Introduction
In the high-stakes world of options trading, margin plays a pivotal role. This form of collateral enables traders to amplify their purchasing power, allowing them to control a larger position with less capital outlay. However, with great potential comes great responsibility, as margin can also magnify both profits and losses. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of margin on option trading, empowering traders with the knowledge to navigate this complex financial landscape effectively.
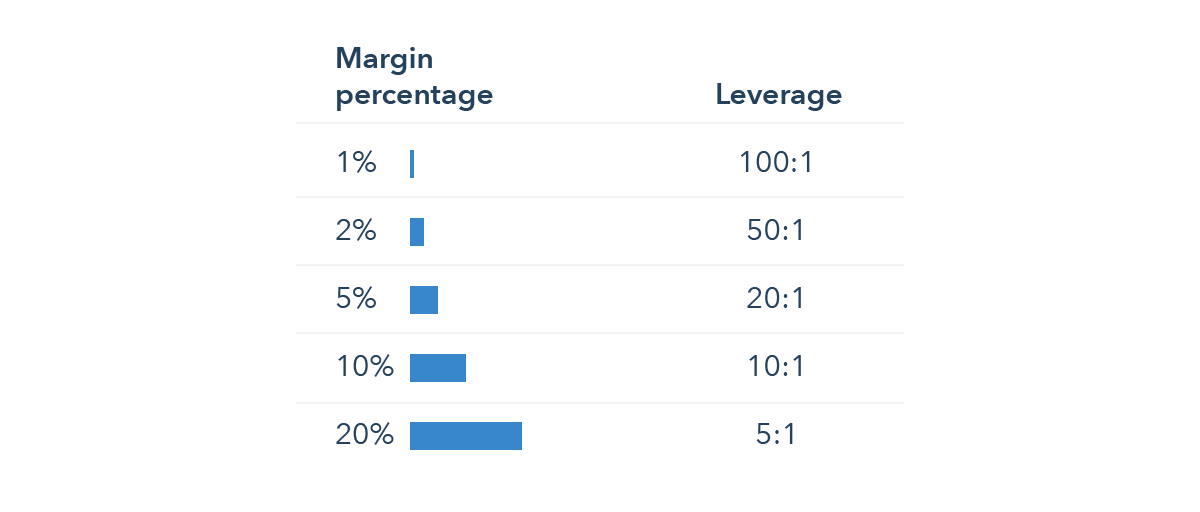
Image: www.ig.com
Understanding Margin: A Primer
Margin is a type of loan provided by a broker to facilitate option trades. It allows traders to leverage their existing capital to potentially amplify returns. This is achieved by borrowing money from the broker and using it in combination with their own funds to purchase options contracts.
The Mechanics of Margin Trading
When trading options on margin, the trader is essentially entering into a collateral agreement with the broker. The options contracts themselves serve as collateral, while the margin account acts as a placeholder for the borrowed funds. The broker sets margin requirements, specifying the minimum amount of equity that must be maintained in the margin account to cover potential losses.
Benefits of Margin Trading
- Increased Leverage: Margin trading enhances purchasing power, enabling traders to control a larger position with smaller capital. This can potentially lead to higher returns.
- Greater Flexibility: Margin provides traders with increased flexibility, allowing them to capitalize on opportunities that may not otherwise be available.
- Diversification: Margin trading can facilitate diversification by enabling traders to spread their risk across different options contracts.

Image: www.youtube.com
Risks of Margin Trading
- Magnified Losses: While margin can magnify potential profits, it can also magnify losses. If the value of the options contracts falls below a certain threshold, the trader may be required to add more funds to the margin account or risk having their positions liquidated.
- Margin Calls: Brokers can issue margin calls when the value of the options contracts drops below the margin requirements. This obligates the trader to contribute additional funds within a specified timeframe.
- Interest Charges:Margin loans typically accrue interest charges, which can erode profits over time.
Key Considerations for Margin Trading
- Risk Tolerance: Only engage in margin trading if you have a high risk tolerance and understand the potential consequences.
- Market Analysis: Thoroughly research and analyze market conditions before entering into margin trades.
- Margin Requirements: Understand the margin requirements set by your broker and ensure that you can meet them consistently.
- Exit Strategies: Have a clear exit strategy in place that outlines your maximum loss tolerance and trading targets.
- Margin Monitoring: Monitor your margin account regularly to ensure that you are meeting margin requirements and mitigating risks.
Recent Trends and Developments
- Increased Regulation: Regulators are implementing tighter controls and requirements on margin trading to minimize excessive leverage.
- Advanced Risk Management Tools: Brokers are developing sophisticated risk management tools to assist traders in monitoring and managing their margin exposure.
- Educational Initiatives: Exchanges and brokerage firms are promoting educational initiatives to increase awareness and understanding of margin trading.
Margin On Option Trading
Image: blog.injective.com
Conclusion
Margin trading is a powerful tool that can enhance the potential returns and flexibility of options trading. However, it is crucial to understand the associated risks and proceed with caution. By following the guidelines outlined in this comprehensive guide, traders can navigate the complexities of margin trading and make informed decisions that align with their financial goals. To further explore this topic, consider consulting reputable resources and consulting with a financial advisor or experienced options trader.






