Introduction
In the fast-paced world of finance, options trading has emerged as a powerful investment strategy with the potential to amplify returns. Options, derivative instruments that confer the right—but not the obligation—to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predefined price, grant traders flexibility and leverage. However, tapping into these benefits hinges on a crucial element: margin requirements. Margin trading, the practice of borrowing funds from a brokerage firm to increase purchasing power, carries inherent risks that traders must fully comprehend to navigate the options market successfully.
Image: ejizajif.web.fc2.com
What are Margin Requirements in Options Trading?
Margin requirements, expressed as a percentage, are set by brokerages to determine the minimum amount of capital traders must maintain in their accounts to trade options on margin. These requirements vary depending on the underlying asset, strike price, and expiration date of the option contract. Essentially, margin acts as collateral, safeguarding brokerages against potential losses if the market moves against the trader’s position.
How Margin Requirements are Calculated
The calculation of margin requirements for options trading involves several factors:
- The option premium: This is the price paid to purchase the option contract.
- The underlying asset’s current market price: The price of the underlying stock, currency, or commodity influences margin requirements.
- The strike price: This is the price at which the trader can exercise the option to buy or sell the underlying asset.
- The expiration date: Options with shorter expiration dates typically have lower margin requirements than those with longer expirations.
- The trader’s trading strategy: Buying a call option, for instance, has different margin requirements compared to buying a put option.
Benefits of Trading Options on Margin
Leverage: Margin trading allows traders to access a greater amount of capital, increasing their purchasing power and potentially enhancing returns.
Flexibility: Trading options on margin provides traders with the ability to implement various trading strategies, hedging positions, and expressing different market views.
Time Value: Margin trading can enable traders to capture the time value of options, which decays as the expiration date approaches.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/margin-Final-872dda45cc4243cc958fe841e452a1b0.jpg)
Image: freeeco.com
Risks of Trading Options on Margin
Margin calls: If the value of the underlying asset moves significantly against the trader’s position, the brokerage may issue a margin call, requiring the trader to deposit additional funds or liquidate positions to meet the minimum margin requirement.
Unlimited Loss Potential: Unlike traditional stock trading, losses in options trading are not limited to the initial investment. Traders can lose more than their invested capital when trading on margin.
Volatility Risk: Options prices fluctuate rapidly due to market volatility, which can magnify potential losses for margin traders.
Options Trading Margin Requirements
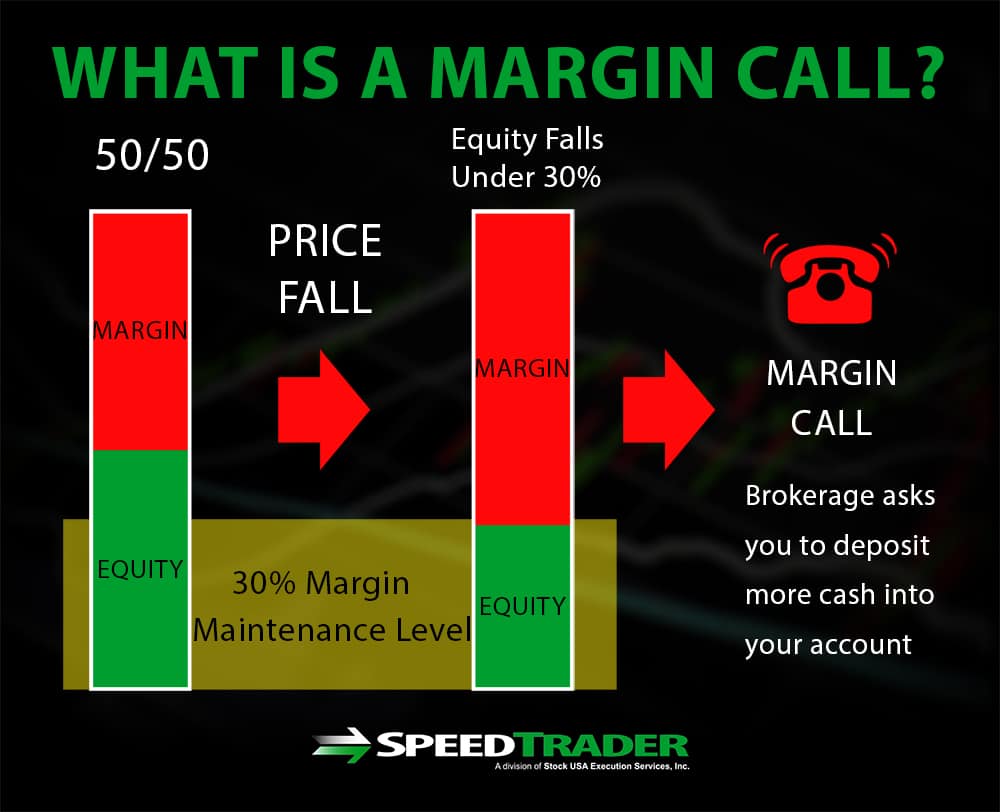
Image: speedtrader.com
Conclusion
Options trading margin requirements are essential safeguards in the high-stakes game of options trading. By understanding the mechanisms and risks associated with margin trading, traders can harness the potential benefits while mitigating the inherent vulnerabilities. Whether you’re a seasoned pro or a novice venturing into the world of options, comprehending margin requirements is paramount to navigating the complex and rewarding landscape of options trading.






