Unveiling the Realm of Options Trading: Call vs Put
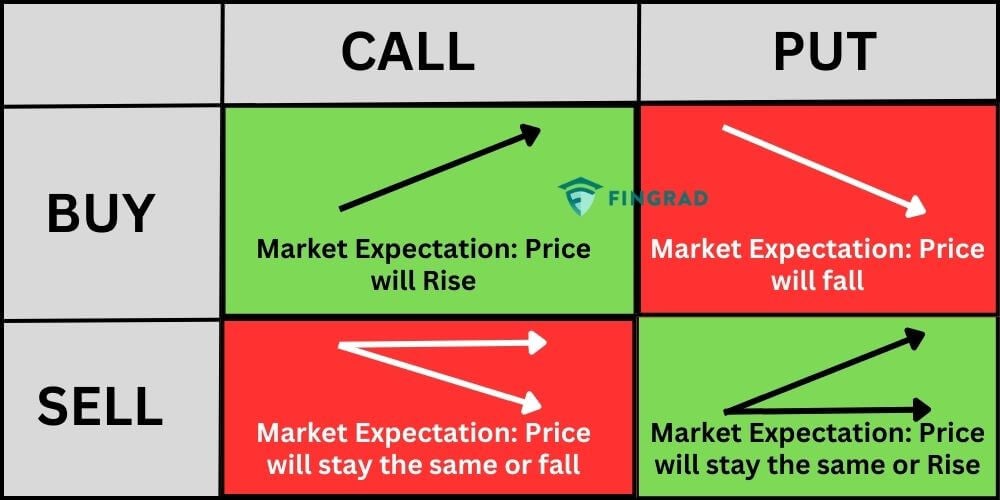
Image: tradebrains.in
Options trading, particularly involving call and put options, has emerged as a valuable tool for investors aspiring to navigate the dynamic and lucrative world of financial markets. These versatile instruments empower traders with the potential to enhance their portfolios, manage risk, and capture market opportunities. In this detailed guide, we delve into the intricacies of call and put options trading, exploring their fundamental concepts, strategies, and applications. By comprehending the mechanics of these options, traders can unlock new avenues for financial growth.
Call Options: Exploring the BULLish Side
Call options bestow upon traders the right, but not the obligation, to purchase an underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) on or before a specified expiration date. Fundamentally, call options are employed when traders anticipate an upward movement in the value of the underlying asset. By purchasing a call option, the trader gains the ability to capitalize on this anticipated price increase.
Real-World Example: Suppose an investor believes the stock of XYZ Corporation will rise in the coming weeks. To capitalize on this prediction, they acquire a call option with a strike price of $50 and an expiration date of one month from now. If the stock price climbs to $55 before expiration, the trader can exercise their right to buy the stock at the lower strike price, locking in a profit of $5 per share.
Put Options: Embracing the BEARish Outlook
Put options, on the other hand, grant traders the right, not the obligation, to sell an underlying asset at a specified strike price on or before expiration. Put options are typically utilized when traders anticipate a decline in the value of the underlying asset. By acquiring a put option, the trader secures the right to sell the asset at a higher price than the prevailing market price.
Real-World Application: Envision a situation where an investor fears a potential decline in the stock price of ABC Company. To mitigate this risk, they purchase a put option with a strike price of $100 and an expiration date of two months from now. If the stock price falls to $90 before expiration, the trader can exercise their option to sell their shares at $100, effectively minimizing potential losses.
Strategies and Considerations for Option Traders
The realm of options trading encompasses a myriad of strategies tailored to diverse investor goals and risk appetites. Covered calls, for instance, involve selling (writing) a call option while owning the underlying asset. This strategy allows traders to generate income from their existing holdings while capping potential upside. Conversely, selling (writing) put options conveys the obligation to buy the underlying asset if it falls below the strike price.
Understanding the factors influencing option prices, such as the underlying asset’s volatility and time to expiration, is crucial for successful option trading. Volatility measures the extent of price fluctuations in the underlying asset, and options on more volatile assets tend to be more expensive. Time decay, on the other hand, gradually reduces the value of options as they approach their expiration date.

Image: tradebrains.in
Call And Put Options Trading
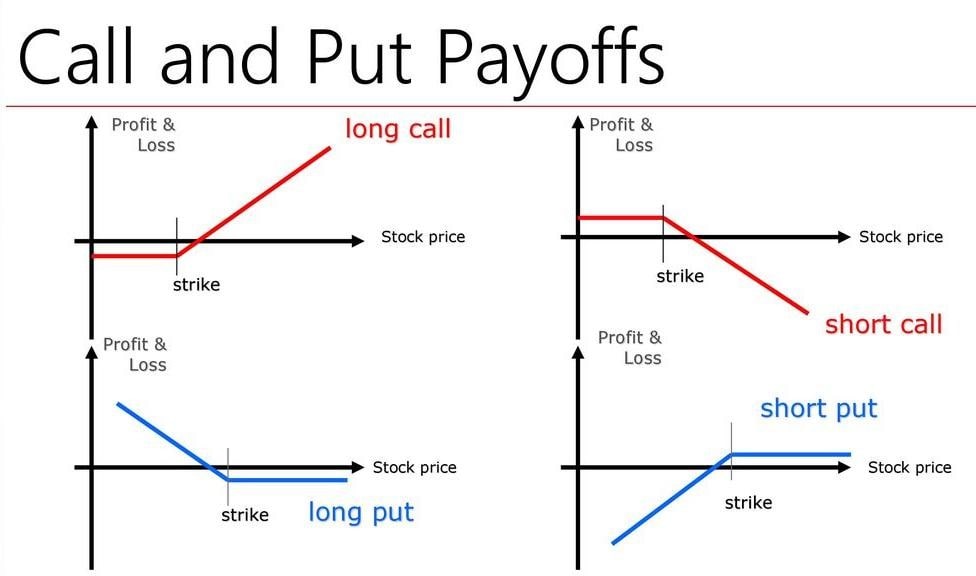
Image: libertex.com
Conclusion: Unveiling the Power of Options Trading
Call and put options provide traders with versatile tools for navigating financial markets, enabling them to execute complex strategies and capitalize on market movements. By embracing the concepts outlined in this guide, traders can confidently explore the world of options trading, effectively managing risk while unlocking new avenues for financial success.






