Options trading is a type of financial contract that gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price on or before a certain date. Options contracts are often used as a way to hedge against risk or to speculate on the future price of an asset.
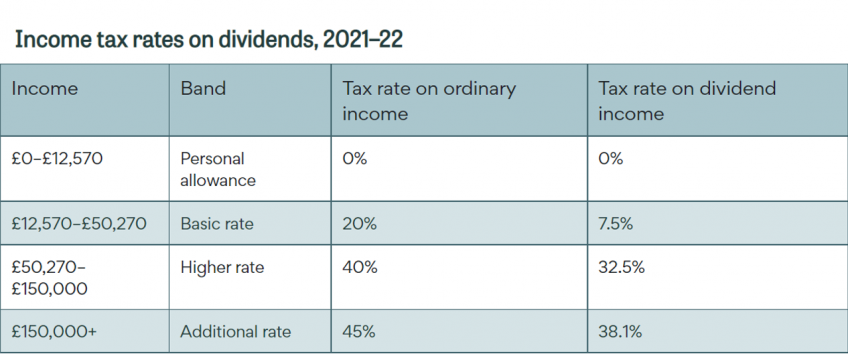
Image: ifs.org.uk
When you trade options, you will be responsible for paying taxes on any profits you make. The amount of tax you will pay will depend on your tax bracket and the type of options contract you traded.
Short-Term vs. Long-Term Options Trading
The tax treatment of options trading depends on whether the options contract is considered a short-term or a long-term investment. A short-term options contract is one that is held for less than one year. A long-term options contract is one that is held for more than one year.
Profits from short-term options trading are taxed as ordinary income. This means that you will pay your regular income tax rate on any profits you make. Profits from long-term options trading are taxed at a lower capital gains rate. The capital gains rate depends on your tax bracket. The maximum capital gains rate is 20%.
Types of Options Contracts
There are two main types of options contracts: calls and puts. A call option gives the buyer the right to buy an underlying asset at a predetermined price on or before a certain date. A put option gives the buyer the right to sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price on or before a certain date.
The tax treatment of call and put options is the same. Any profits you make from trading them will be taxed either as ordinary income or capital gains, depending on the holding period.
Covered vs. Naked Options Trading
Another factor that can affect the tax treatment of options trading is whether the option is covered or naked. A covered option is one that is backed by an underlying asset. A naked option is one that is not backed by an underlying asset.
Profits from trading covered options are taxed as capital gains. Profits from trading naked options are taxed as ordinary income. This is because naked options are considered to be a type of speculation.
Image: www.fishbowlapp.com
FAQs
Q: How do I calculate the amount of tax I will pay on options trading profits?
A: The amount of tax you will pay on options trading profits depends on your tax bracket and the type of options contract you traded.
Q: What are the tax consequences of exercising an options contract?
A: When you exercise an options contract, you will be responsible for paying taxes on any profit you make. The amount of tax you will pay will depend on your tax bracket and the type of options contract you traded.
Q: Can I deduct losses from options trading on my taxes?
A: Yes, you can deduct losses from options trading on your taxes. However, the amount of the loss that you can deduct is limited to the amount of gain that you have made from options trading in the same year.
How Much Tax Is Deducted From Options Trading

Image: www.coursehero.com
Conclusion
Options trading can be a complex and rewarding investment strategy. However, it is important to be aware of the tax implications of options trading before you get started. If you are not sure how to calculate the amount of tax you will pay on options trading profits, you should consult with a tax advisor.
Are you interested in learning more about options trading? You can find more information on our website or by contacting us.






