Option trading involves navigating the intricacies of risk management. Understanding the concept of liquidation and its implications is essential for traders seeking to preserve their capital and maximize their profits.
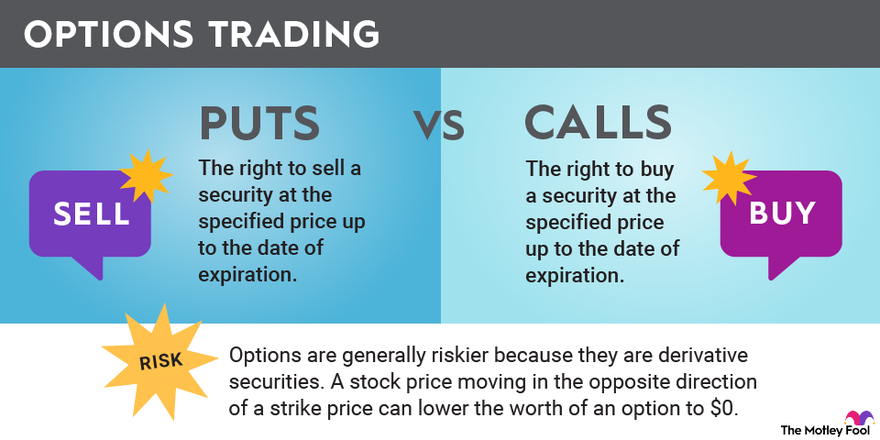
Image: www.fool.com
Definition and Importance of Liquidation in Option Trading
Liquidation, in the context of option trading, refers to the closing out of an open option position by buying or selling an equal and opposite contract. It effectively releases the trader from their contractual obligation and realizes the profit or loss associated with the trade.
Comprehending liquidation is paramount for several reasons. It allows traders to:
- Lock in profits: Upon favorable market conditions, liquidation enables traders to secure their gains before the position swings against them.
- Manage losses: In unfavorable market scenarios, liquidation serves as a risk-management tool to limit potential losses.
- Realize gains or losses: Traders can close out their positions to realize profits or accept losses and move on to the next opportunity.
Types of Liquidation in Option Trading
Different liquidation strategies exist, each tailored to specific situations. Let’s explore the most common approaches:
1. Market Order Liquidation
A market order is executed immediately at the prevailing market price. This method offers speed and convenience but can result in price slippage, especially during volatile market conditions.

Image: speedtrader.com
2. Limit Order Liquidation
A limit order is placed at a specified price, allowing traders to have better control over the execution price. However, this method carries the risk of remaining unfilled if the market price moves significantly away from the preset limit.
3. Stop Order Liquidation
A stop order triggers an automatic liquidation at a predetermined price. This strategy is typically used to lock in profits or limit losses upon reaching a certain market level.
4. Trailing Stop Order Liquidation
A trailing stop order adjusts its trigger price dynamically, following the movement of the underlying asset. This method ensures that traders remain profitable as long as the trend continues in their favor.
Factors to Consider for Effective Liquidation
Deciding when and how to liquidate an option position requires careful consideration of various factors:
1. Market Conditions
Volatility, market sentiment, and overall economic factors can significantly impact liquidation decisions. In volatile markets, traders may opt for market orders to ensure a timely exit, while in stable markets, limit orders can offer more precise execution.
2. Time Sensitive Contracts
Short-term options, such as weekly or daily contracts, demand timely liquidation due to their rapid decay in value. Longer-term options provide more flexibility and allow traders to wait for favorable market conditions.
3. Risk Tolerance
Every trader has a unique risk appetite that should influence liquidation decisions. Some traders prioritize profit preservation, while others are willing to take on more risk in pursuit of higher rewards.
4. Trading Plan
Developing a structured trading plan that outlines entry and exit strategies is crucial. This plan provides a disciplined approach to handling market fluctuations and emotions.
Option Trading Liquidation

Image: www.pinterest.com
Conclusion
Liquidation is an indispensable component of successful option trading. By understanding the types of liquidation, factors to consider, and implementing a robust trading plan, traders can effectively manage risk, capture profits, and navigate the complexities of option market trading. Remember to approach liquidation with a balanced blend of knowledge, strategy, and risk assessment to maximize your trading outcomes.






