In the volatile world of options trading, managing risk is paramount. One crucial tool that every trader should master is the stop-loss order. A stop-loss order is a conditional order that automatically exits a position when the price of the underlying asset reaches a predetermined level, limiting potential losses.

Image: www.tradingwithrayner.com
Importance of Stop-Loss Orders
Stop-loss orders play a vital role in protecting your portfolio from heavy losses. They prevent you from holding losing positions for too long, which can lead to significant drawbacks. Consider this scenario: you buy call options expecting the stock price to rise. However, due to unforeseen circumstances, the stock price takes a sharp downturn. A well-placed stop-loss order will automatically sell your call options, minimizing your losses before they snowball.
Types of Stop-Loss Orders
There are three main types of stop-loss orders:
- Stop-Loss Order: Executes once the price falls below (for short positions) or rises above (for long positions) a specified price.
- Stop-Limit Order: Combines a stop-loss order with a limit order, ensuring the position is exited at a specific price or better.
- Trailing Stop-Loss Order: Moves the stop price dynamically as the underlying asset price moves favorably, protecting profits while still controlling risk.
Determining Stop-Loss Levels
The key to using stop-loss orders effectively lies in determining the optimal stop-loss level. Multiple factors need to be considered, including:
- Risk tolerance: How much loss are you willing to absorb?
- Volatility of the underlying asset: More volatile assets require wider stop-loss levels.
- Profit target: Consider the expected reward-to-risk ratio of the trade.
- Market conditions: Adjust stop-loss levels in response to market trends and news events.
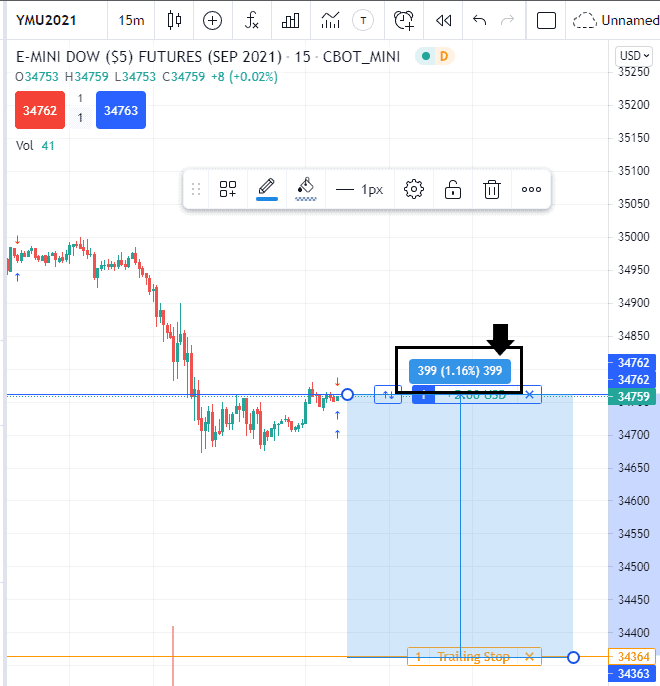
Image: tradamaker.com
Tips for Effective Stop-Loss Use
To harness the full potential of stop-loss orders, follow these professional tips:
- Use realistic stop levels: Avoid setting stop-loss orders too tightly, as they may get triggered by temporary price fluctuations.
- Don’t overtrade: Allocate only a small portion of your trading capital to each trade, reducing the impact of potential losses.
- Monitor your positions closely: Regularly review your positions and adjust stop-loss levels as necessary.
Expert Advice from Seasoned Traders
“Stop-loss orders are not a magic wand that can guarantee profits, but they are a powerful tool for managing risk,” advises Thomas Marlow, a seasoned options trader. “The key is to find a stop-loss level that provides adequate protection without limiting profit opportunities.”
“Don’t be afraid to adjust stop-loss levels as market conditions evolve,” adds Lisa Rodriguez, a professional trader. “The goal is to balance protection with flexibility.”
Common FAQs on Options Trading Stop-Loss
- Q: When should I use a stop-loss order?
A: Anytime you enter a trade with the potential for loss. - Q: What’s the difference between a stop-loss order and a limit order?
A: A stop-loss order exits a position when the price falls below a specific level, while a limit order exits at a specific price. - Q: Can I set multiple stop-loss orders?
A: No, only one stop-loss order can be active for each position at any given time.
Options Trading Stop Loss
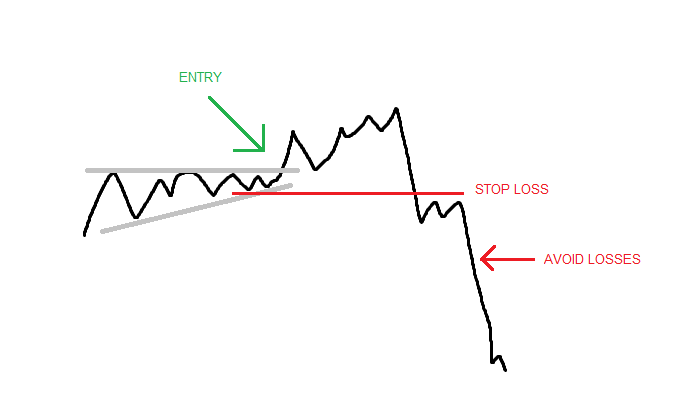
Image: www.buildalpha.com
Conclusion
Options trading stop-loss orders are essential tools for managing risk and preserving capital. By implementing the strategies and advice outlined in this article, you can enhance your options trading skills and limit potential losses, providing a solid foundation for long-term trading success.
Are you interested in learning more about options trading stop-loss orders? We invite you to explore our comprehensive resources and connect with our community of expert traders. Together, let’s navigate the dynamic world of options trading with confidence and precision.






