A Personal Tale of Tax Filing Unveils the Labyrinth of Options Trading Reporting
Options trading can be a complex field, not just in terms of understanding strategies and market dynamics, but also when it comes to navigating the intricacies of tax reporting. I once found myself entangled in a web of tax confusion after my first foray into trading options. The complexities of reporting capital gains and losses, wash sales, and other nuances left me bewildered. But through diligent research and expert consultations, I unraveled the tax labyrinth and emerged with a firm grasp on my reporting responsibilities.
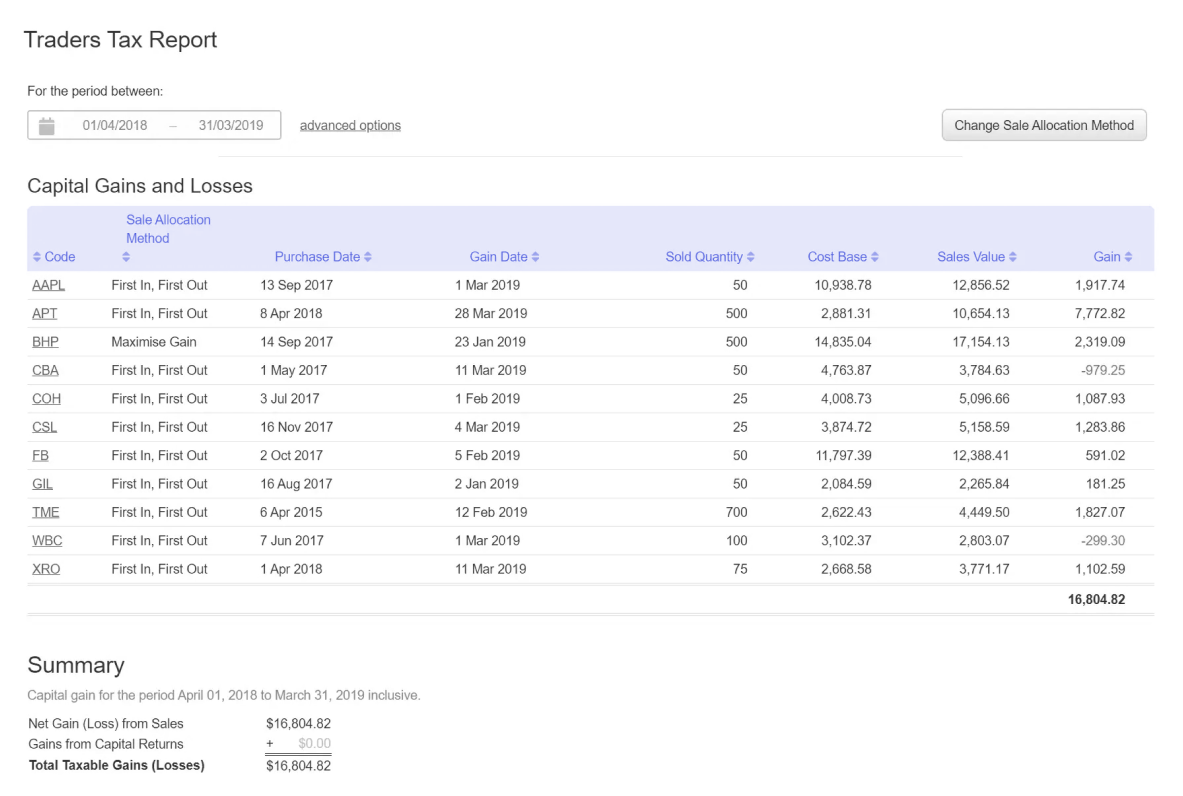
Image: www.sharesight.com
Deciphering the Enigma: A Comprehensive Guide to Options Tax Reporting
Options trading involves buying and selling contracts that give traders the right (but not the obligation) to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specified time frame. These transactions can generate capital gains or losses, depending on whether the options are exercised or expire worthless. Understanding the rules and penalties associated with options tax reporting is paramount to avoid hefty fines and penalties.
1. Capital Gains and Losses: The Foundation of Taxable Events
Capital gains and losses are a common result of options trading. When you sell an option contract for a profit, you realize a capital gain. Conversely, if you sell an option contract at a loss, you incur a capital loss. These gains and losses need to be reported on your tax return and can impact your overall tax liability.
2. Wash Sales: The Intricacies of Loss Deferral
Wash sales occur when you sell an option contract and repurchase a substantially identical contract within 30 days. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) considers this a wash sale and disallows the claiming of a capital loss. Instead, the loss is added to the cost basis of the newly acquired option.

Image: www.youtube.com
3. Straddles: Navigating the Tax Maze
Straddles are trading strategies involving simultaneous purchases of both a call and a put option with the same strike price and expiration date on the same underlying asset. If the straddle results in an overall loss, the IRS will apply the wash sale rules, and the losses may not be claimed until the straddles are closed.
4. Covered Calls: Gaining Clarity Amid Confusion
Covered calls involve selling a call option while already owning the underlying asset. If the call is exercised, the sale is treated as a sale of the underlying asset, and proceeds are treated as capital gains or losses. However, if the call expires unexercised, the trader may have to pay a short-term capital gains tax on the difference between the premium received and the premium paid to acquire the call.
5. Section 1256 Contracts: Special Rules for Traders
Section 1256 contracts are specifically designed for options traders and provide tax advantages. If a transaction meets the criteria for a Section 1256 contract, the profits are taxed at 60% long-term capital gains and 40% short-term capital gains, regardless of the actual holding period.
Stay Informed: Tracing the Latest Developments in Options Tax Reporting
The landscape of options tax reporting is constantly evolving, with updates, clarifications, and new regulations emerging frequently. To ensure compliance and optimize tax savings, it’s crucial to stay informed about the latest changes and consult with tax experts if necessary. Engaging in discussions on forums and social media platforms, where seasoned traders and tax professionals share insights and experiences, can provide valuable updates on the subject.
Expert Advice for Navigating the Tax Maze
Navigating options tax reporting can be a daunting task, but with the right guidance, you can avoid potential pitfalls. Here are a few expert tips to help you navigate the process:
- Maintain Accurate Records: Keep a detailed record of all your options trades, including the date of purchase, strike price, expiration date, and proceeds.
- Identify Applicable Tax Forms: Use Form 1099-B to report capital gains and losses from options trading, and Schedule D (Form 1040) to report your overall capital gains and losses.
- Seek Professional Assistance: If your options trading involves complex strategies or involves high-value transactions, consider consulting with a tax professional to ensure accurate reporting and maximize your tax savings.
- Understand the Wash Sale Rules: Wash sales can significantly impact your tax reporting. Familiarize yourself with the rules and take steps to avoid triggering them if possible.
- Stay Informed: Regularly check for updates and amendments to tax regulations related to options trading.
FAQ: Demystifying Options Tax Reporting
Q: How are straddles taxed?
A: Straddles are subject to the wash sale rules, and any losses may only be claimed when the straddles are closed.
Q: What is the tax treatment of Section 1256 contracts?
A: Profits from Section 1256 contracts are taxed 60% as long-term capital gains and 40% as short-term capital gains, regardless of the holding period.
Q: Is there a specific form for reporting options trading gains and losses?
A: Yes, you use Form 1099-B for reporting capital gains and losses from options trading.
Q: Do I need to report my options trading even if I don’t make any profit?
A: Yes, you need to report all your options trades, regardless of whether you made a profit or loss.
Q: Can I deduct losses from options trading against my regular income?
A: Net capital losses from options trading can only be used to offset capital gains, up to $3,000 per year.
Options Trading Tax Reporting
Conclusion: A Gateway to Informed Options Trading Decisions
Understanding options tax reporting is not just a compliance necessity but a key to unlocking significant tax savings. By staying informed about the latest regulations, following the expert advice provided, and consulting with professionals when needed, you can navigate the complexities of options tax reporting with ease. Remember, tax filing should not be a daunting task but an opportunity to optimize your tax liability and make informed financial decisions. Are you ready to delve deeper into the world of options trading tax reporting?






