Introduction
The world of finance is vast and multifaceted, with a multitude of investment vehicles available to traders. Two popular derivatives that have gained significant traction are futures and options contracts, each with its unique characteristics and risk-return profiles. Understanding the differences between futures and options is crucial for investors seeking to optimize their trading strategies and make informed decisions.

Image: www.thetechedvocate.org
Definition and History
Futures Contracts
A futures contract is a standardized agreement to buy or sell a specific quantity of an underlying asset like a stock, commodity, currency, or bond at a predetermined price and date in the future. Futures contracts are traded on regulated exchanges, which set the contract specifications and provide a platform for buyers and sellers to connect.
Options Contracts
In contrast, an options contract grants the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specific price known as the strike price within a specified period. The buyer of an option has the option to exercise their right (but is not obligated to), while the seller of an option has the obligation to fulfill the contract if the buyer chooses to exercise.

Image: www.ifmcinstitute.com
Key Differences
1. Obligation vs. Optionality
The fundamental difference between futures and options lies in the obligation associated with each contract. In a futures contract, both parties are obligated to complete the transaction, while in an options contract, the buyer has the choice of exercising their right or not.
2. Settlement
Futures contracts are typically settled in cash, while options contracts can be settled either in cash or physical delivery of the underlying asset. In most cases, options buyers choose to close out their position by selling the option contract rather than taking delivery.
3. Margin Requirements
futures and options have different margin requirements based on the underlying asset involved and the type of contract. Margin acts as collateral to cover potential losses, and meeting margin requirements is crucial to maintain a trading position.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Futures Contracts
Advantages:
- High leverage potential
- Standardized contracts provide transparency
- Price discovery and hedging opportunities
Disadvantages:
- Obligation to fulfill the contract
- Potential for unlimited losses
- Margin calls and risk of liquidation
Options Contracts
Advantages:
- Limited/defined risk
- Optionality provides flexibility
- Potential for strategic income generation
Disadvantages:
- Time limited
- Premium cost may diminish value
- Complex to analyze and trade effectively
Conclusion
Futures and options are versatile trading instruments with distinct features, providing investors with varied risk-reward profiles. Futures contracts are suitable for traders seeking leverage and price discovery, while options offer more flexibility and limited risk. Understanding the nuances of each contract type is paramount for making informed investment decisions and achieving long-term trading success. Whether you’re an experienced trader or just starting in the world of derivatives, grasping the differences between futures and options is a crucial step toward navigating the financial markets.
Are you eager to delve deeper into the world of futures or options trading? Share your thoughts and questions in the comments section, and we’ll be glad to engage with you on this fascinating topic.
Futures Vs Option Trading
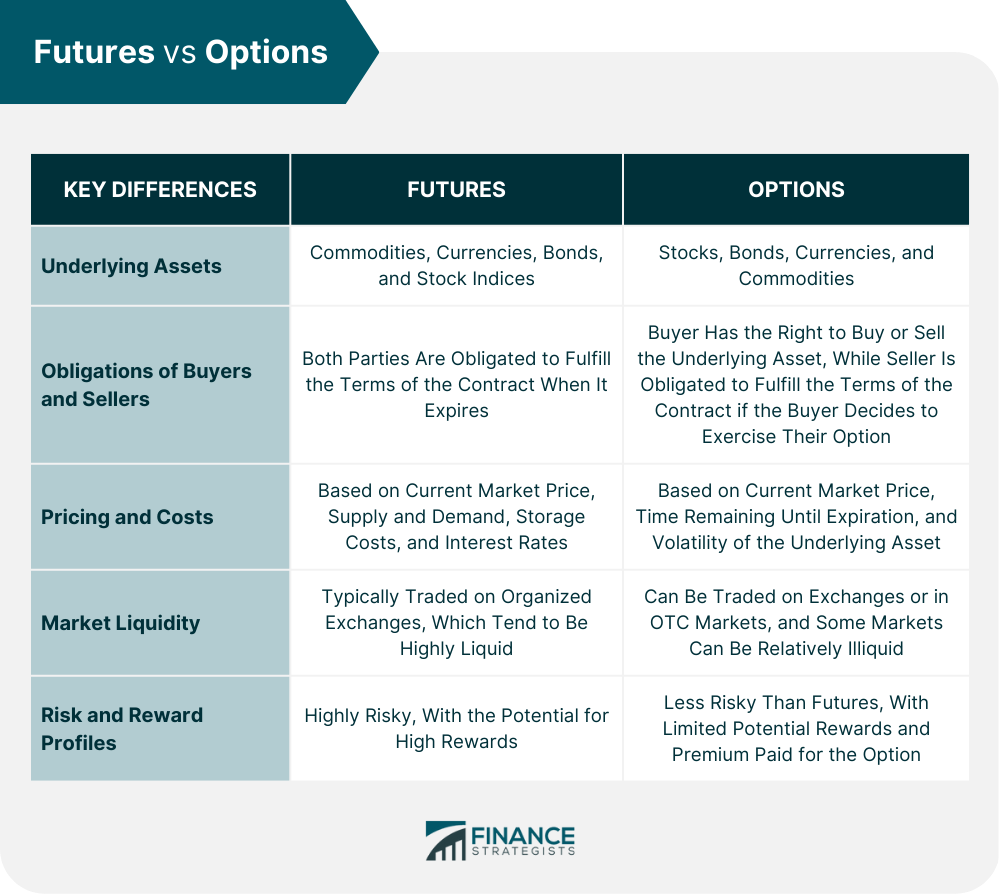
Image: www.financestrategists.com
FAQ
Q: What is the main difference between futures contracts and options contracts?
A: The main difference is that futures contracts obligate buyers and sellers to complete the transaction at a future date, while options contracts grant the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to complete the transaction.
Q: How are futures and options settled?
A: Futures contracts are typically settled in cash, while options contracts can be settled either in cash or by delivering the underlying asset.
Q: What are margin requirements for futures and options?
A: Margin requirements vary depending on the underlying asset and the type of contract. Meeting margin requirements is crucial to maintain a trading position.
Q: What are the advantages and disadvantages of futures contracts?
A: Advantages include high leverage potential, standardized contracts, and price discovery opportunities. Disadvantages include the obligation to fulfill the contract, potential for unlimited losses, and margin calls.
Q: What are the advantages and disadvantages of options contracts?
A: Advantages include limited risk, flexibility, and income generation potential. Disadvantages include time limitations, premium costs, and complex analysis and trading strategies.






