Introduction
Options, versatile financial instruments that grant investors the right but not the obligation to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specified price on a specific date, are essential tools for managing risk and generating returns in the financial markets. To effectively navigate the intricate world of options trading, it is paramount to understand the concept of option Greeks, a set of metrics that measure an option’s sensitivity to various underlying factors. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of option Greeks, empowering traders with the knowledge to make informed decisions and maximize their trading outcomes.
![Options Greeks Cheat Sheet [FREE Download] - HowToTrade](https://howtotrade.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/options-greeks-cheat-sheet-2048x1448.png)
Image: howtotrade.com
Delta: A Measure of Price Sensitivity
Delta, one of the fundamental Greeks, quantifies the change in an option’s value relative to a change in the underlying asset’s price. It indicates the number of shares of the underlying asset that an option controls. A positive delta for a call option suggests that its value will increase as the underlying asset price rises, while a negative delta for a put option implies the opposite. The delta of an option changes dynamically throughout its life, reflecting the non-linear relationship between option value and underlying asset price. Understanding delta is crucial for traders to assess their potential profit or loss from changes in the underlying asset’s price.
Gamma: Sensitivity to Delta
Gamma, considered the second-order derivative of an option’s value, measures the rate of change in delta with respect to the underlying asset’s price. It indicates the sensitivity of the delta to changes in the underlying asset’s price. A positive gamma implies that the delta of the option is increasing at an increasing rate, suggesting the option’s price is becoming more sensitive to changes in the underlying asset’s price. Conversely, a negative gamma indicates that the delta of the option is decreasing at an increasing rate, suggesting the option’s price is becoming less sensitive to changes in the underlying asset’s price. Traders can use gamma to gauge the potential acceleration or deceleration of an option’s delta, providing insights into its responsiveness to market conditions.
Theta: Time Decay
Theta measures the rate of decay in an option’s value as time passes. The time value of an option, representing the premium paid for the option’s right but not obligation, erodes over time as the option approaches its expiration date. Theta quantifies this time decay, indicating the amount by which the option’s value decreases each day. A negative theta implies that the option is losing value over time, emphasizing the importance of careful timing in options trading. Traders can use theta to manage their risk by assessing the impact of time decay on their option positions.
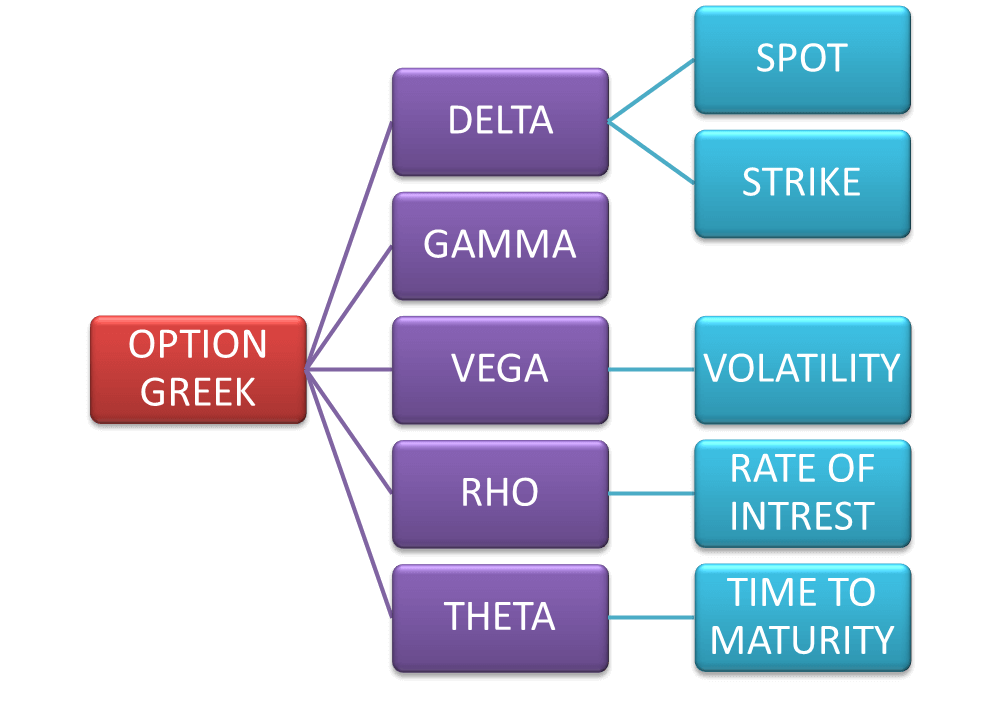
Image: tradingfuel.com
Vega: Volatility Sensitivity
Vega measures an option’s sensitivity to changes in the implied volatility of the underlying asset. Implied volatility, a measure of expected price fluctuations, is a critical determinant of option pricing. Vega quantifies the change in an option’s value for a given change in implied volatility. A positive vega implies that the option’s value will increase as implied volatility increases, while a negative vega indicates the opposite. Traders can use vega to gauge the impact of volatility changes on their option positions, allowing them to make informed decisions in volatile market conditions.
Rho: Interest Rate Sensitivity
Rho measures an option’s sensitivity to changes in the risk-free interest rate. Interest rates play a significant role in option valuation, as they affect the time value of money. Rho quantifies the change in an option’s value for a given change in the risk-free interest rate. A positive rho implies that the option’s value will increase as interest rates increase, while a negative rho indicates the opposite. Traders can use rho to assess the impact of interest rate changes on their option positions, enabling them to adjust their strategies accordingly.
Option Trading Greeks Pdf

Image: www.youtube.com
Conclusion
Option Greeks, a comprehensive suite of metrics, provide invaluable insights into the dynamics of option pricing and risk. By understanding the significance of each Greek, traders can make informed decisions, optimize their trading strategies, and navigate the intricate world of options trading with greater confidence and potential for success. This guide serves as a valuable resource, empowering traders with the knowledge and understanding necessary to unlock the full potential of option Greeks and maximize their trading outcomes.






