The stock market can be a wild ride, and for many investors, options trading offers a way to leverage their investments and potentially increase their returns. But before you dive into the exciting world of options, it’s crucial to understand the costs involved. Just like buying and selling stocks, options trading isn’t free, and the fees associated with it can significantly impact your profit margins. This article will shed light on the different types of options trading fees, how they’re calculated, and how to navigate them effectively.
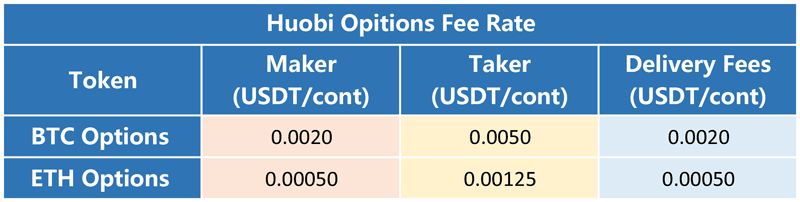
Image: huobiglobal.zendesk.com
Imagine this: you’re analyzing a promising stock and believe it’s about to surge in price. You decide to purchase a call option, giving you the right to buy the stock at a certain price in the future. However, the thrill of that potential profit is quickly tempered by the hefty broker fees you realize after the trade is executed. This is a common scenario among options traders who haven’t fully grasped the nuances of these fees. Knowing the costs upfront can help you make informed decisions and potentially avoid costly surprises.
Understanding the World of Options Trading Fees
Options trading fees encompass various charges levied by your broker for facilitating buy and sell orders. These fees can vary significantly depending on your broker, the type of option you’re trading, and the trading platform you use. A clear understanding of these costs is essential for maximizing your profitability in the dynamic world of options trading.
Let’s break down the key categories of options trading fees:
Common Types of Options Trading Fees
1. Brokerage Fees
Brokerage fees are probably the most obvious type of options trading fee. These are the commissions your broker charges for executing your buy or sell orders. These fees can be fixed, meaning they’re a flat amount per transaction, or they can be based on a percentage of the contract’s value. Some brokers may also offer commission-free trading, which sounds appealing but often comes with other fees lurking behind the scenes. It’s crucial to carefully review the terms and conditions of your broker’s fee structure to understand if they’re charging you elsewhere.

Image: moneycoachescanada.ca
2. Contract Fees
In addition to brokerage fees, options contracts themselves carry an intrinsic cost, often referred to as contract fees or commissions. These fees are charged by the options exchange where the trade is executed and are typically a small amount per contract. While seemingly minor, these fees can add up over time, especially if you engage in frequent options trading.
3. Clearing Fees
Clearing fees are another expense associated with options trading. These fees are levied by the clearinghouse that handles the settlement of your trades. Essentially, clearinghouses act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers, ensuring that all transactions are finalized correctly and that the financial obligations of each party are fulfilled. Clearing fees typically range from a few dollars to a few cents per contract, depending on the specific clearinghouse and the trading volume.
4. Regulatory Fees
Regulatory fees are essentially taxes charged by government entities to help oversee and regulate the financial markets. These fees are usually a small percentage of the transaction value and are often collected by the clearinghouse alongside clearing fees. Understanding these regulatory fees can be crucial for calculating your overall costs and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations.
5. Margin Interest
Options trading often involves leveraging, which means using borrowed money to amplify your potential gains and losses. If you use margin to purchase options, you’ll be charged interest on the borrowed funds. The interest rate charged on margin accounts can vary based on your broker and the current market conditions. It’s crucial to understand the margin interest rate you’ll be charged and factor it into your overall trading costs.
Navigating Options Trading Fees: Tips from the Experts
Understanding the numerous fees associated with options trading is only half the battle. The real challenge lies in navigating these costs effectively to minimize the impact on your profits. Here are some expert tips to help you make the most of your trading experience:
1. Choose the Right Broker: Selecting a broker with competitive fee structures and a user-friendly platform is essential. Research different brokers, compare commission rates, and consider additional benefits such as educational resources and research tools. Remember, a low commission rate alone doesn’t guarantee a lucrative trading experience. Look for a broker that provides value for your investment, whether it’s through reduced fees, advanced trading tools, or insightful market analysis.
2. Negotiate Fees: While it may seem daunting, don’t be afraid to negotiate your brokerage fees with your provider. Especially if you’re a high-volume trader, you may be able to secure reduced commissions or other favorable terms. Consider showcasing your trading volume and highlighting your commitment to the platform. By demonstrating your value as a customer, you can potentially unlock more attractive fee structures.
3. Explore Discount Brokers: Discount brokers often provide lower commission rates compared to traditional full-service brokers. While they may not offer fancy research tools or personalized investment advice, they excel in providing efficient execution of orders at competitive prices. Explore options like Robinhood, TD Ameritrade, and Interactive Brokers to find a discount broker that aligns with your trading style and needs.
4. Analyze Trading Costs: It’s crucial to track your trading expenses to understand how fees are impacting your profits. Most brokers provide detailed statements outlining your trading activity and associated costs. Regularly review these statements to identify any unexpected fees or areas where you can optimize your trading strategy.
FAQs: Addressing Your Questions about Options Trading Fees
Q: Are options trading fees fixed or variable?
A: Options trading fees can be either fixed or variable, depending on the broker and the specific services they offer. Fixed fees are typically charged as a flat amount per transaction, while variable fees are calculated based on a percentage of the contract’s value. Keep in mind that some brokers may offer commission-free trading, which often comes with other fees lurking behind the scenes.
Q: How can I minimize options trading fees?
A: There are several strategies to minimize options trading fees. First, choose a broker with competitive commission rates and a user-friendly platform. Second, consider negotiating your brokerage fees, especially if you’re a high-volume trader. Third, explore discount brokers, which often offer lower fees compared to traditional full-service brokers. Finally, be mindful of other fees associated with options trading, such as clearing fees and regulatory fees, and seek ways to minimize these costs.
Q: What is the difference between brokerage fees and contract fees?
A: Brokerage fees are charges levied by your broker for executing your buy or sell orders. Contract fees, on the other hand, are fees charged by the options exchange where the trade is executed. While seemingly minor, these fees can add up over time, especially if you engage in frequent options trading.
Options Trading Fees
Conclusion: Embrace the World of Options Trading with Informed Clarity
Navigating the world of options trading fees can be a complex process. Understanding the various fees, their impact on your profits, and strategies to minimize them is crucial for success. By embracing a proactive approach, researching brokers carefully, and negotiating your fees, you can set yourself up for smart and informed options trading.
Are you ready to delve deeper into the world of options trading? Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below, and let’s embark on a journey of profitable trading together.






