Title: The Ultimate Guide to Short vs. Long Vertical Spreads in Options Trading: Maximizing Your Returns

Image: investdale.com
Introduction:
In the enigmatic realm of options trading, where opportunities abound amidst calculated risks, the choice between short and long vertical spreads is akin to a tantalizing dance. Both strategies hold immense promise, but understanding their intricacies is crucial for successful navigation. This comprehensive guide will delve into the depths of short vs. long vertical spreads, empowering you with the knowledge to craft profitable trades in this dynamic market.
Short vs. Long Vertical Spreads: A Comparative Analysis
Vertical spreads are price-neutral option strategies involving the simultaneous buying and selling of options with different strike prices and expiration dates. The key distinction between short and long vertical spreads lies in their profit potential and risk profile.
Short Vertical Spread:
- Buy: One put or call option at a lower strike price
- Sell: One put or call option at a higher strike price
- Difference: The net premium received upon entering the trade
A short vertical spread is designed to capitalize on a neutral to slightly bearish market outlook. The trader expects the underlying asset to remain within a specific range, with a limited potential for significant upward or downward movement. This strategy generates a profit if the underlying price remains between the two strike prices at expiration.
Long Vertical Spread:
- Buy: One put or call option at a lower strike price
- Sell: One put or call option at a higher strike price
- Difference: The net premium paid upon entering the trade
In contrast, a long vertical spread reflects a bullish or bearish outlook. The trader anticipates significant movement in the underlying asset, believing it will either rise or fall beyond the chosen strike prices. If their prediction materializes, the spread generates a profit.
Choosing the Right Strategy: Risk and Reward
The choice between short and long vertical spreads hinges upon the trader’s risk tolerance and market expectations.
Short Vertical Spread:
- Lower risk: Limited profit potential, maximum loss defined at the difference between strike prices and premium received
- Suitable: Neutral or slightly bearish market outlook, volatility expectations within a moderate range
Long Vertical Spread:
- Higher risk: Unlimited profit potential, theoretical maximum loss exceeding the net premium paid
- Suitable: Bullish or bearish market outlook, anticipating significant price movement, higher volatility expected
Conclusion:
The decision between short and long vertical spreads is a critical component of options trading. By carefully considering the risk-reward profile of each strategy and aligning it with market expectations, traders can optimize their returns and navigate the complexities of this dynamic market. This guide has provided a comprehensive understanding of these strategies, empowering readers to make informed choices and maximize their profitability in the world of options trading.
Image: unofficed.com
Short Vs Long Vertical Spread In Options Trading
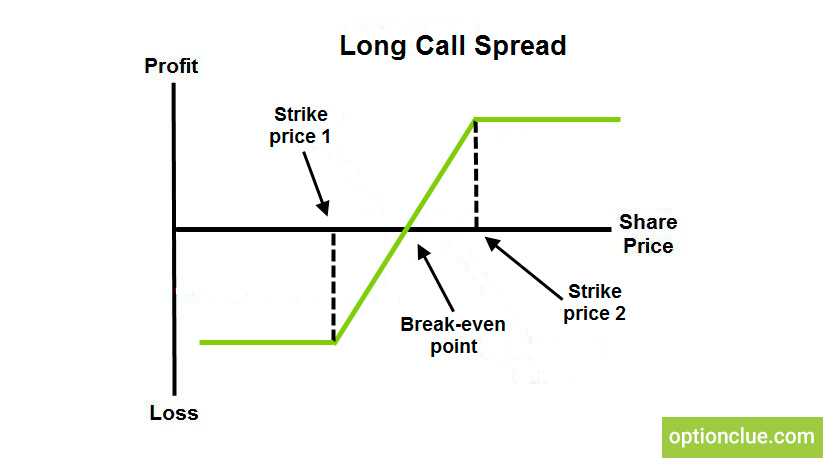
Image: optionclue.com






