Options trading offers a vast array of strategies and terminologies, and “strangle” ranks among the most intriguing. While it may sound ominous, a strangle strategy involves a calculated trade that can yield substantial returns. In this article, we embark on an in-depth exploration of what a strangle in options trading entails, its components, application, and the pivotal decisions involved.
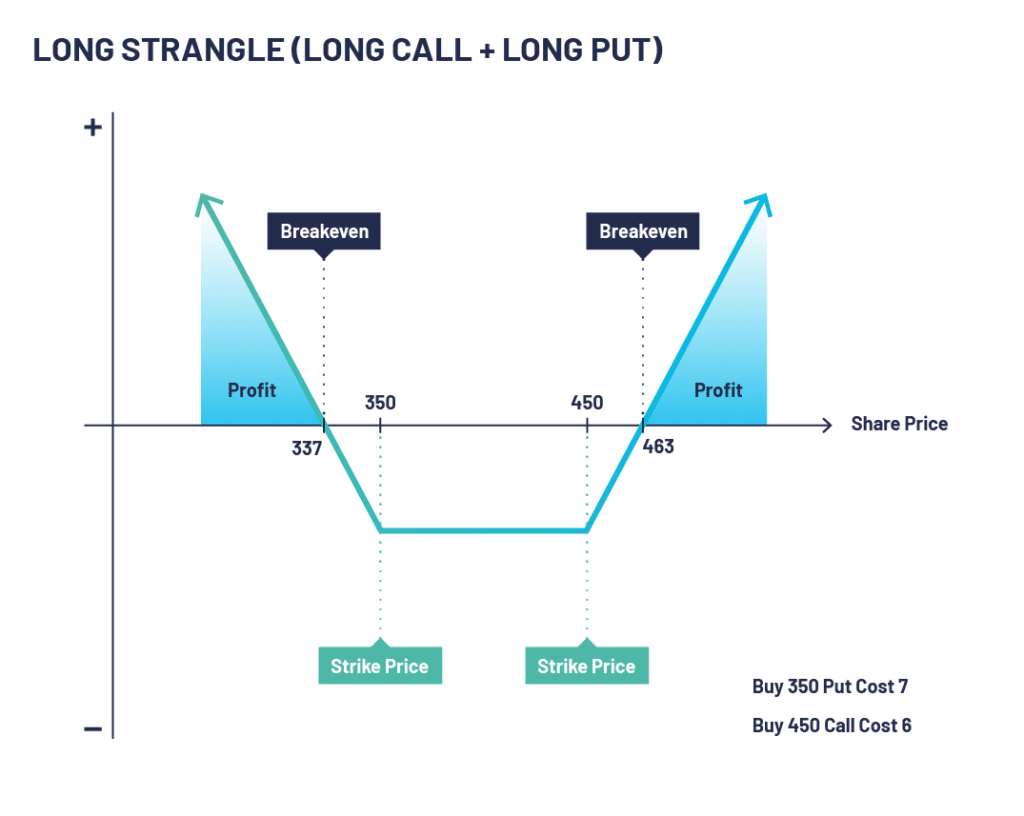
Image: optionsdesk.com
A strangle strategy centers around the simultaneous purchase of both a call option and a put option with the same expiration date but different strike prices. The call option grants the right to buy the underlying asset at a specified strike price, while the put option grants the right to sell it. These options are typically out-of-the-money (OTM), meaning their strike prices are above (for the call option) or below (for the put option) the current market price of the underlying asset.
Anatomy of a Strangle
To delve into the mechanics of a strangle strategy, let’s use an example: Suppose the current price of IBM stock is $120. An investor could purchase a one-month call option with a strike price of $130 and a one-month put option with a strike price of $110. The call option gives the investor the right to buy IBM stock at $130, while the put option gives them the right to sell it at $110. This simultaneous purchase of both a call and a put option forms the essence of a strangle strategy.
Profit Potential
The profit potential of a strangle strategy stems from its ability to capitalize on significant price movements, whether to the upside or downside. If the stock price rises above the strike price of the call option, the investor can exercise the call and purchase the stock at a lower price than the current market value. Conversely, if the stock price falls below the strike price of the put option, the investor can exercise the put and sell the stock at a higher price than the current market value. In either scenario, the investor stands to gain a profit.
Risks and Considerations
While the profit potential of a strangle strategy is enticing, it’s crucial to acknowledge the inherent risks involved. Both call and put options purchased in the strangle strategy have a time decay component, meaning their value decreases as time passes. This means that even if the stock price does move in the desired direction, the investor may not generate sufficient profit to offset the time decay losses.
Moreover, the wider the gap between the strike prices of the call and put options, the greater the potential profit but also the higher the overall cost of the strategy. Striking the right balance between risk and reward is paramount for successful strangle trading.
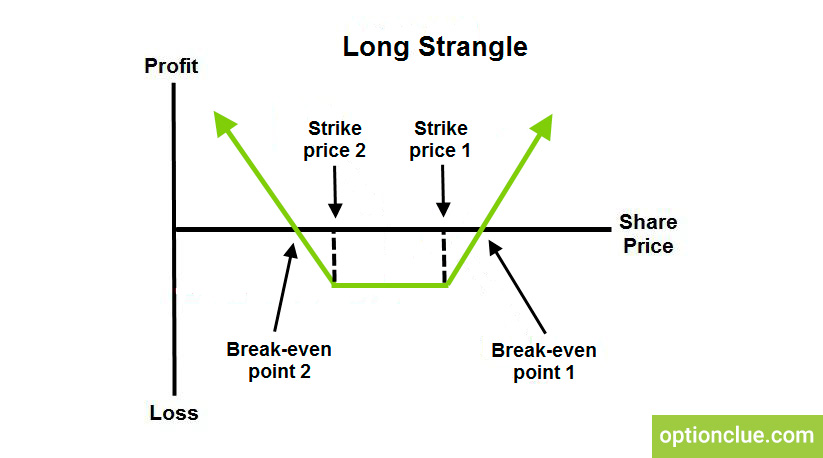
Image: optionclue.com
Tips and Expert Advice
- Research and Due Diligence: Before executing a strangle strategy, conduct thorough research on the underlying asset, market conditions, and historical volatility.
- Choose Liquid Options: Opt for options with ample trading volume and open interest to ensure ample liquidity and minimize bid-ask spreads.
- Manage Risk: Implement risk management techniques such as setting stop-loss orders and position sizing to mitigate potential losses.
- Monitor the Trade: Continuously monitor the performance of your strangle strategy and make adjustments as necessary based on market developments.
- Seek Professional Guidance: If unsure about the nuances of strangle trading, seek guidance from an experienced financial advisor or options trading professional.
Conclusion
A strangle strategy in options trading offers a compelling way to potentially profit from significant market movements. However, it’s essential to fully grasp the risks and complexities involved before implementing such a strategy. By conducting thorough research, understanding the mechanics of a strangle, and implementing sound risk management practices, investors can enhance their chances of success. Whether you’re a seasoned options trader or a curious novice, completing this article with a comprehensive understanding of strangles will undoubtedly empower your trading journey.
Would you like to learn more about strangle options trading or explore other options strategies? If so, I encourage you to continue researching and expanding your knowledge in this captivating realm of financial markets.
What Is Strangle In Options Trading

Image: businessfirstfamily.com
FAQ
- Q: What is the purpose of a strangle strategy?
A: A strangle strategy aims to profit from significant price movements in either direction, whether the underlying asset’s price rises or falls.
- Q: What is the difference between a strangle and a straddle?
A: In a strangle strategy, the strike prices of the call and put options are different. In contrast, in a straddle strategy, the strike prices of the call and put options are the same.
- Q: What is the optimal time frame for a strangle strategy?
A: Shorter-term strangle strategies, such as those with expiration dates within one month, tend to be more volatile and have higher potential returns, but they also carry increased risk.
- Q: How much capital is required for a strangle strategy?
A: The amount of capital required for a strangle strategy depends on the strike prices of the options chosen and the premium paid. It’s important to consider the total cost of the strategy and ensure adequate capital is available.
- Q: Is a strangle strategy suitable for all market conditions?
A: No, a strangle strategy is generally more effective in volatile and trending markets. In range-bound markets, the time decay of the options can erode profits.






