Conquering the Realm of Option Trading: What It Entails
Option trading has emerged as a captivating realm where traders venture to amplify their potential profits by harnessing the power of options contracts. Options, akin to financial instruments, bestow the right—but not the obligation—to buy or sell a specific asset at a predetermined price, offering traders an array of strategic possibilities.
Image: blog.shoonya.com
Understanding the intricacies of option trading is paramount to navigating this complex landscape. At its core, an option contract represents a wager on the future price trajectory of an underlying asset, whether a stock, commodity, index, or currency. The two primary types of options are calls, which confer the right to purchase the underlying asset, and puts, which empower the holder to sell the underlying asset.
Delving into the History and Significance of Option Trading
The roots of option trading can be traced back to the 17th century when agricultural merchants employed options to hedge against price volatility in their commodities. Over time, options have evolved into sophisticated financial tools, gracing the portfolios of astute investors and traders alike.
The advent of standardized options in the 1970s revolutionized the market, enabling the creation of the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE). This centralized platform fostered transparency and standardization, propelling option trading into the mainstream.
Mastering the Mechanics of Option Trading: Options Terminologies and Concepts
To fully grasp option trading, it is imperative to familiarize oneself with its key terminologies and concepts.
- Call option: Grants the holder the right to buy the underlying asset at the strike price on or before the expiration date.
- Put option: Entitles the holder to sell the underlying asset at the strike price on or before the expiration date.
- Strike price: The predetermined price at which the underlying asset can be bought or sold.
- Expiration date: The day on which the option contract expires and becomes worthless.
- Premium: The price paid by the option buyer to acquire the contract.
- Intrinsic value: The difference between the current price of the underlying asset and the strike price (for calls) or the strike price minus the current price of the underlying asset (for puts).
- Time value: The portion of the option premium that reflects the remaining time until expiration.
Exploring the Latest Trends and Developments in Option Trading
The option market is a dynamic and ever-evolving landscape, influenced by macroeconomic factors, geopolitical events, and technological advancements. Keeping abreast of the latest trends and developments is crucial for astute traders.
The rise of electronic trading platforms has streamlined option trading, reducing transaction costs and enhancing market liquidity. Moreover, the advent of complex option strategies, such as multi-leg spreads, has expanded the opportunities for sophisticated traders.
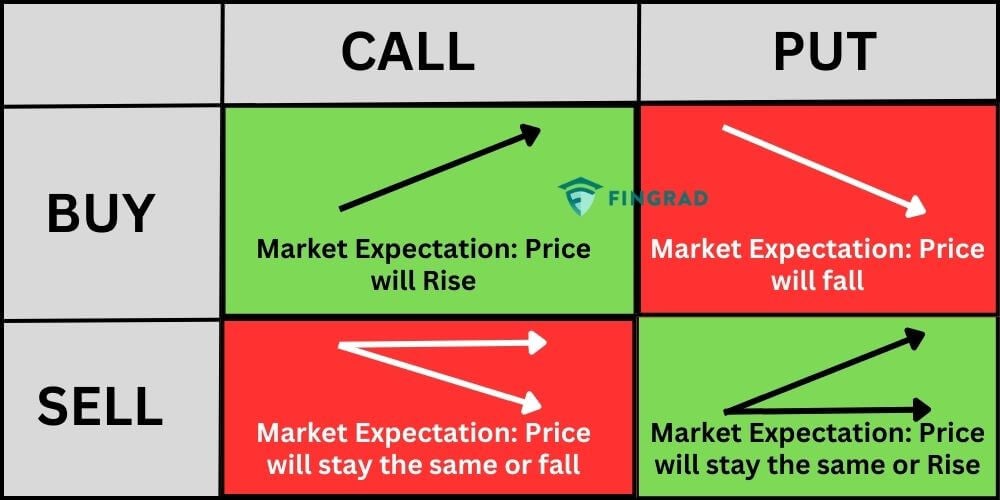
Image: tradebrains.in
Expert Advice and Tips for Navigating the Option Market
Navigating the option market effectively requires a blend of knowledge, experience, and meticulous planning.
1. Define clear trading objectives and risk tolerance. Determine your financial goals and ascertain the level of risk you are prepared to accept.
2. Conduct thorough research. Analyze underlying assets, market trends, and option pricing models to make informed decisions.
3. Manage risk effectively. Employ stop-loss orders, position sizing, and hedging strategies to mitigate potential losses.
4. Exercise prudence in premium payments. The premium represents a significant cost in option trading; assess the potential reward versus risk before purchasing contracts.
5. Leverage technology to enhance trading. Utilize trading platforms that offer charting tools, real-time data, and risk management features.
Common FAQs Related to Option Trading
- What is the difference between a call and a put option?
- A call option bestows the right to buy, while a put option confers the right to sell the underlying asset.
- What factors affect option prices?
- The price of the underlying asset, time to expiration, volatility, interest rates, and supply and demand influence option prices.
- Can I lose money in option trading?
- Yes, option trading involves risk, and it is possible to lose money. It is crucial to manage risk effectively and trade within your financial means.
- Do I need to own the underlying asset to trade options?
- No, you do not need to own the underlying asset to trade options. Options provide a way to speculate on the price movements of the underlying asset without owning it.
Option Trading Means
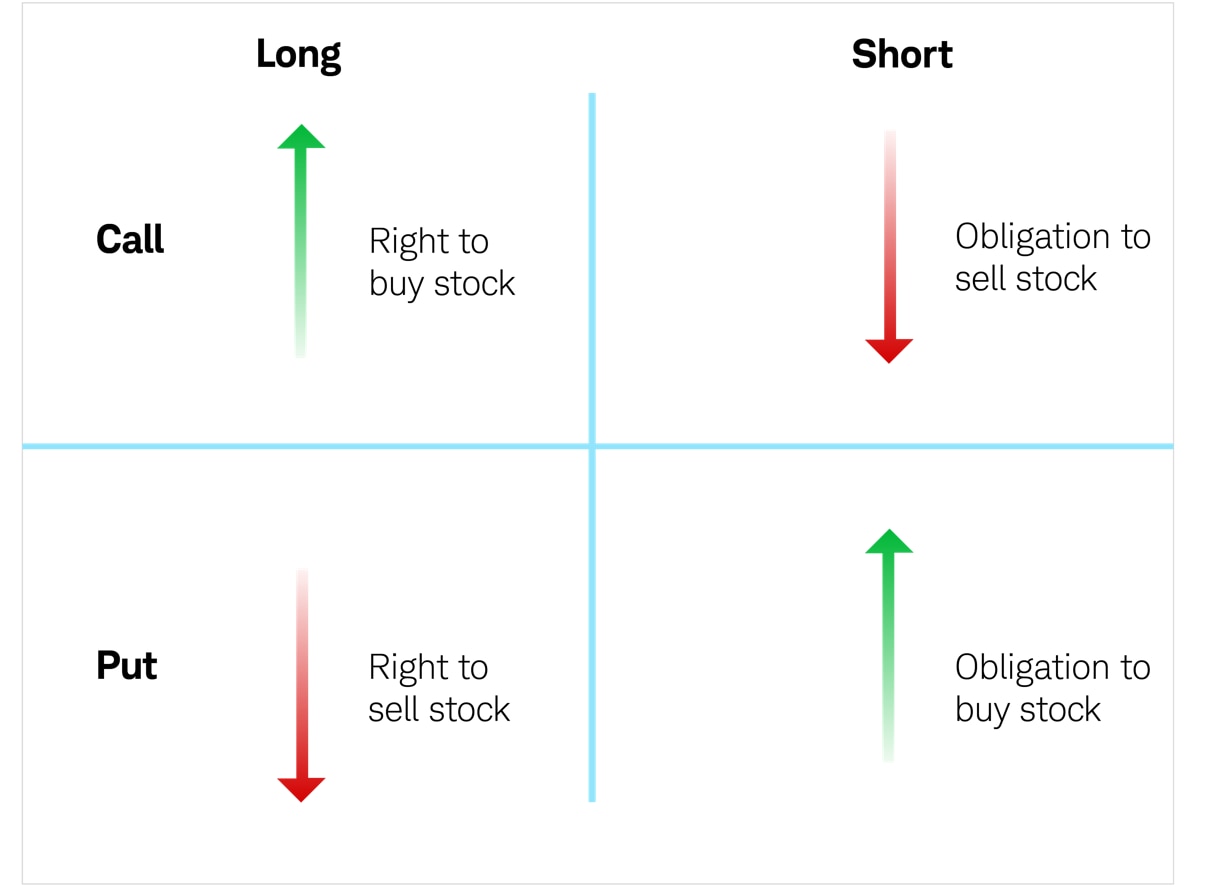
Image: www.schwab.com
Conclusion: Embracing the Potential of Option Trading
Option trading presents a captivating avenue for traders seeking to amplify their profit potential while managing risk. By comprehending the intricacies of options and incorporating the expert advice shared, you can embark on your path in the exhilarating realm of option trading. Whether you are a seasoned veteran or just dipping your toes into the waters, the allure of option trading awaits your curious mind.






