In the realm of financial markets, options trading stands out as a versatile tool that grants traders with fascinating opportunities to shape their portfolio strategies. Whether it’s the allure of potentially exponential returns or the desire to hedge against risks, options offer a potent blend of flexibility and risk management that has captivated traders for decades. At the core of this vast landscape lies a fundamental distinction: trading options long versus short. Understanding the intricacies of these polar opposites is paramount in mastering the art of options trading.
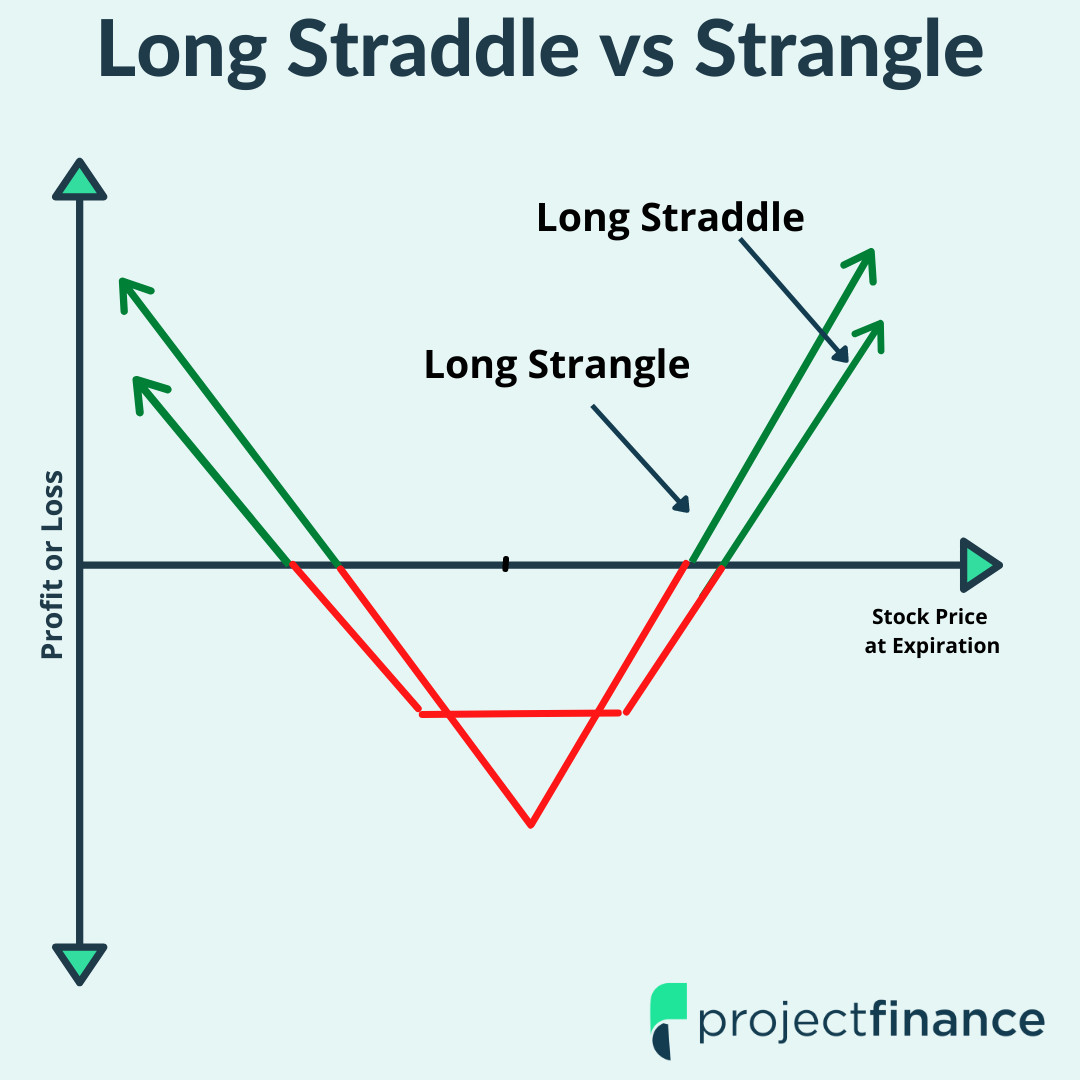
Image: www.projectfinance.com
Diving into the Long Side: Rights and Responsibilities
Traders who engage in the “long” side of options trading acquire the right, but not the obligation, to purchase (in the case of a call option) or sell (in the case of a put option) an underlying asset at a predetermined price on or before a specified expiration date. Think of it as having a “keys in hand” approach, where you possess the prerogative to unlock the potential of the underlying asset’s price fluctuations. This alluring opportunity comes with a premium payment, which represents the price for acquiring such rights.
Unveiling the Short Side: Obligations and Potential Rewards
On the flip side of the spectrum lies the “short” side of options trading. Here, traders assume the obligation to fulfill the terms of an options contract should the holder exercise their right. In a call option scenario, this translates to selling the underlying asset at the strike price, while in a put option scenario, it entails buying the underlying asset at the strike price. Taking the short stance involves receiving a premium, reflecting the compensation for assuming this commitment.
Striking a Balance: The Art of Long and Short
Navigating the options market effectively demands a delicate balance between the long and short sides. Each perspective presents unique advantages and potential pitfalls, and it’s by comprehending the intricacies of both that traders unlock the true power of this versatile financial instrument.

Image: www.ispag.org
Advantages of Going Long:
-
Unlimited Profit Potential: With call options, the profit potential is boundless, capped only by the underlying asset’s ability to surge in value.
-
Leverage: Options trading offers an inherent form of leverage, amplifying both potential profits and losses.
-
Hedging Downside Risk: Put options provide a tactical defense against potential declines in the underlying asset’s price.
Disadvantages of Going Long:
-
Limited Timeframe: Options have a finite lifespan, which means the profit window is constrained by the option’s expiration date.
-
Premium Cost: The premium paid upfront represents a non-refundable investment, potentially eroding profits if the underlying asset’s price movement falls short of expectations.
Advantages of Going Short:
-
Premium Income: Selling options (going short) generates immediate premium income, which can offset potential losses if the option expires worthless.
-
Defined Risk: Unlike long options, short options have a capped loss potential, limited to the premium received.
-
Income Generation: Even in declining markets, writing (selling) put options can offer a steady stream of income.
Disadvantages of Going Short:
-
Unlimited Loss Potential: While the profit potential for long options is capped, the loss potential for short options is unbounded.
-
Margin Requirements: Short options often require traders to maintain higher margin balances, potentially affecting other trading activities.
-
Assignment Risk: In the case of a call option, short sellers face the obligation to deliver the underlying asset if assigned.
Options Trading Long Vs Short
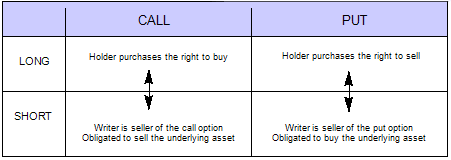
Image: help.tradestation.com
Conclusion: Empowering Traders with Informed Choices
Venturing into the realm of options trading unlocks a world of possibilities for both seasoned veterans and aspiring traders seeking to enhance their portfolio strategies. Understanding the distinct nuances of long versus short options empowers traders with the knowledge to tailor their approach based on individual risk tolerance, time horizons, and financial goals. By embracing the opportunities and navigating the pitfalls inherent in each perspective, traders can harness the full potential of options trading and strive towards successful outcomes in the dynamic financial markets.






