In the world of financial markets, futures and options are two of the most commonly traded derivatives. Both derivatives allow investors to speculate on the future price of an underlying asset, but their structures and risks are very different. In this article, we will explain the key differences between future and option trading, and how to choose the right strategy for your investment objectives.
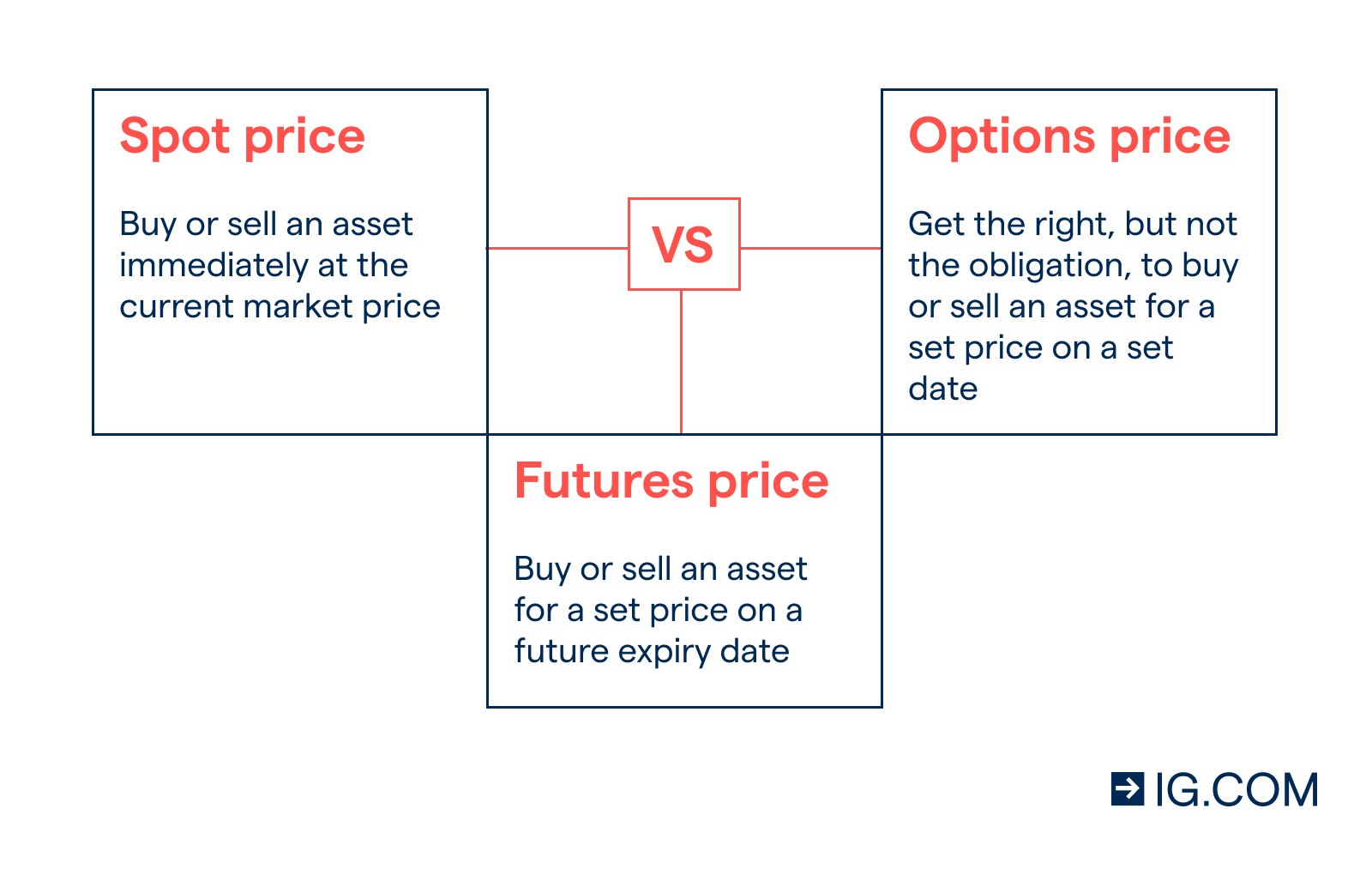
Image: www.slidemake.com
Futures Contracts
A future contract is a legally binding agreement to buy or sell a specific amount of an underlying asset at a predetermined price on a specific date in the future. When you enter into a futures contract, you are obligated to complete the transaction on the specified date, regardless of whether or not the underlying asset’s price has changed.
Futures contracts are traded on futures exchanges, and they are standardized contracts, meaning that the terms of the contract are set by the exchange and cannot be altered. The underlying assets for futures contracts can include commodities such as oil, gas, and wheat, as well as financial instruments such as stocks and bonds.
The main advantage of futures contracts is that they provide investors with a high degree of leverage. This means that investors can control a large amount of the underlying asset with a relatively small amount of capital. However, futures contracts are also more risky than options because investors are obligated to complete the transaction, even if the underlying asset’s price moves against them.
Option Contracts
An option contract is a contract that gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specified price on or before a specified date. Unlike futures contracts, option contracts are not standardized, and the terms of the contract can be customized to meet the specific needs of the buyer and seller.
The underlying assets for option contracts can include anything from stocks and bonds to commodities and currencies. The most common types of option contracts are call options and put options. Call options give the buyer the right to buy the underlying asset at the specified price, while put options give the buyer the right to sell the underlying asset at the specified price.
The main advantage of option contracts is that they give investors the ability to limit their risk. This is because investors can choose to exercise the option only if the underlying asset’s price moves in their favor. However, option contracts are also more expensive than futures contracts, and they have a limited life span.

Image: rmoneyindia.com
Difference Between Future And Option Trading
https://youtube.com/watch?v=6ZlWqeRqQG4
Which Type of Derivative is Right for You?
The best way to decide which type of derivative is right for you is to consider your investment objectives and risk tolerance. If you are looking for a high degree of leverage and are willing to accept the risk of being obligated to complete the transaction, then futures contracts may be a good option for you. However, if you are looking to limit your risk and are willing to pay a higher price, then option contracts may be a better choice.
It is important to note that futures and options are complex financial instruments, and they should only be traded by investors who understand the risks involved. If you are new to derivatives, it is recommended that you consult with a financial advisor before trading anything.






