Futures trading, a sophisticated realm of financial markets, invites investors seeking leverage and risk management tools. Among its many facets, options margin stands as a crucial cornerstone. This article delves into the intricacies of futures trading options margin, shedding light on its advantages, complexities, and how it influences market dynamics.
Image: blog.injective.com
Defining Futures Trading Options Margin
Options margin refers to the initial deposit required by an exchange to hold a futures options contract. Options contracts grant the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) a specific underlying asset, such as a stock or commodity, at a predetermined price and expiration date. Unlike futures contracts, which obligate buyers to purchase or sellers to deliver the underlying asset, options provide flexibility and the potential for speculative profits or risk hedging.
Advantages of Options Margin
Options margin offers several advantages to traders:
- Leverage: Margins allow traders to control a substantial futures contract position with a relatively small initial investment, providing the potential for magnified returns.
- Risk Management: Options can serve as risk management tools in futures trading. For instance, investors can employ put options to hedge against downside market risks or call options to anticipate potential price appreciation.
- Flexibility: Options margin grants traders flexibility in executing various strategies, from hedging to speculation, allowing them to tailor positions to specific market conditions.
Complexities of Options Margin
Despite its advantages, options margin also requires careful consideration of several complexities:
- Margin Requirements: Exchanges set specific margin requirements for different futures options contracts, which vary based on factors such as underlying asset volatility and contract expiration date.
- Maintenance Margin: Traders must maintain a minimum margin level, known as maintenance margin, throughout the life of an options contract. Failure to meet margin calls can lead to position liquidations.
- Risk and Liability: Options trading involves inherent risk. Option buyers have limited risk to the premium paid, while option sellers face potentially unlimited losses if the underlying asset price moves against their position.
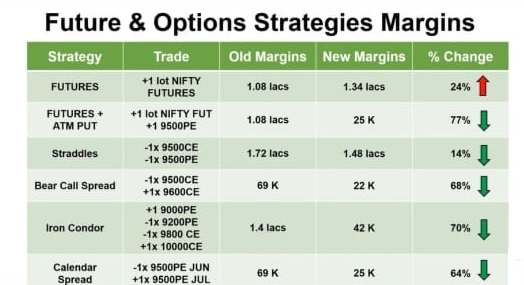
Image: www.theoptioncourse.com
Impact on Market Dynamics
Options margin significantly influences futures trading dynamics:
- Increased Liquidity: Options margin allows more traders to participate in futures markets, enhancing liquidity and depth in these markets.
- Price Discovery: The premiums paid for options provide valuable market information, aiding in price discovery and volatility estimation.
- Risk Absorption: Options absorb market volatility, mitigating its impact on futures prices.
Futures Trading Options Margin

Image: www.wallstreetmojo.com
Conclusion
Futures trading options margin is a powerful tool that can amplify trading outcomes and enhance risk management strategies. However, its complexities require thorough understanding and careful risk management. By leveraging options margin effectively, traders can maximize their opportunities while navigating the dynamic and volatile world of futures trading. It is imperative to consult regulatory and professional sources to gain a comprehensive understanding of margin requirements and market risks before engaging in futures trading.






