In the labyrinthine world of financial markets, options trading emerges as a sophisticated yet compelling strategy that can amplify potential gains and mitigate risks. Options, as financial instruments, present traders with unique opportunities to speculate on the future direction of underlying assets without the burden of ownership. This guide delves into the intricacies of options trading, exploring its foundational concepts, strategies, and potential rewards and perils.
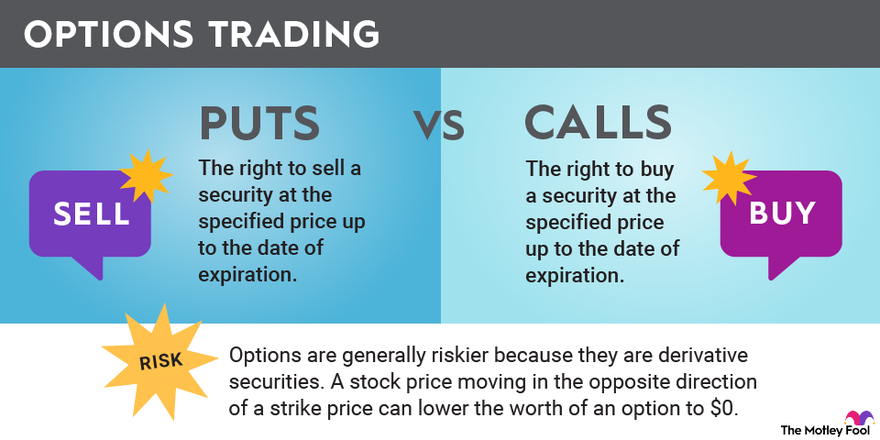
Image: www.fool.com
Understanding Options: A Gateway to Market Speculation
Imagine having the ability to bet on the rise or fall of a stock, commodity, or even an index, without the obligation to buy or sell the underlying asset itself. This transformative power is what options trading offers. An option contract grants the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) a specified quantity of the underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) on or before a certain date (expiration date).
The allure of options trading lies in its flexibility. Buyers and sellers of options can tailor their positions to specific market outlooks, risk appetites, and investment horizons. Holders of call options anticipate price increases, while put option holders wager on price declines. Moreover, options offer leverage, allowing traders to control significant underlying positions with a fraction of the capital required for outright purchases.
Anatomy of an Option Contract: Unraveling the Elements
To navigate the complexities of options trading, a thorough understanding of the anatomy of an option contract is essential. Each contract comprises several key components:
- Underlying Asset: The security or index on which the option is based (e.g., stock, ETF, commodity).
- Strike Price: The price at which the buyer can buy (call option) or sell (put option) the underlying asset.
- Expiration Date: The date on which the option contract expires and becomes worthless.
- Premium: The price paid by the option buyer to acquire the right to exercise the option.
- Option Type: Call or put, depending on the buyer’s intended action (buy or sell).
- Option Class: American or European, referring to the exercise timeline and geographic constraints.
Option Pricing: Deciphering the Value Spectrum
The value of an option is a dynamic interplay of various factors, including the price of the underlying asset, time remaining until expiration, volatility, and interest rates. Option pricing models, such as the Black-Scholes model, attempt to quantify these factors and determine the fair market value of an option contract.
Understanding option pricing is crucial for informed decision-making. Intricate calculations involve analyzing intrinsic value, which represents the potential profit if the option is exercised immediately, and time value, which diminishes as the expiration date approaches. Traders must carefully assess these dynamics to determine whether an option is overvalued or undervalued and decide on appropriate trading strategies.

Image: www.forbes.com
Option Strategies: Navigating the Spectrum of Possibilities
The versatility of options trading extends beyond the simple buying or selling of contracts. Traders can employ a wide array of option strategies to align with their specific market views and risk tolerance. Some of the most common strategies include:
- Covered Calls: Selling call options against an existing underlying asset position.
- Protective Puts: Buying put options to hedge a long position in an underlying asset.
- Bull Call Spreads: Combining a long call option with a short call option at a higher strike price.
- Bear Put Spreads: Combining a short put option with a long put option at a lower strike price.
- Iron Condors: A neutral strategy involving concurrent sales of call spreads and put spreads at varying strike prices.
Risks of Options Trading: Steering the Course with Caution
While options trading presents lucrative opportunities, it also comes with inherent risks that must be carefully considered. The time-sensitive nature of options means that value decays as expiration approaches, potentially leading to losses if market movements fall short of expectations. Unfavorable price fluctuations in the underlying asset can quickly erode option premia, resulting in substantial financial setbacks.
Furthermore, the use of leverage in options trading can amplify both potential gains and losses. Traders employing leveraged positions must meticulously manage risk and vigilantly monitor market conditions to avoid disastrous financial blowouts. Options trading is not suitable for all investors and requires a deep understanding of market dynamics, risk management techniques, and emotional control.
The Psychology of Options Trading: Understanding Behavioral Biases
The world of options trading is not immune to the psychological biases that influence human behavior in financial markets. Greed, fear, herd mentality, and overconfidence can lead traders to make irrational decisions that compromise their financial well-being.
Educating oneself about these biases and developing strategies to mitigate their effects is essential for long-term success in options trading. Discipline, objectivity, and emotional control are paramount to navigating the psychological roller coaster that often accompanies market participation.
Whatbis Options Trading

Image: www.webull.com
Conclusion: Options Trading – A Gateway to Financial Possibilities and Prudent Risk Management
Options trading offers a potent combination of flexibility, leverage, and potential financial rewards. By understanding the foundational concepts, strategies, and risks involved, traders can harness the power of options to enhance their market acumen. However, it is imperative to approach options trading with prudence, comprehensive knowledge, and a steadfast commitment to risk management.
The world of options trading awaits, beckoning those willing to navigate its complexities and embrace its transformative power. With a clear understanding of its intricacies and a disciplined approach to risk management, traders can navigate this financial labyrinth and potentially reap the rewards that await those who dare to venture into its depths.






