In the dynamic world of finance, options trading has emerged as a potent tool for navigating market uncertainty. Among the various types of options contracts, put options hold a unique position, empowering investors to protect against downside risks and profit from falling asset prices. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of put options trading, shedding light on its definition, history, and practical applications in the financial markets.
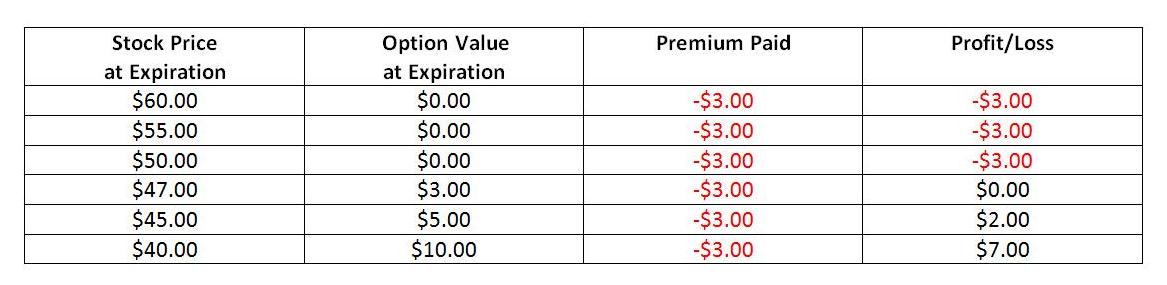
Image: www.onlinefinancialmarkets.com
Delving into the World of Put Options
Simply put, a put option grants the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to sell an underlying asset at a predetermined strike price on or before a specified expiration date. In essence, put options bestow upon their holders the flexibility to sell an asset at a guaranteed price, providing a safety net against potential declines in its value.
As a hypothetical example, if you purchase a put option on Apple stock with a strike price of $150 and an expiration date in three months, you have the right to sell 100 shares of Apple stock at $150 per share at any time up until the expiration date. In this scenario, if the price of Apple stock falls below $150, you can exercise the put option, selling the shares at the higher strike price and profiting from the price difference.
Historical Evolution of Put Options
The origins of put options can be traced back to the 18th century, where they were initially utilized as insurance contracts in the agricultural sector. Over time, their applications extended to the financial markets, where they evolved into a sophisticated hedging and speculative tool.
The Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) played a pivotal role in the development of standardized put options in the 1970s. These standardized contracts brought greater transparency and liquidity to the options market, attracting a wider range of investors.
Put Options Trading: A Detailed Exploration
Understanding the mechanisms behind put options trading is crucial for making informed decisions. Below are several key concepts to grasp:
- Option Premium: The price an investor pays to acquire a put option.
- Strike Price: The predetermined price at which the underlying asset can be sold.
- Expiration Date: The date on which the put option expires and becomes worthless if unexercised.
- Intrinsic Value: The difference between the strike price and the underlying asset’s current market price (if positive).
- Time Value: The premium paid for the option’s remaining time until expiration.
The value of a put option is influenced by numerous factors, including the underlying asset’s price, volatility, interest rates, and time to expiration. Traders must carefully consider these factors when determining the potential profitability of a put option strategy.
Image: binaryoptionsjournal.com
Latest Trends and Developments in Put Options Market
The put options market is constantly evolving, with advancements in technology and regulatory changes shaping its landscape. Here are some notable trends and developments:
- Increased Electronic Trading: Electronic platforms have facilitated the growth of put options trading, providing fast execution and greater transparency.
- Expansion of Underlying Assets: Put options are now available on a wide range of underlying assets, including stocks, indices, commodities, and currencies.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Regulators are closely monitoring the put options market to ensure fair and orderly trading practices.
Tips and Expert Advice for Successful Put Options Trading
Harnessing the power of put options requires a combination of knowledge, skill, and a disciplined approach. Here are some valuable tips and expert advice to enhance your trading strategy:
- Define Trading Objectives: Clearly outline your investment goals before entering any put options trade.
- Understand Risk Tolerance: Put options trading carries inherent risks. Determine your risk tolerance and allocate funds accordingly.
- Monitor Market Conditions: Pay close attention to market trends, volatility, and other factors that may impact put option prices.
- Use Technical Analysis: Leverage technical indicators and charting techniques to identify potential entry and exit points for put options trades.
- Consider Margin Trading (Caution): Margin trading can magnify potential profits but also amplifies risks. Exercise caution when using leverage.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the potential benefits of put options trading?
A: Put options can provide downside protection, income generation, and speculative opportunities, depending on the chosen strategy.
Q: How do I determine the profitability of a put option?
A: You need to consider the option premium, strike price, underlying asset price, and potential price movements.
Q: Can I lose more than my initial investment in put options trading?
A: Only if you use margin trading. With a standard put option, your maximum loss is limited to the option premium paid.
What Is Put Options Trading
Conclusion
Put options trading offers investors a powerful tool for navigating market volatility and potentially profiting from downside moves in asset prices. By comprehending the nuances of put options, their applications, and the latest trends in the market, investors can make informed decisions and enhance their trading strategies.
Are you interested in delving deeper into the world of put options trading? If so, consider exploring additional resources or reaching out to a financial advisor for personalized guidance.






