Introduction
Options trading presents a vast and multifaceted landscape of strategies, each designed to cater to specific risk tolerances, market expectations, and profit objectives. Among the array of available approaches, vertical spreads stand out as a versatile and nuanced technique that enables traders to tailor their positions to suit their unique trading goals. This comprehensive guide delves into the depths of vertical spread option trading, unraveling its concepts, exploring its intricacies, and equipping traders with the knowledge to navigate its dynamic waters.
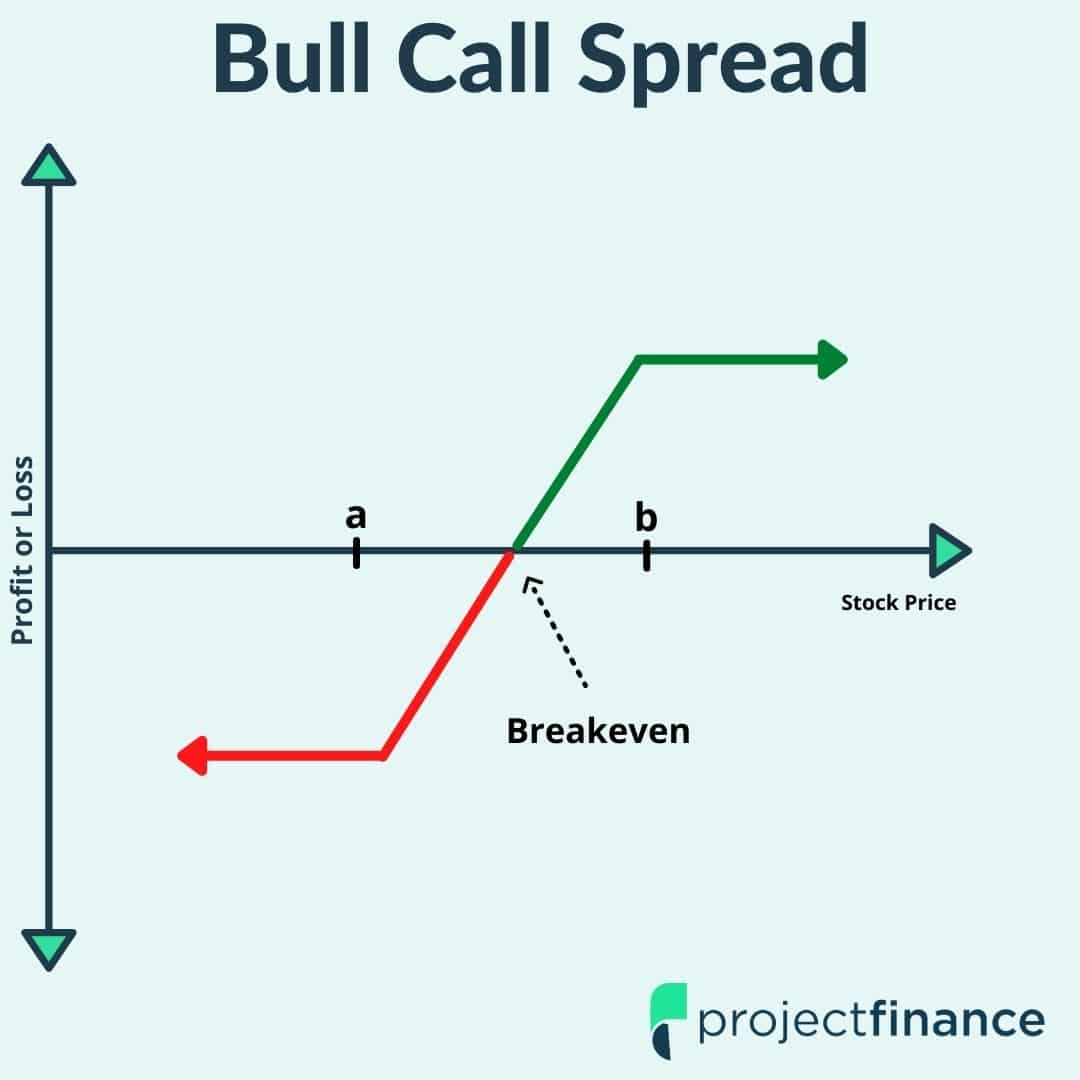
Image: telegra.ph
Vertical spreads, in essence, involve the simultaneous purchase and sale of options with different strike prices for the same underlying asset but with the same expiration date. By combining a long position in one option with a short position in another, traders can craft a customized risk-reward profile that aligns with their desired market outlook. The flexibility of vertical spreads lies in their ability to adjust the spread width (the difference between strike prices) and the number of contracts involved, enabling traders to fine-tune their strategies to match the prevailing market conditions.
Unraveling the Types of Vertical Spreads
The vertical spread family comprises a diverse range of strategies, each tailored to address specific market expectations. The three primary categories, bull call spreads, bear call spreads, and bear put spreads, serve as the foundation of this trading universe.
- Bull Call Spreads: Consisting of a long call option at a lower strike price and a short call option at a higher strike price, bull call spreads are crafted with an optimistic market outlook. The maximum profit for bull call spreads occurs when the underlying asset’s price rises above the higher strike price.
- Bear Call Spreads: Employing a long call option at a higher strike price and a short call option at a lower strike price, bear call spreads anticipate a decline or sideways movement in the underlying asset’s price. The maximum profit for bear call spreads is realized when the underlying asset’s price remains below the lower strike price.
- Bear Put Spreads: Combining a long put option at a higher strike price and a short put option at a lower strike price, bear put spreads express a bearish or neutral market outlook. The maximum profit for bear put spreads materializes when the underlying asset’s price falls below the lower strike price.
Delving into the Specifics of Vertical Spreads
Beyond the basic types of vertical spreads lies a nuanced world of variations, each offering unique advantages and drawbacks.
- Neutral Spreads: Neutral spreads, such as calendar spreads and butterfly spreads, are characterized by a balanced risk-reward profile. They seek to capitalize on time decay and volatility without taking a directional stance on the underlying asset’s price movement.
- One-Sided Spreads: One-sided spreads, such as ratio spreads and strip spreads, involve an imbalance between the number of contracts on the long and short side. These spreads offer the potential for higher returns but come with increased risk exposure.
- Combination Spreads: Combination spreads, like condor spreads and iron butterflies, combine elements of multiple spread types. They aim to enhance the risk-reward profile or create more complex market exposures.
Mastering the Nuances of Vertical Spread Pricing
The price of a vertical spread is a crucial factor that influences its profitability. Traders must carefully consider the interplay of the individual option prices, the spread width, and the prevailing implied volatility. By understanding the pricing dynamics, traders can optimize their spread selection to match their profit objectives.
- Credit Spreads: Credit spreads involve selling an option and buying an option at a higher or lower strike price. These spreads generate a net premium at the inception of the trade and aim to profit from the decay of time value.
- Debit Spreads: Debit spreads entail buying an option and selling an option at a higher or lower strike price. These spreads require an upfront payment of a net premium and seek to profit from a favorable movement in the underlying asset’s price.
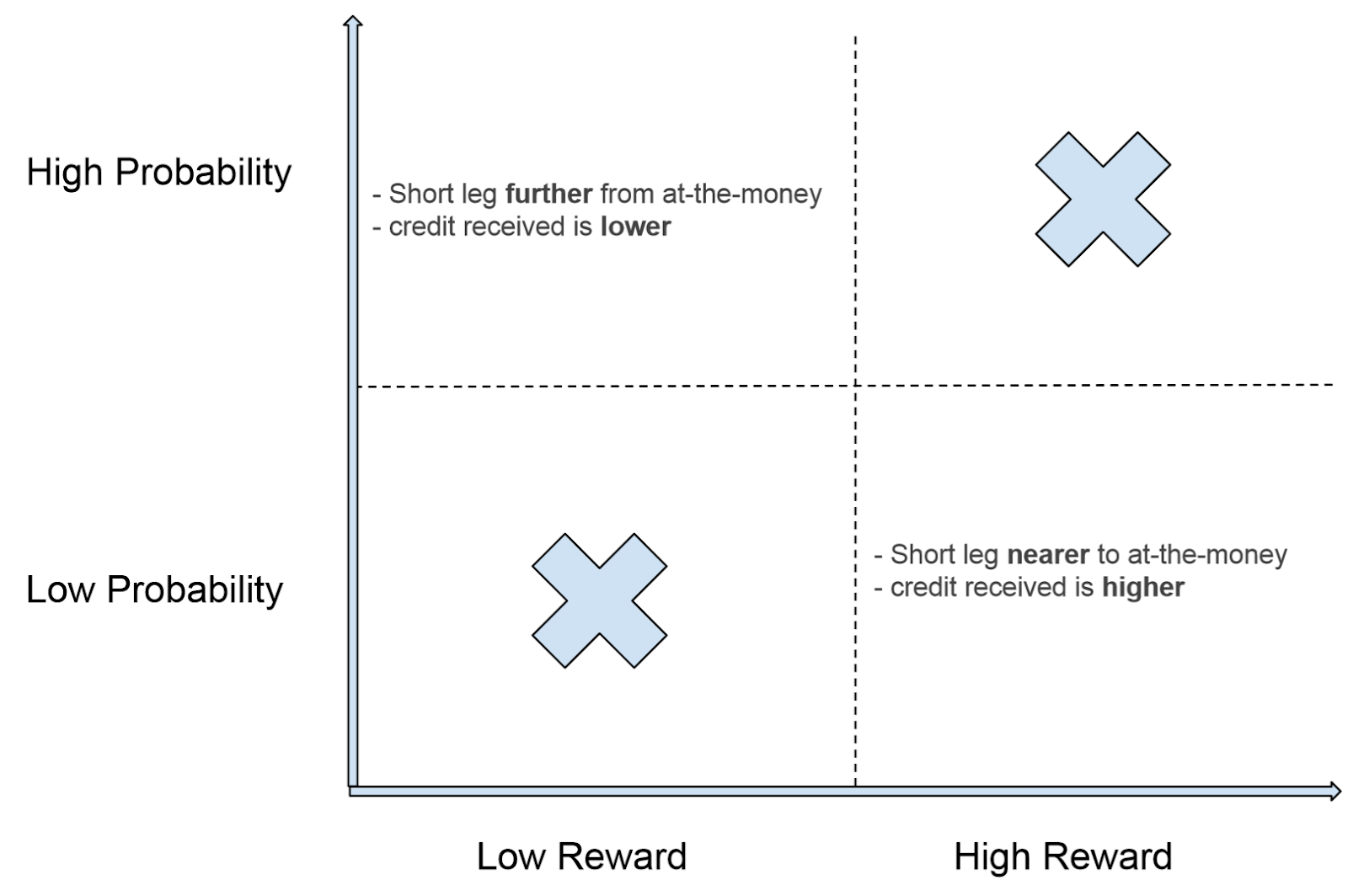
Image: blog.optionsamurai.com
Vertical Spread Option Trading Strategies

Image: optionalpha.com
Conclusion
Vertical spread option trading strategies empower traders with a versatile tool to navigate the complex financial markets. By embracing the concepts and mastering the nuances of vertical spreads, traders can harness their potential to craft tailored positions that align with their risk tolerance and profit objectives. Whether adopting neutral spreads for income generation or deploying one-sided spreads for potential windfalls, vertical spreads offer a diverse range of solutions for both seasoned traders and those just starting their options trading journey.






