Introduction
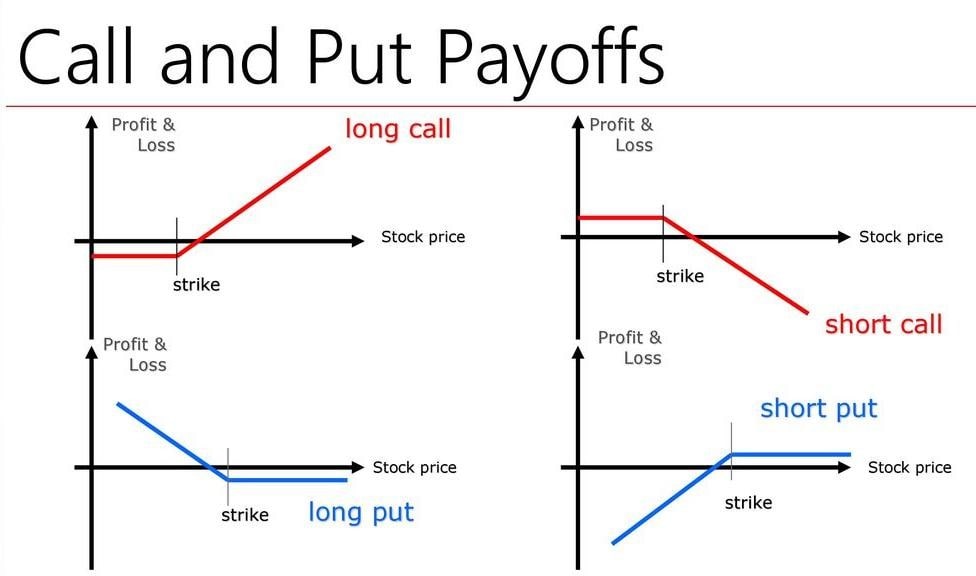
Image: libertex.com
In the ever-volatile world of finance, mastering the intricacies of options trading can prove invaluable. One such powerful tool is the put option, a financial instrument that grants the holder the right, not the obligation, to sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price on or before a specific date. Understanding put options trading is not merely a theoretical exercise but a practical skill that can empower traders to navigate market fluctuations with confidence.
This article delves into the multifaceted universe of put options trading, shedding light on its history, fundamental concepts, and practical applications. Through real-world examples, we will unveil the nuances of put trading, exploring both its potential rewards and inherent risks. By the conclusion of this comprehensive guide, investors will have gained a solid foundation in put options trading, enabling them to make informed decisions in the quest for financial success.
A Glimpse into the History of Put Options
The origins of put options can be traced back to the bustling trading pits of 17th-century Amsterdam, where astute traders devised this innovative instrument to hedge their risk against price fluctuations. Fast forward to the 20th century, put options gained prominence in the United States, becoming a cornerstone of modern options trading. Today, they play a pivotal role in the financial landscape, empowering investors with sophisticated tools for navigating market uncertainty.
Understanding the Basics of Put Options
At its core, a put option represents a contract between two parties: the buyer and the seller. The buyer acquires the right (but not the obligation) to sell a specific quantity of an underlying asset, such as stocks, bonds, or commodities, at a predetermined strike price on or before a specified expiration date. In exchange for this right, the buyer pays a premium to the seller.
Crucially, put options thrive in bearish markets, where investors anticipate a decline in the underlying asset’s price. By purchasing a put option, investors can effectively bet against the market, potentially profiting from a drop in value.
Real-World Examples of Put Options Trading
To illustrate the practical application of put options, let’s delve into two real-world examples:
-
Assume you believe the stock of Company XYZ is overvalued and poised for a downturn. By purchasing a put option with a strike price below the current market price, you gain the right to sell your XYZ shares at the strike price, irrespective of how low the stock price falls. If your prediction holds true and XYZ’s stock price plummets, you can exercise your put option and sell your shares at the higher strike price, securing a profit.
-
Alternatively, imagine you own a valuable painting that you intend to sell within the next year. However, you are concerned about potential market fluctuations that could diminish its value. To protect your investment, you could purchase a put option on the painting. This way, regardless of any unforeseen market downturns, you are guaranteed to receive the predetermined strike price when you sell your masterpiece.
Exploring the Advantages of Put Options
The judicious use of put options offers several compelling advantages:
-
Hedging against Risk: Put options provide a valuable tool for investors seeking to mitigate risk. By acquiring a put option, one can effectively insure an underlying asset against a potential decline in value.
-
Speculating on Market Trends: Put options empower traders to speculate on anticipated market movements. If an investor believes an asset’s price will fall, they can purchase a put option to potentially profit from the decline.
-
Generating Income: Put options can be used to generate income through a strategy known as “selling covered puts.” This involves selling a put option while simultaneously owning the underlying asset. If the asset’s price holds steady or rises, the put option will expire worthless, and the seller will retain the premium received from the sale.
Navigating the Risks of Put Options
As with any financial instrument, put options trading comes with inherent risks:
-
Limited Profit Potential: Unlike call options, which offer unlimited profit potential, put options have a capped profit potential defined by the difference between the strike price and the underlying asset’s price at expiration.
-
Time Decay: The value of a put option erodes over time as the expiration date approaches. This time decay can significantly impact profitability, especially if the underlying asset’s price remains relatively stable.
-
Loss of Premium: The premium paid for a put option is non-refundable. If the underlying asset’s price rises or remains steady, the put option will expire worthless, and the premium paid will be lost.
Conclusion
Put options are powerful financial instruments that can enhance an investor’s ability to navigate market uncertainty. By understanding the fundamental concepts and practical applications of put options, traders can unlock a wealth of opportunities to protect their investments, speculate on market trends, and generate income. However, it is imperative to recognize the inherent risks associated with put options trading and proceed with caution. By carefully considering the advantages and risks, investors can harness the full potential of put options to achieve their financial goals. Armed with this comprehensive guide, may your trading endeavors be marked by wisdom, prudence, and enduring success.
![How to BUY a PUT Option - [Option Trading Basics] - Tradersfly Options ...](https://i.pinimg.com/originals/52/5f/da/525fda0acf94f16c1e8a56569bf21b08.jpg)
Image: www.pinterest.cl
Put Options Trading Examples
Image: www.asktraders.com






