to Options Trading
The realm of financial markets holds a myriad of investment vehicles, and among them lies the fascinating world of options trading. Options, with their inherent flexibility and potential for significant returns, have garnered immense popularity amongst both seasoned investors and those seeking alternative investment strategies. At the heart of options trading lies the concept of “puts” and “calls.” In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of a put option, empowering you with a solid foundation to navigate the options trading landscape.
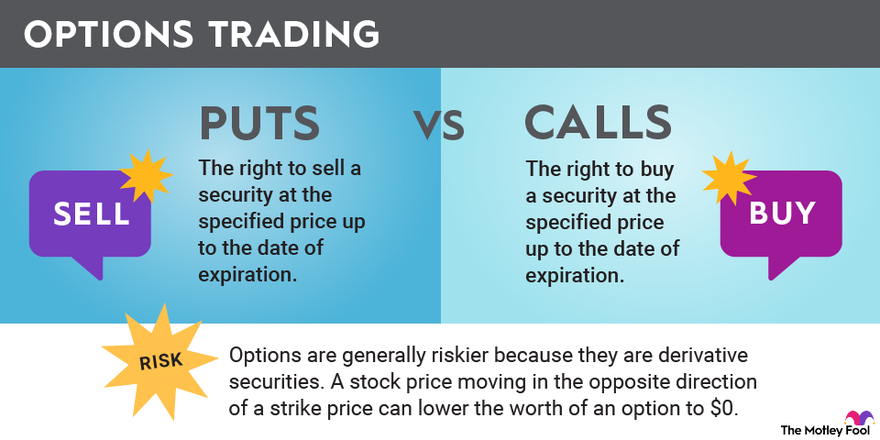
Image: www.fool.com
Options, as financial instruments, essentially confer the right, not the obligation, to buy (in the case of a call) or sell (in the case of a put) an underlying asset at a predetermined price (the strike price) on or before a specified expiration date. These versatile instruments provide investors with an array of opportunities, ranging from hedging risks to speculating on price movements.
Anatomy of a Put Option
A put option, in its essence, grants the holder the right to sell an underlying asset, such as a stock, commodity, or currency, at the agreed-upon strike price before the expiration date. This right is encapsulated within the option contract and can be exercised at the holder’s discretion within the stipulated time frame.
The dynamics of a put option hinge upon the relationship between the underlying asset’s price and the strike price. If the price of the asset falls below the strike price, the holder of the put option stands to benefit. Conversely, if the price of the asset rises above the strike price, the option loses value and may even expire worthless.
Profits and Losses with Put Options
The profit potential of a put option stems from its inverse relationship with the underlying asset’s price. As the price of the asset declines, the value of the put option increases. This appreciation in value allows the holder to exercise their right to sell the asset at the higher strike price, pocketing the difference as profit.
On the flip side, if the price of the underlying asset surges, the value of the put option diminishes. In such scenarios, the holder may choose not to exercise the option, letting it expire worthless. This outcome underscores the inherent risk associated with options trading.
Market Trends and Developments in Put Options
The landscape of options trading is constantly evolving, with market trends and developments shaping the strategies and decisions of investors. One notable trend has been the rise of exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that track the performance of specific indices or sectors. These ETFs, mirroring the underlying assets, offer investors a convenient and diversified exposure to options markets.
Another significant development has been the increased adoption of algorithmic trading in options. Sophisticated algorithms, armed with advanced data analysis capabilities, have enabled traders to execute complex trading strategies with greater precision and speed.
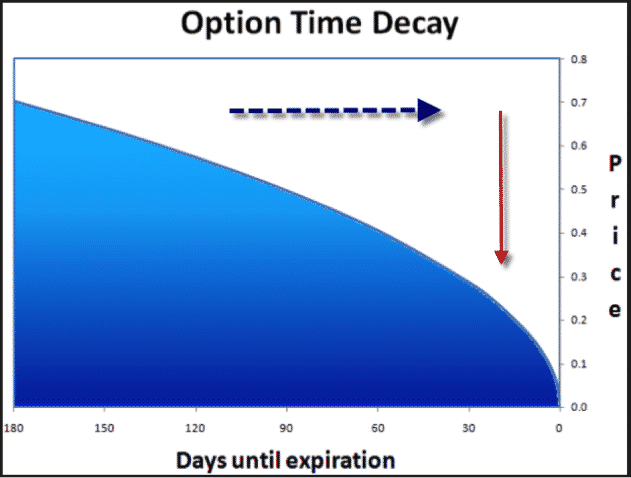
Image: optionstradingiq.com
Expert Advice for Navigating Put Options
Navigating the complexities of put options requires a combination of knowledge, experience, and expert guidance. Here are a few tips and expert advice to help you navigate this dynamic market:
– **Understand the risks:** Before venturing into options trading, it is crucial to fully grasp the risks involved. Carefully evaluate your investment goals, risk tolerance, and financial situation to determine if options are an appropriate investment vehicle for you.
– **Research and Knowledge:** Successful options trading hinges upon thorough research and a comprehensive understanding of the underlying assets and market dynamics. Stay informed about economic conditions, industry trends, and geopolitical events that may influence the performance of the assets you are considering.
– **Choose the Right Strike Price:** The strike price plays a pivotal role in the profitability of a put option. Choose a strike price that aligns with your investment goals and risk tolerance. A lower strike price offers greater profit potential but also carries higher risk, while a higher strike price provides a lower probability of profit but at a reduced risk.
– **Monitor Position Regularly:** Options markets are highly dynamic, and the value of your position can fluctuate rapidly. Monitor your positions regularly to assess their performance and make adjustments as necessary.
Frequently Asked Questions about Put Options
- Q: What is the difference between a put and a call option?
- A: A put option grants the holder the right to sell an underlying asset at the strike price before the expiration date, while a call option confers the right to buy the asset at the strike price within the same timeframe.
- Q: How long do put options last?
- A: The expiration date of a put option is typically set by the options exchange and can range from a few weeks to several months.
- Q: Can I lose money with a put option?
- A: Yes, you can lose money with a put option if the price of the underlying asset rises above the strike price before the expiration date.
What Is A Put In Options Trading
Conclusion
Options trading, with its inherent flexibility and profit potential, can be a compelling investment strategy for both seasoned investors and those seeking alternative investment vehicles. Understanding the dynamics of a put option is fundamental to navigating this dynamic market.
Remember, as with any investment, a thorough understanding of the associated risks is paramount. Careful research, coupled with expert guidance, will serve you well as you embark on your options trading journey. If you are considering venturing into the realm of options trading, I encourage you to diligently explore the resources available, seek expert advice, and proceed with a measured and informed approach. The world of options trading awaits your curiosity and diligent exploration.






