Unveiling the Power of Puts in Options Trading
When venturing into the world of options trading, understanding the intricacies of different options types becomes paramount for achieving trading success. Among the array of options contracts, “puts” hold a significant place, offering traders unique opportunities and risk management strategies. This comprehensive guide delves into the depths of put options, unraveling their definition, mechanics, uses, and key considerations for effective implementation in your trading endeavors.

Image: www.youtube.com
Defining the Essence of Puts
In the realm of options trading, a put option grants the holder the right, but not the obligation, to sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price (known as the strike price) on or before a specific date (the expiration date). In essence, a put option provides the holder with the potential to profit from a decline in the price of the underlying asset. It is often utilized as a hedging mechanism against downside risk or as a speculative tool to capture price movements in the desired direction.
Unraveling the Unique Traits of Puts
Understanding the distinguishing characteristics of put options is crucial for successful trading:
- Right to Sell: Put options confer the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price, not an obligation. Holders can choose to exercise this right at any time before the expiration date or let it expire worthless if the market moves against their favor.
- Underlying Asset: Put options derive their value from the performance of an underlying asset, which can be a stock, ETF, commodity, or other financial instrument.
- Strike Price: This predetermined price represents the level at which the holder can sell the underlying asset if they choose to exercise the option.
- Expiration Date: Put options have a finite lifespan, and the expiration date marks the last day the option can be exercised.
- Premium: When purchasing a put option, traders pay a premium, which represents the cost of acquiring the right to sell the underlying asset.
Exploring the Mechanics of Put Trading
The mechanics of trading put options involve two primary transactions:
- Buying a Put: Buying a put option conveys the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price before the expiration date. This strategy is commonly employed when traders anticipate a decline in the underlying asset’s price.
- Selling a Put: Selling a put option obligates the seller to buy the underlying asset at the strike price if the option is exercised by the holder. This strategy is often used when traders expect the underlying asset’s price to remain stable or rise.
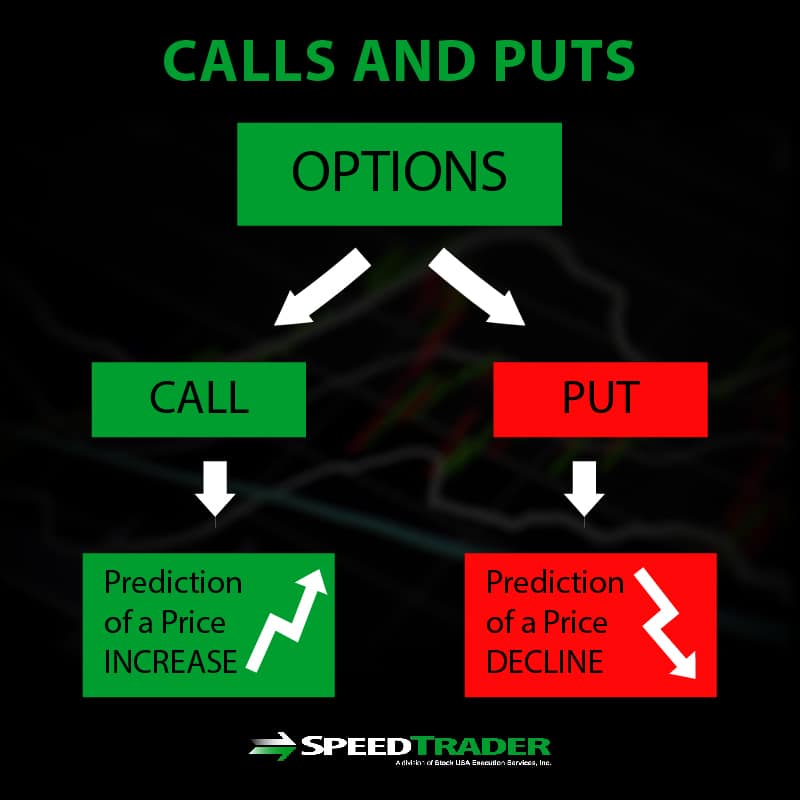
Image: japaneseclass.jp
Unveiling the Diverse Applications of Puts
The versatility of put options extends beyond hedging and speculation, encompassing a wide range of trading strategies:
- Hedging Against Risk: Put options serve as a defensive tool against potential losses in existing positions. By buying a put option on an underlying asset, traders can limit their exposure to downside risk in case of adverse price movements.
- Speculating on Price Declines: Traders can speculate on falling prices by buying put options. If the underlying asset’s price declines below the strike price, the put option gains value, offering profit potential.
- Income Generation: Selling put options can generate income if the underlying asset’s price remains stable or rises. However, this strategy involves the obligation to buy the asset if the option is exercised.
- Collar Strategies: Put options can be combined with other options, such as call options, to create collar strategies. These strategies aim to limit both potential profits and losses while still benefiting from price movements within a predefined range.
Navigating the Key Considerations for Effective Put Trading
To maximize the potential of put options, traders must carefully consider the following factors:
- Underlying Asset Analysis: Thoroughly research and analyze the underlying asset’s historical performance, industry trends, and economic factors to make informed trading decisions.
- Strike Price Selection: Choosing the right strike price is crucial. Consider the current market price, volatility, and your trading objectives.
- Expiration Date Selection: Determine the appropriate expiration date based on your trading strategy and market outlook.
- Market Volatility: Volatility plays a significant role in option pricing. Higher volatility leads to higher option premiums and greater potential for profit but also increased risk.
- Risk Management: Options trading involves inherent risk. Employ proper risk management techniques, such as setting stop-loss orders and limiting position size, to minimize potential losses.
In Options Trading What Is A Put
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/10OptionsStrategiesToKnow-02_2-8c2ed26c672f48daaea4185edd149332.png)
Image: scuba-dawgs.com
Conclusion: Unleashing the Power of Puts in Your Trading
In options trading, puts offer a versatile tool for managing risk, speculating on price declines, and generating income. By understanding their unique characteristics, mechanics, applications, and key considerations, traders can effectively incorporate puts into their trading strategies and harness their potential to enhance their trading outcomes. Remember to conduct thorough research, approach trading with a well-defined plan, and prioritize risk management to navigate the complexities of the options market with greater confidence.







