A Dive into the Intricacies for Informed Decision-Making
As an avid option trader, I’ve often encountered a labyrinth of queries and uncertainties surrounding the tax implications of my endeavors. Embarking on this exploration, I discovered a fascinating tapestry of rules and regulations that shape the taxation of option trading income. Let’s navigate these intricacies together, ensuring you’re equipped with the knowledge to make informed decisions that maximize your returns and minimize your tax liability.

Image: www.daytrading.com
General Taxation Principles for Option Trading Income
Options, financial instruments that grant the buyer the right but not the obligation to buy (call option) or sell (put option) an underlying asset at a predefined price, are classified as capital assets. Gains or losses from options trading are taxed as capital gains or losses, typically at more favorable rates compared to ordinary income taxes. However, the tax treatment of option premiums may vary depending on the specific circumstances.
Short-Term vs. Long-Term Gains
The holding period of an option plays a crucial role in determining its tax classification. Options held for less than one year (short-term) are taxed at ordinary income tax rates, while those held for one year or more (long-term) qualify for preferential capital gains tax rates. This distinction emphasizes the importance of strategic planning to optimize tax efficiency.
Exercise, Sale, or Expiration of Options
When an option is exercised or sold, the difference between the sale price and the premium paid is considered a capital gain or loss. If an option expires unexercised, the premium paid is treated as a capital loss. It’s essential to document all transaction details, including premiums paid, exercise prices, and expiration dates, to accurately assess your tax liability.
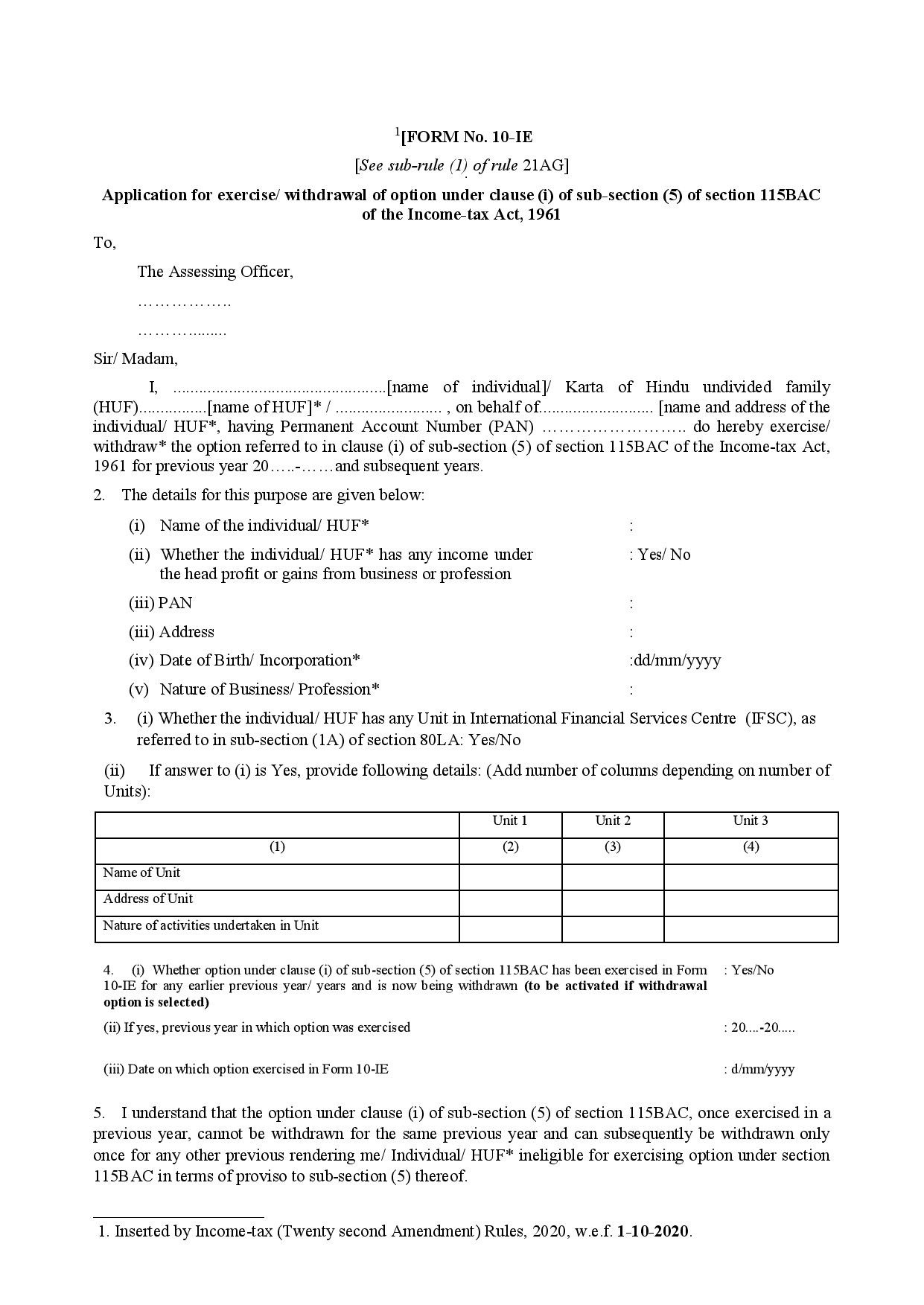
Image: www.itaxxsoftware.com
Wash Sale Rules
Wash sale rules prevent taxpayers from artificially creating capital losses by selling and repurchasing substantially identical options. If a loss-making option is sold and a replacement option is acquired within 30 days, the loss is disallowed for tax purposes. This rule encourages genuine investment decisions and prevents tax avoidance strategies.
Mark-to-Market (MTM) Accounting
Certain traders who meet specific criteria may opt for MTM accounting for their options strategies. Under MTM, unrealized gains or losses on open option positions are recognized annually for tax purposes. This method allows traders to capture year-end tax benefits but also exposes them to potential tax implications in subsequent years.
Tips and Expert Advice for Navigating the Tax Maze
- Stay organized and meticulously track all option transactions, including premiums paid, exercise prices, and expiration dates.
- Consult with a qualified tax professional to tailor a tax strategy specific to your individual circumstances.
- Consider the holding period of options to optimize your tax efficiency and avoid short-term capital gains tax rates.
- Understand and comply with wash sale rules to avoid disallowance of capital losses.
- Explore MTM accounting if you meet the criteria and are comfortable with its implications.
FAQ on Option Trading Income Taxes
Q: How are premiums paid for options taxed?
A: Premiums are typically not taxed upon payment. They become part of your cost basis when calculating capital gains or losses upon exercise, sale, or expiration of the option.
Q: Are unrealized gains on open option positions taxable?
A: Under the MTM accounting method, unrealized gains are recognized for tax purposes. However, this is not the case for traditional traders who use the cash accounting method.
Q: What happens if I mistakenly sell a long-term option at a loss and buy a replacement within 30 days?
A: The loss will be disallowed under wash sale rules. It’s crucial to be aware of this rule to avoid unintended tax consequences.
Income Tax On Option Trading

Image: dailytrademantra.com
Conclusion
Understanding the income tax implications of option trading empowers you to make informed decisions that align with your financial goals. By navigating the complexities discussed in this article, you can maximize your tax efficiency while actively participating in the dynamic world of option trading.
If you’re intrigued by the intricacies of option trading and taxation, I encourage you to delve deeper into the subject. The wealth of knowledge available empowers you to confidently conquer the challenges and reap the rewards of this multifaceted market.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be construed as professional financial or tax advice. Always consult with a qualified financial or tax professional before making any investment decisions or implementing any tax strategies.







