Introduction
In the world of financial markets, options offer a versatile instrument for traders to navigate risk and seek profit. Among the various options strategies, spreads stand out as a powerful tool that allows traders to mitigate risk while amplifying profit potential. This article delves into the intricacies of spread trading in options, guiding you through its mechanisms, applications, and the latest developments in this sophisticated trading approach.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Which_Vertical_Option_Spread_Should_You_Use_Sep_2020-04-759d6cab537d49608cd9888d31796ed5.jpg)
Image: www.investopedia.com
Understanding Spreads in Option Trading
A spread in option trading involves the simultaneous buying and selling of options contracts that share the same underlying asset but differ in strike price or expiration date. This creates a net position where the gains or losses from one option offset those of the other, effectively reducing overall risk. Spreads can be tailored to suit specific risk-tolerance levels, trading styles, and market expectations.
Types of Spread Strategies
-
Call Spreads: These spreads involve combinations of long and short call options. They can be bullish or bearish, depending on the relative strikes and expiration dates of the options. Call spreads can limit upward potential in exchange for reducing risk and potentially capturing income from the premium difference.
-
Put Spreads: Similarly, put spreads combine long and short put options. They provide a bearish or protective stance, benefiting from a decline in the underlying asset’s price. Put spreads can generate income while limiting the downside risk associated with holding long positions.
Factors to Consider When Trading Spreads
-
Strike Prices: The distance between the strikes of the options in a spread directly impacts the profit potential and risk. Wider strikes create greater potential but also higher risk, while narrower strikes reduce volatility.
-
Expiration Dates: The remaining time to expiration affects the value and complexity of the spread. Options with shorter time horizons tend to be more sensitive to price movements, while longer-term options offer a more extended period to benefit from potential market moves.
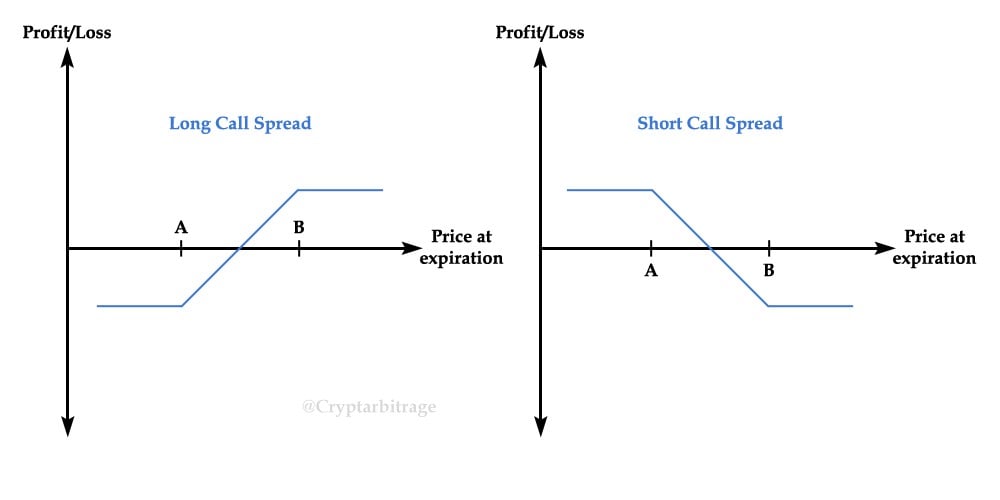
Image: insights.deribit.com
Applications of Spread Trading
-
Risk Management: Spreads are renowned for their risk-reducing capabilities. By offsetting gains and losses, traders can participate in options trading while minimizing the potential for catastrophic losses.
-
Income Generation: Bearish spreads and certain bullish spreads can generate income from the premium difference between the options. This allows traders to capitalize on moderate or sideways price movements.
-
Advanced Trading Techniques: Spreads can be used in conjunction with other options strategies, such as straddles, strangles, and condor spreads, to create complex risk and return profiles tailored to specific market conditions.
Latest Trends and Developments
-
Automated Spread Trading: Technological advancements have enabled the automation of spread trading strategies. Algorithmic platforms allow traders to execute and manage spreads efficiently, leveraging real-time data and pre-defined rules.
-
Spread Trading Analysis Tools: Comprehensive tools are available to assist traders in analyzing and selecting optimal spread strategies. These tools analyze historical data, pricing, and volatility to identify potentially profitable spread opportunities.
Spread In Option Trading
Conclusion
Spread trading in options empowers traders to navigate market volatility, manage risk effectively, and enhance their profit potential. By understanding the types, mechanisms, and applications of spread strategies, traders can harness the benefits of this advanced trading technique. As financial markets continue to evolve, staying abreast of the latest trends and leveraging technological advancements is crucial for successful execution of spread trading.






