In the volatile energy landscape, predicting the direction of natural gas prices can be a daunting task. However, savvy investors have a powerful tool at their disposal: natural gas (NG) futures options. These dynamic contracts offer traders a unique combination of control and flexibility, allowing them to hedge against price fluctuations or capitalize on anticipated movements.

Image: fadukuvo.web.fc2.com
Navigating the Fundamentals of NG Futures Options
Futures options are derivative contracts that give buyers or sellers the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price on a future date. In the case of NG futures options, the underlying asset is the futures contract for natural gas.
By purchasing an option, the holder gains the option premium, which is the price paid for the contract. This premium represents the potential profit or loss, depending on whether the market price of natural gas moves in the expected direction by the option’s expiration date.
Types of NG Futures Options
There are two main types of NG futures options: calls and puts. Call options give holders the right to buy the underlying futures contract at a specified price, while puts grant the right to sell. The strike price, which is the predetermined price for the transaction, determines the potential profit or loss.
Benefits and Risks of Trading NG Futures Options
Benefits:
-
Control: Options allow traders to control the direction of potential trades without taking direct ownership of the underlying asset.
-
Leverage: Options provide leverage, allowing traders to magnify their potential profits with a smaller capital investment compared to trading futures directly.
-
Hedging: Options can be used as a risk-management tool to hedge against unfavorable price movements or to lock in profits.
Risks:
-
Limited Profit Potential: Unlike futures contracts, options have a limited profit potential, capped at the value of the underlying asset’s movement.
-
Premium Loss: If the market price does not move in the anticipated direction, the entire premium paid for the option may be lost.
-
Expiration Date: Options have a finite lifespan, and their value can expire worthless if they are not exercised before the expiration date.
Harnessing Expert Insights and Actionable Tips
-
Calibrate Expectations: Understand the limitations and potential risks of options trading. Avoid setting unrealistic profit expectations or chasing losses.
-
Manage Volume: Trade options in manageable volumes that align with your risk tolerance and financial capacity.
-
Monitor Market Conditions: Keep a pulse on news, geopolitical events, and macroeconomic factors that can influence natural gas prices.
-
Employ Technical Analysis: Use historical price data and technical indicators to identify potential trading opportunities.
Conclusion
Natural gas futures options empower traders with a versatile tool to enhance market participation and control. This article has provided a comprehensive overview of the fundamentals, types, and strategies involved in NG futures options trading. By leveraging expert insights and actionable tips, traders can navigate the complexities of this dynamic market and harness its potential for both hedging and profit-making opportunities. Remember, investing in options involves inherent risks, so thorough research and diligent risk management practices are crucial for successful trading.
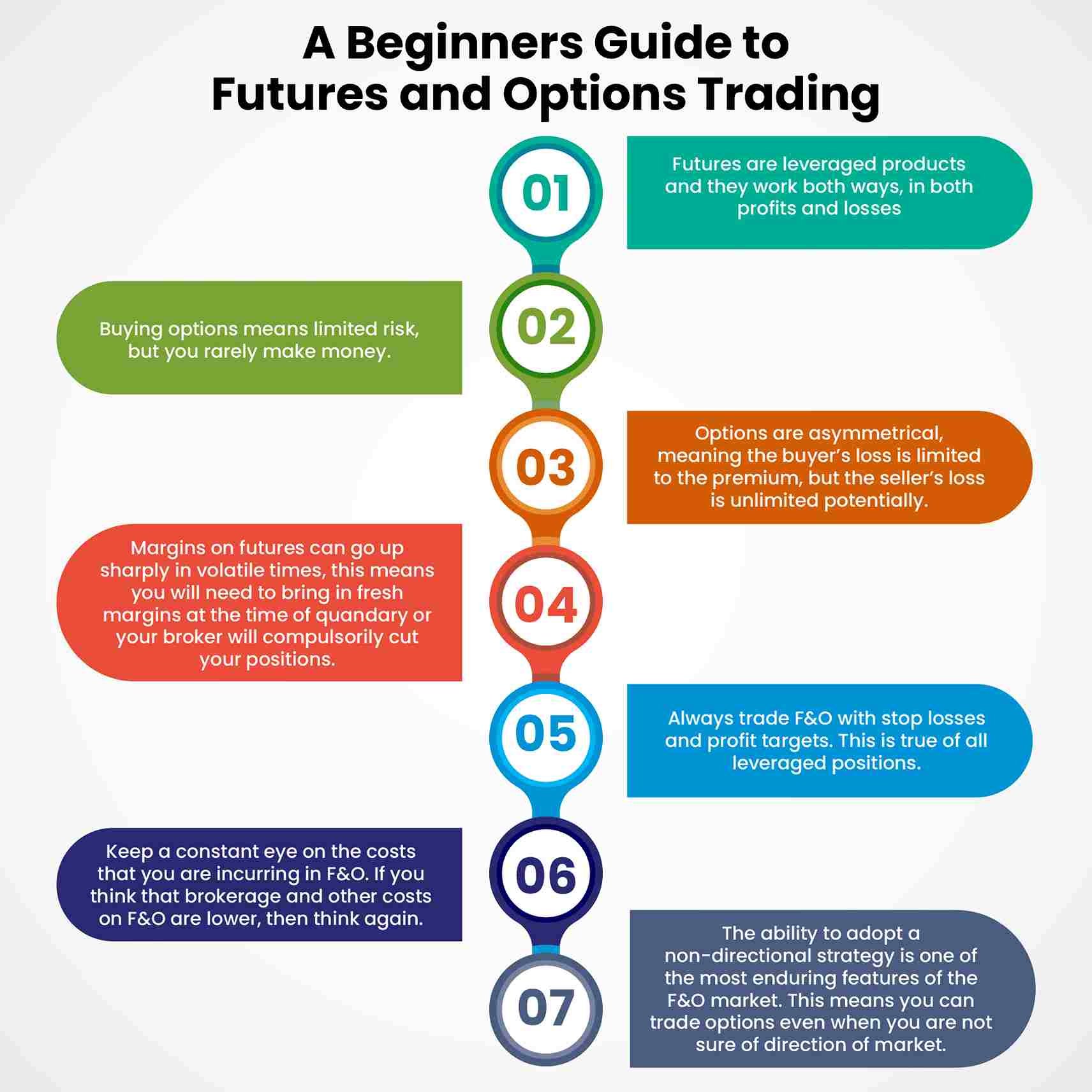
Image: www.setindiabiz.com
Trading Ng Futures Options

Image: www.youtube.com






