Introduction
Options trading is a complex but potentially lucrative strategy in which traders have the right to buy or sell an underlying asset at a certain price on or before a specific date. Trailing stops are a valuable tool for managing risk and maximizing profits in options trading by automatically adjusting the stop-loss level as the price of the underlying asset moves in your favor.

Image: app.tradingsim.com
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of trailing stops for options trading, explaining their mechanisms, advantages, drawbacks, and how to use them effectively to enhance your trading strategy.
Understanding Trailing Stops
Definition and Mechanism
A trailing stop is a type of stop order that moves with the price of the underlying asset, maintaining a specified distance from the current market price. For example, you could set a trailing stop for an option that is 5% below the current price of the underlying asset. As the price of the underlying asset rises, your trailing stop will also move up correspondingly by 5%. If the price of the underlying asset falls below your trailing stop, your option will be automatically sold to limit your losses or take profits.”
Trailing Percentage vs. Fixed Amount
Trailing stops come in two main forms: trailing percentage stops and trailing fixed amount stops. Trailing percentage stops move as a percentage of the current price of the underlying asset. For example, a trailing stop set at 5% will move up and down by 5% as the price of the underlying asset fluctuates. Trailing fixed amount stops, on the other hand, move by a fixed dollar amount regardless of the price of the underlying asset. Choosing the right type of trailing stop depends on your individual trading strategy and risk appetite.

Image: www.youtube.com
Applications of Trailing Stops
Risk Management and Profit Maximization
Trailing stops are primarily used for two purposes: managing risk and maximizing profits. By automatically adjusting the stop-loss level as the price of the underlying asset moves in your favor, you can ensure that you lock in profits while limiting potential losses. This is especially beneficial in volatile markets where prices can fluctuate rapidly.
Moreover, trailing stops allow you to target specific profit levels. By setting a trailing stop at a predetermined profit margin, you can capture potential gains while allowing your option to continue running if the market continues to move in your favor.
Types of Options Trading Strategies
Trailing stops are suitable for different types of options trading strategies, including covered calls, naked puts, iron condors, and strangles. In most cases where you are selling premium (i.e., short options), trailing stops can help you lock in gains and manage risk. For strategies where you are buying premium (i.e., long options), trailing stops can help you limit losses and potentially increase profit.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
• Automated Risk Management: Trailing stops eliminate the need for manual monitoring and adjustment of stop-loss levels, providing you with peace of mind and reducing the risk of human error.
• Objective Decision Making: Trailing stops remove emotion from the trading process by automatically adjusting the stop-loss level based on predefined rules, preventing you from making rash decisions.
• Capture Gains: Trailing stops allow you to capture potential profits by automatically moving the stop-loss level upwards as the price of the underlying asset rises.
Disadvantages
• Lagging Indicators: Trailing stops can lag behind sudden market reversals, exposing you to the risk of substantial losses if the market moves sharply against you.
• Slippage: Trailing stops can lead to slippage, as orders may not be executed at the exact price you specify due to market fluctuations or liquidity issues.
Tips and Expert Advice
• Set Realistic Parameters: Determine an appropriate trailing percentage or fixed amount based on your risk tolerance and the volatility of the underlying asset.
• Monitor Market Volatility: Adjust your trailing stop levels as market volatility changes to ensure that you have an appropriate amount of protection.
• Consider a Trailing Take Profit: In addition to a trailing stop-loss, consider setting a trailing take profit level at which your option will be automatically sold if the underlying price reaches your target gain.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How do I set a trailing stop for an option?
A: Contact your broker or use your trading platform to enter a trailing stop order. The specific steps may vary depending on the platform or broker.
Q: What is a reasonable trailing percentage?
A: The appropriate trailing percentage varies based on the underlying asset, market volatility, and your risk tolerance. Common ranges include 5-20% for short options and 10-30% for long options.
Q: Can I use trailing stops with different types of options strategies?
A: Yes, trailing stops can be used with various options strategies, including covered calls, naked puts, iron condors, and strangles.
Trailings Stops For Options Trading
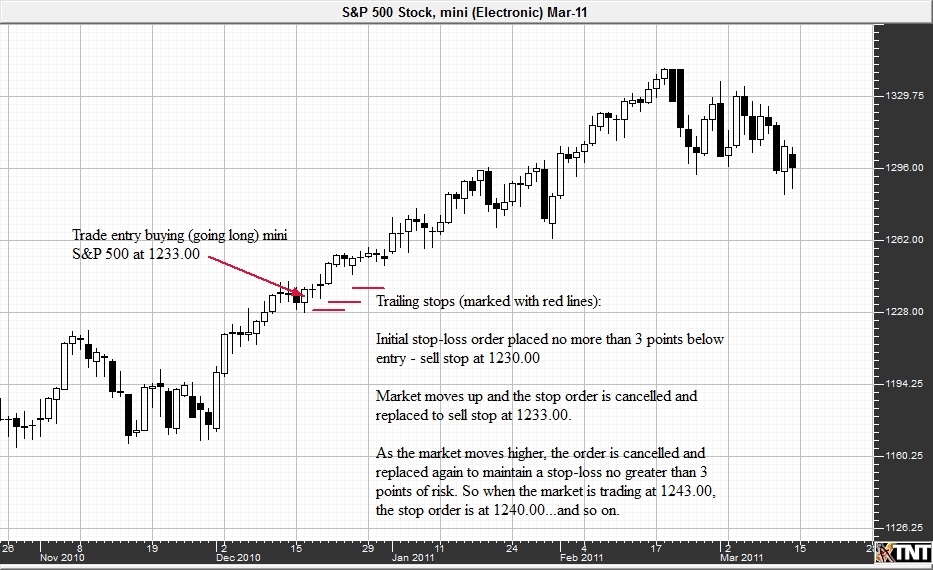
Image: www.mql5.com
Conclusion
Trailing stops are a powerful tool for options traders to manage risk and enhance profit potential. By understanding the mechanics, advantages, and limitations of trailing stops, you can incorporate them effectively into your trading strategy.
If you are new to options trading, it is recommended to consult with an experienced trader or financial advisor to fully understand the risks and complexities involved.






