Trading Options vs. Shorting Stocks: A Comparative Guide
Trading options and shorting stocks are both strategies employed in the financial markets to potentially generate profits. However, these techniques differ significantly in their execution, risks, and rewards, warranting a thorough understanding for informed investment decisions.
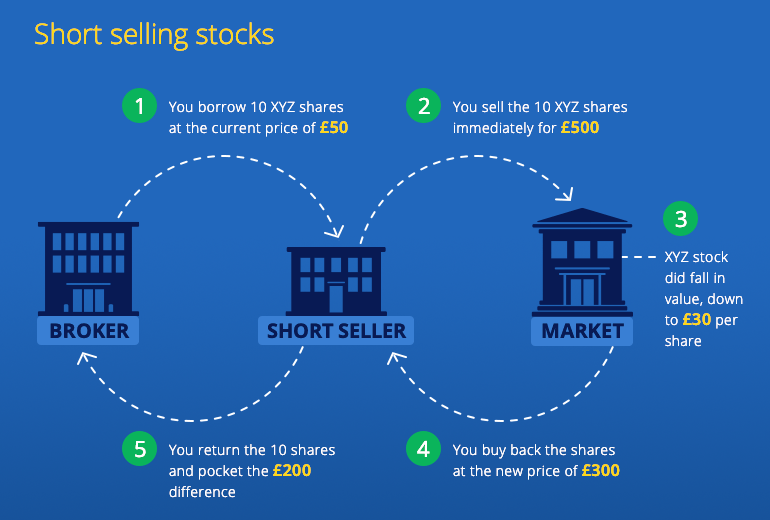
Image: behalfessay9.pythonanywhere.com
Understanding Options Trading
Options are contracts that grant the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specific price on or before a specified date. This flexibility allows investors to speculate on the future direction of an asset without the commitment of purchasing or selling the underlying security outright. Options trading involves the payment of a premium, which represents the cost of acquiring the right to execute the contract.
Understanding Shorting Stocks
Shorting stocks is a strategy where the investor borrows shares of a company and immediately sells them on the open market, hoping to buy them back later at a lower price and return them to the lender. If the stock price declines as anticipated, the short seller profits from the difference between the selling and buying prices minus any borrowing costs. However, if the stock price rises, the short seller incurs a loss potentially greater than the initial investment.
Key Differences: Options Trading vs. Shorting
- Ownership of the Underlying Asset: In options trading, the buyer does not own the underlying asset but merely holds the right to buy or sell it. In shorting, the investor effectively borrows the underlying stock and becomes temporarily liable for its return.
- Risk Exposure: Options trading typically offers limited risk, as the maximum loss is capped at the premium paid, while shorting stocks involves unlimited potential loss if the stock price rises significantly.
- Cost of Entry: Shorting stocks typically has lower upfront costs compared to options trading, as there is no premium payment required. However, short sellers may incur borrowing fees or margin interest charges over time.
- Flexibility: Options provide greater flexibility, allowing investors to adjust their positions by modifying or exercising the contracts. Shorting stocks is a less flexible strategy, with limited exit strategies once the position is initiated.
- Time Horizon: Options contracts have fixed expiration dates, while short stock positions can be held indefinitely, depending on market conditions and borrowing availability.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ShortSellingvs.PutOptions-eff3cf41a5f549978c295eef47fbc2bd.png)
Image: www.investopedia.com
Trends and Developments
The popularity of options trading has surged in recent years, driven by the proliferation of retail trading platforms and increased market volatility. Advances in technology have made options trading more accessible, with automated trading tools and sophisticated analytics platforms enabling investors to refine their strategies.
Meanwhile, shorting stocks remains a popular strategy for experienced traders and hedge funds, although regulatory changes and market conditions can impact its viability. Short interest data is often closely monitored as an indicator of market sentiment and potential market moves.
Expert Tips for Options Trading and Shorting
- Conduct Thorough Research: Understand the underlying asset, market dynamics, and risks involved before engaging in either strategy.
- Manage Risk Effectively: Implement risk management techniques such as position sizing, diversification, and stop-loss orders to minimize losses.
- Seek Professional Advice: Consider consulting with financial advisors or brokers for guidance, especially if you are new to options trading or shorting stocks.
- Monitor Market Conditions: Stay informed about market events, economic data, and geopolitical developments that can impact stock prices.
- Set Realistic Expectations: Understand that these strategies can be profitable but also involve inherent risks. Set realistic expectations and avoid overleveraging your investments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Which strategy is better, options trading or shorting stocks?
A1: The better strategy depends on individual risk tolerance, time horizon, and investment goals. Options trading offers limited risk, while shorting stocks has unlimited potential loss but also the opportunity for higher profits.
Q2: Is it possible to lose more money than invested when shorting stocks?
A2: Yes, if the stock price rises significantly, short sellers can incur losses that exceed their initial investment.
Q3: How do I start options trading?
A3: Open an account with an online brokerage firm that offers options trading and conduct thorough research before placing your first trade.
Options Trading Vs Shorting

Image: www.linkedin.com
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between options trading and shorting is crucial for investors seeking to navigate the financial markets effectively. By weighing the risks and rewards, utilizing prudent risk management techniques, and seeking professional advice when necessary, investors can maximize their potential for success in either of these strategies.
Are you ready to explore options trading vs. shorting further? Join our community of traders today to gain access to exclusive insights, trading strategies, and support.






