Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of financial markets, day trading has emerged as an adrenaline-pumping endeavor, where traders seek to capitalize on short-term price fluctuations within a single trading day. However, navigating the realm of day trading requires a comprehensive understanding of the diverse financial instruments available, each with unique characteristics and intricacies. Among these instruments, stocks, futures, and options stand out as the most popular choices for day traders, offering both opportunities and challenges. In this guide, we will delves into the intricacies of stocks vs. futures vs. options day trading, exploring their advantages, disadvantages, and suitability for different trading styles.

Image: www.livestreamtrading.com
Understanding Stocks
Stocks, also known as shares, represent fractional ownership in a publicly traded company. When purchasing a stock, a trader essentially becomes a shareholder, entitled to a portion of the company’s earnings and assets. The value of a stock fluctuates based on factors such as company performance, market conditions, and investor sentiment. Stock day trading involves actively buying and selling stocks throughout the trading day, seeking to profit from short-term price movements.
-**Transparency:** Stock markets are highly regulated, ensuring transparency in pricing and execution.
-**Liquidity:** Stocks are among the most liquid financial instruments, making it easy to enter and exit positions quickly.
-**Dividend Income:** Many stocks pay dividends to shareholders, providing a potential source of income in addition to capital gains.
-**Volatility:** Stock prices can be highly volatile, leading to substantial losses if not managed carefully.
-**High Capital Requirement:** Day trading stocks typically requires significant capital to achieve meaningful profits.
-**Limited Leverage:** Unlike futures and options, stocks offer limited leverage, restricting potential returns but also reducing the risk of excessive losses.
Unveiling Futures
Futures contracts are standardized agreements to buy or sell a specified underlying asset, such as a commodity, currency, or stock index, at a predetermined price on a future date. Futures trading involves speculating on the future direction of the underlying asset’s price. Day traders buy and sell futures contracts during the trading day, seeking to profit from short-term price movements.
-**Leverage:** Futures contracts offer high leverage, enabling traders to control a larger amount of capital with a lower upfront investment.
-**Hedging:** Futures can be used as a hedging tool to offset risks associated with other investments.
-**Access to a Diverse Range of Assets:** Futures contracts are available for a wide range of underlying assets, providing traders with greater diversification options.
-**Complexity:** Futures contracts can be more complex than stocks, requiring a deeper understanding of financial markets.
-**Settlement Risk:** Futures contracts involve a legal obligation to deliver or take delivery of the underlying asset on the expiration date.
-**Unpredictable Margins:** Futures traders are subject to margin calls, where they may be required to post additional funds to cover potential losses.
Exploring Options
Options are financial contracts that give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specific price on or before a certain date. Options trading involves speculating on the likelihood and direction of price movements. Day traders utilize options to generate income by buying and selling options contracts based on their expectations.
-**Limited Risk:** Options offer limited downside risk, as the maximum loss is capped at the premium paid.
-**Flexibility:** Options provide traders with flexibility to tailor strategies based on their risk tolerance and market outlook.
-**Income Generation:** Options can be used to generate income through various strategies, such as selling covered calls or buying put options.
-**Time Decay:** Option premiums lose value over time, even if the underlying asset price remains unchanged.
-**Complexity:** Options trading can be complex, requiring a comprehensive understanding of option pricing and risk management.
-**Bid-Ask Spread:** Options typically have wider bid-ask spreads compared to futures or stocks, which can limit profitability.

Image: www.pinterest.com
Matching Day Trading Instruments to Trading Styles
The selection of the most suitable day trading instrument largely depends on an individual trader’s risk tolerance, capital availability, and trading style. For those with a higher risk appetite and access to larger capital, futures and options may offer greater potential returns due to their leverage and flexibility. However, these instruments also come with higher complexity and risk.
Stocks, on the other hand, are more appropriate for traders with lower risk tolerance and limited capital. While stocks offer less leverage than futures and options, they typically involve lower trading costs and more predictable risks.
Notably, the choice of instrument is not mutually exclusive. Experienced day traders often employ multiple instruments in combination to diversify their portfolio and capitalize on different market conditions.
Stocks Vs Futures Vs Options Day Trading
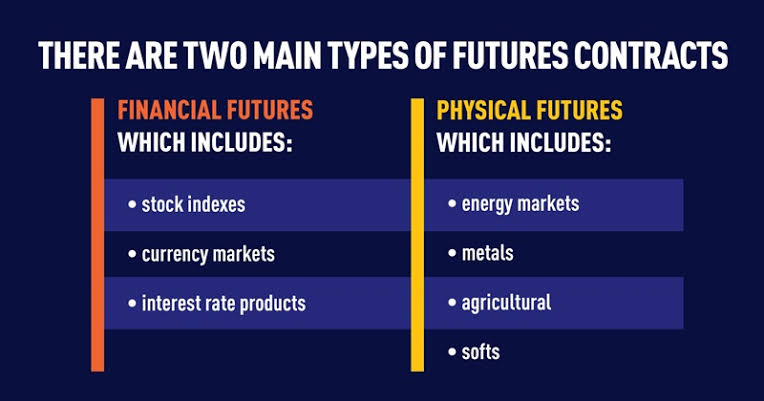
Image: buddymantra.com
Conclusion
The world of day trading presents a captivating arena for traders to hone their skills and seek financial gain. Stocks, futures, and options are the three main financial instruments commonly utilized in day trading. Each instrument offers unique advantages and disadvantages, suiting different trading styles and risk tolerance levels.
Understanding the nuances of each instrument is paramount for successful day trading. Traders must meticulously research, backtest strategies, and continually monitor their performance to navigate the dynamic financial markets effectively. By carefully selecting the appropriate instrument and adopting sound risk management practices, traders can maximize their chances of success in the thrilling world of day trading.






